Summary
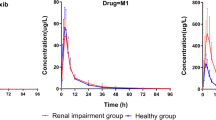
The accumulation and disposition of the non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug isoxicam were investigated following its oral administration to 6 subjects with normal renal function and 13 patients with diminished renal function. Isoxicam was given daily as a single oral dose for 14–15 consecutive days. Steady-state plasma levels were achieved after 13 days. The effect of differences in renal function on the kinetics of isoxicam appeared to be minimal. Accumulation of isoxicam was similar in both groups of subjects and there was no significant difference between the groups in the plasma clearance or terminal half-life of isoxicam. There were substantial differences between individuals in the apparent plasma clearance and half-life of the drug, and this is reflected in the 7-fold range of steady-state plasma isoxicam concentrations encountered in the subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bury RW (1985) Liquid chromatographic assay of isoxicam in human plasma and urine. J Chromatogr 337: 156–159
Downie WW (1982) Comparative studies of isoxicam in rheumatoid arthritis. Sem Arthr Rheum 12 (Suppl 2): 170–174
Fogari R, Bonebrake RA (1982) Aspirin and placebo controlled study of isoxican in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Sem Arth Rheum 12 (Suppl 2): 165–169
Hobbs DC, Twomey TM (1979) Piroxicam pharmacokinetics in man: aspirin and antacid interaction studies. J Clin Pharmacol 19: 270–281
Ishizaki J, Nomura T, Abe T (1979) Pharmacokinetics of piroxicam under fasting and post-prandial states in man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharmaceutics 1: 369–381
Kolle EU, Hengy H, Vollmer KO (1983) Pharmacokinetics of isoxicam in man following oral administration. ArzneimForsch 33: 3–7
Turi G, Boscaro C, de Bastiani G (1983) Double-blind comparative study of isoxicam and naproxen in the treatment of patients with osteo-arthritis. Curr Ther Res 33: 83–88
Yakatan G (1982) Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of isoxicam. Sem Arth Rheum 12: 154–159
Zinnes M, Sircar JC, Lindo N, Schwartz ML, Fabien AC, Shavel Jr. J, Kasnlanis CF, Genzer JD, Lutonoski C, Di Pasquale G (1982) Isoxicam and related 4-hydroxy-N-isoxazolyl-2H-1, 2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide-1, 1 dioxides. Potent non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. J Med Chem 25: 12–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bury, R.W., Whitworth, J.A., Saines, D. et al. Effect of impairment of renal function on the accumulation and disposition of isoxicam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28, 585–588 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544071
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544071