Summary
Ramon y Cajal (1909) adduced evidence that the pyramid cells of the mammalian neocortex have developed from the amphibian stage of the endbrain neurons with only subpial dendritic arborization.
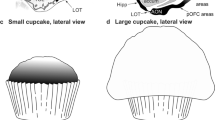
The apical bouquet of the pyramid cells can be regarded as a conservative feature and the basal dendrites as a progressive feature in pallial neuron evolution.
In mammals only neurons of the primitive allocortices, the archicortex and the paleocorticoid, bordering the zonal layer, still represent approximately the amphibian level of pallial neuron evolution. They exhibit the extreme of dendritic extraversion in the mammalian cerebral cortex.
Intermediate forms with relative predominance of the external dendrites over basal dendrites are found in the layer II cell condensations of the periallocortex and proisocortex, i. e., the first and second growth rings of the neocortex (Sanides, 1970). This strongly contrasts with the well-balanced external (apical) and basal dendrites of the pyramid cells of layer II of the isocortex.
For all neurons with predominant subpial dendritic arborization the term “extraverted neurons” was proposed.
In a group of primitive mammals, hedgehogs, bat, and opossum, all over the isocortex moderately extraverted neurons of layer II were demonstrated, corresponding to the type which is found in other mammals only in the older growth rings of the neocortex. Also in these primitive mammals the extraverted isocortex neurons are bound to an accentuated layer II, which resembles the superficial cell condensations of the periallocortex and proisocortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariens Kappers, C. N., Huber, G., Crosby, E. C.: The comparative anatomy of the nervous system of vertebrates, including man. New York: Mac Millan 1936.
Bonin, G. v.: Architecture of the precentral motor cortex and some adjacent areas. In: The precentral motor cortex, ed. by P. Ch. Bucy. Urbana: Univ. Illinois Press 1949.
Brodmann, K.: Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Großhirnrinde. Leipzig: Barth 1909.
Colonnier, M.: Synaptic patterns on different cell types in the different laminae of the cat visual cortex. An electron microscope study. Brain Res. 9, 268–287 (1968).
Diamond, I. T.: The sensory neocortex. Contr. Sens. Physiol. 2, 51–100 (1967).
Domesick, V.: Projections from the cingulate cortex in the rat. Brain Res. 12, 296–320 (1969).
Ebner, F. F.: A comparison of primitive forebrain organization in metatherian and eutherian mammals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 167, 241–257 (1969).
Filimonoff, I. N.: A rational subdivision of the cerebral cortex. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 58, 296–310 (1947).
Globus, A., Scheibel, A. B.: Pattern and field in cortical structure: The rabbit. J. comp. Neurol. 131, 155–173 (1967).
Gray, E. G.: Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex. An electron microscope study. J. Anat. (Lond.) 93, 420–433 (1959).
Heimer, L.: The secondary olfactory connections in mammals, reptiles and sharks. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 167, 129–146 (1969).
Herrick, C. J.: The brain of the tiger salamander. Chicago: Chicago Univ. Press 1948.
Kurepina, M.: Einige Besonderheiten der Struktur des Neocortex bei Fledermäusen im ökologischen Aspekt. J. Hirnforsch. 10, 39–48 (1968).
Lorente de No, R.: Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex. I. The area entorhinalis. J. Psychol. Neurol. (Lpz.) 45, 381–438 (1933).
Lorente de No, R.: Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex. II. Continuation of the study of the ammonic system. J. Psychol. Neurol. (Lpz.) 46, 113–177 (1934).
Meyer, M., Allison, A. C.: Experimental investigations of the connections of the olfactorius tracts in the monkey. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 12, 274–286 (1949).
Noback, C. R., Purpura, D. B.: Postnatal ontogenesis of neurons in cat neocortex. J. comp. Neurol. 117, 291–307 (1961).
O'Leary, J. L.: Structure of the area striata of the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 75, 131–164 (1941).
Polyak, S.: The vertebrate visual system. Chicago: Chicago Univ. Press 1957.
Powell, T. P. S., Mountcastle, V. B.: The cytoarchitecture of the postcentral gyrus of the monkey Macaca mulatta. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 105, 108–120 (1959).
Raisman, G.: An evaluation of the basic pattern of connections between the limbic system and hypothalamus. Amer. J. Anat. 129, 197–202 (1970).
Ramon-Moliner, E.: A tungstate modification of the Golgi-Cox method. Stain Technol. 33, 19–29 (1958).
Ramon-Moliner, E.: The histology of the postcruciate gyrus in the cat. II. A statistical analysis of the dendritic distribution. J. comp. Neurol. 117, 63–76 (1961).
Ramon-Moliner, E.: The histology of the postcruciate gyrus in the cat. III. Further observations. J. comp. Neurol. 117, 229–249 (1961).
Ramon-Moliner, E.: La différentiation morphologique des neurones, Arch. ital. Biol. 105, 149–188 (1967).
Ramon y Cajal, S.: Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés. Paris: Maloine 1909. Reprinted by the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas, Madrid 1955.
Sanides, F.: Die Architektonik des menschlichen Stirnhirns. Monograph. Gesamtgeb. Neurol. Psychiat. Bd. 98, Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1962.
Sanides, F.: Comparative architectonics of the neocortex of mammals and their evolutionary interpretation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 167, 404–423 (1969).
Sanides, F.: Functional architecture of motor and sensory cortices in primates in the light of a new concept of neocortex evolution. In: Advances in primatology, vol. 1, ed. by Ch. Noback and W. Montagna. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts 1970.
Sanides, F.: Representation in the cerebral cortex and its areal lamination pattern. In: The structure and function of nervous tissue. ed. by G. H. Bourne, vol. 5. New York: Academic Press 1972.
Sanides, F., Sas, E.: Persistence of horizontal cells of the Cajal fetal type and of the subpial granular layer in parts of the mammalian paleocortex. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 82, 570–588 (1970).
Sarkisov, S. A., Popova, E. N., Bogolepov, N. N.: Structure of synapses in evolutionary aspect (optic and electron-microscopic studies). In: Evolution of the forebrain, ed. by R. Hassler and H. Stephan. Stuttgart: Thieme 1966.
Simpson, G. G.: The principles of classification and a classification of mammals. Bull. Amer. Mus. Nat. Hist. 85, 1–350 (1945).
Stensaas, L. J.: The development of hippocampal and dorsolateral pallial regions of the cerebral hemisphere in fetal rabbits. III. Twenty-nine millimeter stage, marginal lamina. J. comp. Neurol. 130, 149–161 (1967).
Stephan, H.: Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen am Uncus bei Insectivoren und Primaten. In: Progress in brain research, vol. 3, ed. by W. Bargmann and J. P. Schadé. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1963.
Szentagothai, J.: Architecture of the cerebral cortex. In: Basic mechanisms of the epilepsies, ed. by H. H. Jaspers, A. A. Ward, Jr. and A. Pope. Boston: Little, Brown 1969.
Szentagothai, J.: Les circuits neuronaux de l'écorce cérébrale. Bull. Acad. roy. Méd. Belg. 10, 475–492 (1970).
Vogt, C., Vogt, O.: Allgemeinere Ergebnisse unserer Hirnforschung. J. Psychol. Neurol. (Lpz.) 25, 279–462 (1919).
Vogt, C., Vogt, O.: Weitere Ausführungen zum Arbeitsprogramm des Hirnforschungsinstitutes in Neustadt/Schwarzwald. J. Hirnforsch. 2, 403–427 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanides, F., Sanides, D. The “extraverted neurons” of the mammalian cerebral cortex. Z. Anat. Entwickl. Gesch. 136, 272–293 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00522616
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00522616