Summary
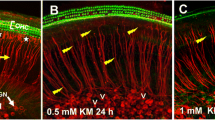
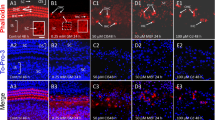
The ototoxicity of kanamycin was investigated in mice treated with the drug either from 6 to 9, 10 to 13, or 15 to 18 days of age. The results showed extensive damage to the outer-hair-cell (OHC) receptors of the cochlea in the 10–13-day group; some less severe damage to the OHC was found in the 6–9-day group, and little damage was observed in the 15–18 day group. The present finding is consistent with the view that the mouse cochlea is most vulnerable to the ototoxic effect of kanamycin during the period of its rapid development, i.e., between 10 and 13 days of age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlier E, Pujol R (1980) Supra-normal sensitivity to ototoxic antibiotic of the developing rat cochlea. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 226: 129–133
Chen C-S (1973) Sensitization for audiogenic seizures in two strains of mice and their FI hybrido. Develop Psychobiol 6: 131–138
Chen C-S, Aberdeen GC (1980) Potentiation of noise-induced audiogenic seizures risk by salicylate in mice as a function of salicylate-noise exposure interval. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 90: 62–65
Chen C-S, Aberdeen DC (1981) The sensitive period for induction of susceptibility to audiogenic seizures by kanamycin in mice. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 232: 215–220
Ehret G (1979) Correlation between cochlear hair cell loss and shifts of masked and absolute behavioral auditory thresholds in the house mouse. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 87: 28–38
Fuller JL, Sjursen FR (1967) Audiogenic seizures in eleven mice strains. J Hered 58: 135–140
Henry KR (1967) Audiogenicseizure susceptibility induced in C57BL/J mice by prior auditory exposure. Science 158: 938–940
Kikuchi K, Hilding D (1965) The development of the organ of Corti in the mouse. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 60: 207–222
Marot M, Uziel A, Romand R (1980) Ototoxicity of kanamycin in developing rats: Relationship with the onset of the auditory function. Hear Res 2:111–113
Norris CH, Cawthon TH, Carroll RC (1977) Kanamycin priming for audiogenic seizures in mice. Neuropharmacology 16: 375–380
Osako S, Tokimoto T, Matsuura S (1979) Effects of kanamycin on the auditory evoked responses during postnatal development of the hearing of the rat. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 88: 359–368
Pujol R, Hilding D (1973) Anatomy and physiology of the onset of auditory function. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 76: 1–10
Tepper JM, Schlesinger K (1980) Acoustic priming and kanamycin-induced cochlear damage. Brain Res 187: 81–95
Uziel A, Romand R, Marot M (1979) Electrophysiological study of the ototoxicity of kanamycin during development in guinea pigs. Hear Res 1: 203–211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deafness Research Foundation. It was carried out while CSC was on leave from Monash University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CS., Saunders, J.C. The sensitive period for ototoxicity of kanamycin in mice: Morphological evidence. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 238, 217–223 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453932
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453932