Summary
-
1.
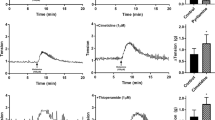
In anaesthetized acute gastric fistula cats the effect was studied of the histamine-H2-receptor-antagonists burimamide and metiamide on histamine-stimulated gastric acid secretion, gastric mucosal blood flow, and acid base balance of the arterial blood and the gastric venous drainage.
-
2.
Both burimamide and metiamide inhibit gastric secretion and gastric mucosal blood flow. The effects of metiamide are more pronounced than those of burimamide. On acid base balance both histamine-H2-receptor-antagonists have essentially the same effects which reflect the reduced loss of H+ from the stomach.
-
3.
The inhibitory effects of burimamide on the stomach are at least in part antagonized by the histamine-H1-receptor-antagonist mepyramine (which presumably prevents burimamide from releasing catecholamines) and by the α-adrenergic blocking agent phenoxybenzamine, providing indirect evidence for the view that these effects of burimamide are mediated by catecholamines.
-
4.
Phenoxybenzamine and mepyramine do not antagonize the gastric inhibitory effects of metiamide indicating that metiamide is void of catecholamine releasing properties.
-
5.
Phenoxybenzamine and mepyramine influence acid base balance only when the inhibition of gastric acid secretion by burimamide was diminished. They prevented the histamine-mediated drop in arterial pO2, indicating that this histamine effect can be attributed to catecholamines, too.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albinus, M., Sewing, K.-Fr.: Does burimamide inhibit gastric acid secretion by a release of catecholamines? Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 279, 417–420 (1973a)
Albinus, M., Sewing, K.-Fr.: Effect of burimamide on gastric acid secretion and gastric mucosal blood flow in cats. Agents and Actions 3, 172 (1973b)
Albinus, M., Sewing, K.-Fr.: Cardiovascular effects of burimamide and metiamide. Agents and Actions (in press) (1974a)
Albinus, M., Sewing, K.-Fr.: Acid base balance in relation to gastric acid secretion stimulated by histamine and pentagastrin in cats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 285, 325–335 (1974b)
Black, J. W.: Speculation about the nature of the antagonism between metiamide and pentagastrin. In: C. J. Wood, M. A. Simkins (Eds.): International Symposium on Histamine H2-Receptor Antagonists. Smith Kline & French Laboratories. Ltd., Welwyn Garden City, pp. 219–224 (1973)
Black, J. W., Duncan, W. A. M., Durant, J. C., Ganellin, C. R., Parsons, M. E.: Definition and antagonism of histamine H2-receptors. Nature (Lond.) 236, 385–390 (1972)
Brodie, B. B., Axelrod, J.: The fate of aminopyrine (Pyramidon) in man and methods for the estimation of aminopyrine and its metabolites in biological material. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 99, 171–184 (1950)
Emmelin, N., Muren, A.: Effects of antihistamine compounds on the adrenaline liberation from the adrenals. Acta physiol. scand. 17, 345–355 (1949)
Grossman, M. I., Konturek, S. J.: Inhibition of acid secretion in dog by metiamide, a histamine antagonist acting on H2-receptors. Gastroenterology 66, 517–521 (1974)
Harris, D. W., Reed, J. D., Smy, J. R., Venables, C. W.: The effects of burimamide and metiamide on basal gastric function in the cat. Brit. J. Pharmacol. (in press) (1974)
Jacobson, E. D., Linford, R. H., Grossman, M. I.: Gastric secretion in relation to mucosal blood flow studied by a clearance technique. J. clin. Invest. 45, 1–13 (1966)
Nickerson, M.: Mechanism of the prolonged adrenergic blockade by haloalkylamines. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 140, 237–250 (1962)
Reed, J. D., Smy, J. R., Venables, C. W., Harris, D. W.: The effect of burimamide on gastric acid secretion and gastric mucosal blood flow in the anaesthetized cat. In: C. J. Wood, M. A. Simkins (Eds.): International Symposium on Histamine H2-Receptor Antagonists. Smith Kline & French Laboratories Ltd., Welwyn Garden City, pp. 231–242 (1973)
Trendelenburg, U.: The action of histamine and pilocarpine on the superior cervical ganglion and the adrenals of the cat. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 9, 481–487 (1954)
Wyllie, J. H., Hesselbo, T.: Inhibition of gastric secretion in man by metiamide. In: C. J. Wood, M. A. Simkins (Eds.): International Symposium on Histamine H2-Receptor Antagonists. Smith Kline & French Laboratories Ltd., Welwyn Garden City, pp. 371–379 (1973)
Wyllie, J. H., Hesselbo, T., Black, J. W.: Effects in man of histamine H2-receptor blockade by burimamide. Lancet 1972II, 1117–1120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albinus, M., Sewing, K.F. The effect of histamine-H2-receptor-antagonists on gastric acid secretion, gastric mucosal blood flow and acid base balance in cats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 285, 337–353 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501463
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501463