Abstract
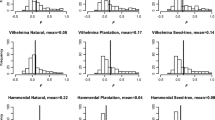
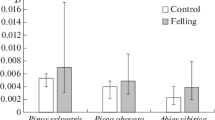
A comparison of the genetic structure for a group of 10 to 15 year old Scots pine trees originating from natural regeneration in an extremely polluted area with the genetic structure of 9 reference populations from the same geographical region but only slightly polluted, have demonstrated differences in alleles and genotypes frequencies. The observed heterozygosity (Ho) was lower by 12% for the group of trees from the polluted area. Fixation index (F) exhibited significant excess of homozygotes (F=0.15) in the group of tolerant trees. Average numbers of alleles per locus was higher by 8% in the group of trees from the polluted site. This differs from results from areas with the novel forest decline. Based on the differences in allele and genotype frequencies one might concluded that some of the alleles have a selective disadvantage or a selective advantage in the group of trees in the studied polluted area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmann, F. and Scholz, F.: 1984, ‘Effects of Selection Pressure by SO2 Pollution on Genetic Structure of Norway spurce (Picea abies) in LectureNotes in Biomatematics’ in H.-R. Gregorius (ed.), Population Genetics in Forestry, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 267–275.
Bergmann, F. and Scholz, F.: 1987, Silvae Genetica 36, 80.
Bergmann, F. and Scholz, F.: 1989, ‘Selection Effects of Air Pollution in Norway spurce (Picea abies) populations’, in F. Scholz, H.-R. Gregorius, and D. Rudin (eds.), Genetic Effects of Air Pollutants in Forest Tree Populations. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 145–160.
Geburek, Th., Scholz, F., Knabe, W., and Vornweg, A. L. 1987, Silvae Genetica 36, 49.
Greń, J.: 1972, Modele i badania statystyki matematycznej, PWN, Warszawa.
Gullberg, U., Yazdani, R., and Rudin, D.: 1982, Silva Fennica 16, 205.
Hedrick, P. W.: 1974, Evolution 29, 362.
Jain, S. K. and Workman, P. L.: 1967, Nature 214, 674.
Kahler, A. L., Allard, R. W., Krzakowa, M., Wherhan, C. F., and Neve, E.: 1980, TAG 56, 31.
Mejnartowicz, L.: 1983, Genetica Polonica 24, 41.
Mejnartowicz, L. and Palowski, B.: 1989, ‘Studies of Scots Pine Populations in Polluted and Clean Areas’, in F. Scholz, H.-R. Gregorius, and D. Rudin (eds.) Genetic Effects of Air Pollutants in Forest Tree Populations, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 115–125.
Müller-Starck, G.: 1985, Silvae Genetica 34, 241.
Müller-Starck, G.: 1989, ‘Genetic Implications of Environmental Stress in Adult Forest Stands of Fagus sylvatica L.’, in F. Scholz, H.-R. Gregorius, and D. Rudin (eds.), Genetic Effects of Air Pollutants in Forest Tree Populations, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 127–142.
Nei, M. and Roychoudhry, A. K.: 1974, Genetics 76, 379.
Prus-Głowacki, W. and Nowak-Bzowy, R.: 1989, Silvae Genetica 38, 55.
Prus-Głowacki, W. and Godzik, S.: 1991, Silvae Genetica 40, 184.
Rudin, D. and Ekberg, T.: 1978, Silvae Genetica 27, 1.
Scholz, F.: 1990, ‘Importance of the Genetic Structure in Tree Species for Forest Ecosystems Under the Influence of Air Pollutants’, in B. Ulrich (ed.), Proc. International Congress on Forest Decline Research: state of Knowledge and Perspectives, Friedrichshafen 2–6.10.1989, pp. 479–497.
Scholz, F. and Bergmann, F.: 1984, Silvae Genetica 33, 238.
Srivastava, H. S. and Singh, 1987, Phytochemistry 26, 597.
Szmidt, A. and Yazdani, R.: 1984, Arboretum Kórnickie 29, 63.
Tomsett, A. B. and Thurman, D. A.: 1988, Plant, Cell and Environment 11, 383.
Venne, H., Scholz, F., and Vornweg, A.: 1989, ‘Effects of Air Pollutants on Reproductive Processes of Poplar (Populus ssp.) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.)’ in F. Scholz, H.-R. Gregorius, and D. Rudin (eds.), Genetic Effects of Air Pollutants in Forest Tree Populations, Springer -Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 89–103.
Yazdani, R. and Rudin, D.: 1982, Hereditas 96, 191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prus-Głowacki, W., Nowak-Bzowy, R. Genetic structure of a naturally regenerating Scots pine population tolerant for high pollution near a zinc smelter. Water Air Soil Pollut 62, 249–259 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00480259
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00480259