Abstract
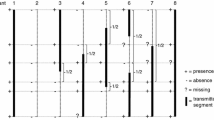
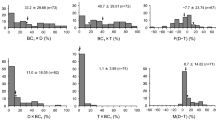
Alcohol dehydrogenase isozymes in Camellia japonica are encoded by two genes, Adh-1 and Adh-2. Both loci are expressed in seeds, and their products randomly associate into intragenic and intergenic dimers. Electrophoresis of leaf extracts reveals only the products of Adh-2. Formal genetic analysis indicated that the two Adh loci are tightly linked (combined estimate of r=0.004). Most segregations fit expected Mendelian ratios, but in some families distorted segregation was observed at Adh-1, Adh-2, or both loci. The deficient progeny class varied across families, and in two apparent backcrosses three rather than two phenotypic classes were recovered. The mechanism underlying these distortions is not known, but evidence is presented that suggests that the phenomenon is genic or segmental in nature. Plausible hypotheses include linkage of the Adh structural genes with a gametophytic self-incompatibility locus, translocation heterozygosity involving the segment bearing Adh-1 and Adh-2, or a combination of these two mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard, R. W. (1956). Formulas and tables to facilitate the calculation of recombination values in heredity. Hilgardia 24235.
Arus, P., and Shields, C. R. (1983). Cole crops (Brassica oleracea L.). In Tanksley, S. D., and Orton, T. J. (eds.), Isozymes in Plant Genetics and Breeding, Part B Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Banuette-Bourrillon, F. (1982). Linkage of the alcohol dehydrogenase structural genes in pearl millet (Pennisetum typhoides). Biochem. Genet. 20359.
Brown, A. H. D. 1980. Genetic basis of alcohol dehydrogenase polymorphism in Hordeum spontaneum. J. Hered. 70127.
Conkle, M. T. (1981). Isozyme variation and linkage in six conifer species. Symposium on isozymes of North American forest trees and forest insects. Pacific Southwest Forest and Range Experiment Station. Berkeley, Calif.
Ellstrand, N. C., Lee, J. M., and Foster, K. W. (1983). Alcohol dehydrogenase isozymes in grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor): Evidence for a gene duplication. Biochem. Genet. 21147.
Freeling, M., and Schwartz, D. (1973). Genetic relationships between the multiple alcohol dehydrogenases of maize. Biochem. Genet. 827.
Fuchinoue, Y. (1979). Analysis of self-incompatibility alleles of major varieties of tea. Jap. Agr. Res. Q. 1343.
Gottlieb, L. D. (1974). Gene duplication and fixed heterozygosity for alcohol dehydrogenase in the diploid plant Clarkia franciscana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 711816.
Grant, V. (1975). Genetics of Flowering Plants Columbia University Press, New York.
Harberd, N. P., and Edwards, K. J. R. (1983). Further studies on the alcohol dehydrogenases in barley: Evidence for a third alcohol dehydrogenase locus, and data on the effect of an alcohol dehydrogenase 1 null mutation in homozygous and in heterozygous condition. Genet. Res. Camb. 41109.
Kondo, K. (1975). Cytological Studies in Cultivated Camellia, Ph.D. dissertation, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
Kondo, K. (1977). Chromosome numbers in the genus Camellia. Biotropica 986.
Moran, G. F., and Hopper, S. D. (1983). Genetic diversity and the insular population structure of the rare granite rock species Eucalyptus caesia Beth. Aust. J. Bot. 31161.
Mulcahy, D. C., and Mulcahy, G. B. (1983). Gametophytic self-incompatibility re-examined. Science 2201247.
Orton, T. J. (1983) Celery and celeriac (Apium graveolens L.). In Tanksley, S. D., and Orton, T. J., (eds.), Isozymes in Plant Genetics and Breeding, Part B Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Roose, M. L., and Gottlieb, L. D. (1980). Alcohol dehydrogenase in the diploid plant Stephanomeria exigua (Compositae): Gene duplication, mode of inheritance and linkage. Genetics 95171.
Rudin, D., and Ekberg, I. (1978). Linkage studies in Pinus sylvestris L.—using macrogametophyte allozymes. Silvae Genet. 271.
Schwartz, D. (1969). Alcohol dehydrogenase in maize: genetic basis for multiple isozymes. Science 164585.
Tanksley, S. D., and Jones, R. A. (1981). Effects of O2 stress on tomato alcohol dehydrogenase activity: Description of a second ADH coding gene. Biochem. Genet. 19397.
Torres, A. M. (1974). Genetics of sunflower alcohol dehydrogenase: Adh-2 nonlinkage to Adh-1 and Adh-1 early alleles. Biochem. Genet. 12385.
Wendel, J. F. (1983). Electrophoretic Analysis of Genetic Variation in Wild and Cultivated Camellia japonica L., Ph.D. dissertation, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
Wendel, J. F. (1984). Electrophoretic identification of polyploid Camellia japonica cultivars and evidence for their sexual origin. Plant Syst. Evol. (in press).
Wendel, J. F., and Parks, C. R. (1982). Genetic control of isozyme variation in Camellia japonica L. (Theaceae). J. Hered. 73197.
Wendel, J. F., and Parks, C. R. (1983). Cultivar identification in Camellia japonica L. using allozyme polymorphisms. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 108290.
Wendel, J. F., and Parks, C. R. (1984). Genetic diversity and population structure of Camellia japonica L. (Theaceae) (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wendel, J.F., Parks, C.R. Distorted segregation and linkage of alcohol dehydrogenase genes in Camellia japonica L. (Theacease). Biochem Genet 22, 739–748 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00485857
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00485857