Summary
The pharmacokinetics of a series of fourteen monoquaternary ammonium ions, with gradually increasing molecular weight, were studied in anaesthetized rats after intravenous bolus injection and/or constant infusion.
Distribution to the eliminating organs and elimination rate into bile, urine and intestinal lumen as well as the plasma disappearance were investigated.
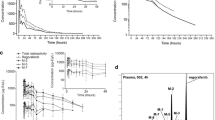
All compounds showed a double exponential plasma disappearance pattern. Initial half lifes (α-phase) varied between 0.5 and 3 min, half lifes of the β-phase varied between 30 and 70 min. Total plasma clearance within the series of compounds ranges from 2.3–13.7 ml/min, in general increasing with molecular weight.
The relative contribution of biliary, urinary, and intestinal elimination to the total plasma clearance varied widely within the series of organic cations.
Renal clearance of all the compounds exceeded that of mannitol, indicating involvement of active renal transport processes. Excretion via the kidneys was the only important excretory pathway for compounds with molecular weights <156. The low biliary excretion of the compounds of M<156 was not due to a deficient hepatic penetration since uptake into the liver was very rapid.
Only the high molecular weight compounds (<156) showed a profound bile/plasma concentration ratio ranging from 13 to 830. For these compounds also an “uphill” excretion process into the gut lumen seems to be involved representing up to 15% of the administered dose.
It is concluded that elimination patterns for organic cations of various structure differ much more than their overall distribution characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibaldi M, Koup JR (1981) Pharmacokinetic concepts — drug binding, apparent volume of distribution and clearance. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20:299–305
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1983) Pharmacokinetics (2nd ed). Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Hirom PC, Hughes RD, Millburn P (1974) The physicochemical factor required for the biliary excretion of organic cations and anions. Biochemical Society Transactions, 544th Meeting, London 2:327–330
Hughes RD, Millburn P, Williams RT (1973a) Molecular weight as a factor in the excretion of monoquaternary ammonium cations in the bile of the rat, rabbit and guinea pig. Biochem J 136:967–978
Hughes RD, Millburn P, Williams RT (1973b) Biliary excretion of some diquaternary ammonium cations in the rat, guinea pig and rabbit. Biochem J 136:979–984
Koudstaal J, Hardonk MJ, Hadders HN (1966) The development of induced vervico vaginal carcinoma in intact and estrogen treated castrated mice studies by histochemical and enzym histochemical methods. Cancer Res 26:1943–1953
Lauterbach F (1977) Intestinal secretion of organic ions and drugs. In: Kramer M (ed) Intestinal permeation. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 178–195
Meijer DKF (1977) The mechanisms for hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of organic cations. In: Kramer M (ed) Intestinal permeation. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 196–208
Meijer DKF, Weitering JG, Vonk RJ (1976) Hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of d-tubocurarine and trimethyl tubocurarine in the rat in vivo and in isolated perfusated rat livers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 198:229–239
Mintun M, Himmelstein KJ, Schroder RL, Gibaldi M, Shen DD (1980) Tissue distribution kinetics of tetraethyl ammonium ion in the rat. J Pharmacokin Biopharm 8:373–409
Mulder GJ, Scholtens E, Meijer DKF (1981) Collection of metabolites in bile and urine from the rat. In: Jacoby WB (ed) Methods in enzymology, vol 77. Academic Press, New York, pp 22–31
Nakae H, Takada K, Asada S, Muranishi S (1981) Transport rates of hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of an organic cation acetyl procainamide ethobromide. Biochem Pharmacol 29:2573–2576
Nakae H, Muranishi S, Asada S, Takada K (1981) Pharmacokinetic study on saturated hepatobiliary transport of acetyl procainamide ethobromide. J Pharm Dyn 4:584–589
Neef C (1983) Structure-pharmacokinetics relationship of quaternary ammonium compounds. Thesis, State University of Groningen, The Netherlands
Neef C, Meijer DKF (1984) Structure-pharmacokinetics relationship of quaternary ammonium compounds: Correlation of physicochemical and pharmacokinetic parameters. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 328:111–118
Neef K, Jonkman JGH, Meijer DKF (1978) Hepatic disposition and biliary excretion of the organic cations thiazinamium and thiazinamium sulfoxide in rats. J Pharm Sci 67:1147–1150
Rennick B (1981) Renal tubule transport of organic cations. Am J Physiol 240:F83-F89
Ruifrok PG (1982) Automated pharmacokinetic analysis: experiences of a user. Biopharm and Drug Disp 3:243–253
Sundwall A, Uthne K, Vessman J (1971) Metabolic disposition of emepronium in the dog with a note on the relationships between plasma concentration and effect. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 29:385–401
Wassermann O (1972) Studies on the pharmacokinetics of bisquaternary ammonium compounds. III. Autoradiographic studies on the substituent dependent distribution pattern of 3H-hexamethonium-derivatives in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 275:251–261
Vonk RJ, Scholtens E, Keulemans GTP, Meijer DKF (1978) Choleresis and hepatic transport mechanisms. IV. Influence of bile salt choleresis on the hepatic transport of the organic cations, d-tubocurarine and N4-acetyl procainamide ethobromide. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 302:1–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neef, C., Oosting, R. & Meijer, D.K.F. Structure-pharmacokinetics relationship of quaternary ammonium compounds. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 328, 103–110 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00512058
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00512058