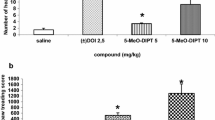
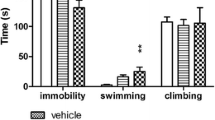
Abstract
Ro 11-2465 (cianopramine, cyan-imipramine) and citalopram (CIT), putative antidepressant drugs, are very potent and selective 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) uptake inhibitors in vitro. This study investigated the effects of these drugs and their desmethyl metabolites, Ro 12-5419 (desmethylcianopramine, cyan-desipramine) and desmethylcitalopram (DCIT), respectively, on the uptake of 5-HT and noradrenaline (NA) in vivo [protection against H 77/77 (4, alpha-dimethyl-metatyramine)-induced displacement of 5-HT and NA] and on related pharmacological activities. All the investigated drugs antagonized H 77/77-induced displacement of 5-HT in the rat brain, though the effects of the metabolites were considerably weaker than those of the parent compounds. The H 77/77-induced displacement of brain NA in rats and mice was antagonized only by Ro 12-5419 and Ro 11-2465. All the drugs potentiated the pressor response to 5-HT in pithed rats; however, Ro 12-5419 and particularly Ro 11-2465 could also block the response when used in higher doses (≧0.1 mg/kg). Only Ro 12-5419 and Ro 11-2465 were able to potentiate the pressor response to NA. Ro 12-5419 also potentiated thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) hyperthermia and antagonized reserpine hypothermia in mice; Ro 11-2465 potentiated the TRH hyperthermia only. CIT and DCIT were inactive in both these tests. Of all the four drugs only CIT and Ro 12-5419 considerably stimulated the hind limb flexor reflex in spinal rats. However, whereas the stimulatory effect of CIT was inhibited by the 5-HT antagonists metergoline and cyproheptadine, that of Ro 12-5419 was counteracted by the NA antagonist phenoxybenzamine only. Ro 11-2465, when used in low doses (ca. 1 mg/kg), slightly potentiated the flexor reflex, whereas in higher doses (4–16 mg/kg) it had no effect itself but antagonized the stimulatory action of the 5-HT agonists fenfluramine, quipazine and LSD. The results obtained indicate that Ro 11-2465 and CIT, as well as their desmethyl metabolites, are also potent 5-HT uptake inhibitors in vivo. However, only CIT and DCIT are concurrently devoid of effect on uptake of NA. In contrast, Ro 11-2465 and particularly Ro 12-5419 appear to also inhibit the uptake of NA. Moreover, Ro 11-2465 appears to block central and peripheral 5-HT receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruinvels J (1971) Evidence for inhibition of the re-uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline by tetrahydronaphthylamine. Br J Pharmacol 42:281–286
Burkard WP (1980) Specific binding sites in rat brain for a new and potent inhibitor of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake: Ro 11-2465. Eur J Pharmacol 61:409–410
Carlsson A, Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Hökfelt T (1969a) Effect of antidepressant drugs on the depletion of intraneuronal brain 5-hydroxytryptamine store caused by 4-methyl-α-ethyl-meta-tyramine. Eur J Pharmacol 5:357–366
Carlsson A, Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Hökfelt T (1969b) Effects of some antidepressant drugs on the depletion of intraneuronal brain catecholamine stores caused by 4,α-dimethyl-meta-tyramine. Eur J Pharmacol 5:367–373
Cavero I, Gomeni R, Lefèvre-Borg F, Roach AG (1980) Comparison of mianserin with desipramine, maprotiline and phentolamine on cardiac presynaptic and vascular postsynaptic α-adrenoceptors and noradrenaline reuptake in pithed normotensive rats. Br J Pharmacol 68:321–332
Chang CC (1964) A sensitive method for spectrophotofluorometric assay of catecholamines. Int J Neuropharmacol 3:643–649
Claassen V, Davies JE, Hertting G, Placheta P (1977) Fluvoxamine, a specific 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol 60:505–516
Coppen A (1967) The biochemistry of affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry 113:1237–1264
Costa e Silva JA, Omer LMO, Ismail S (1983) Cianopramine, a preliminary efficacy study with a new potent serotonin uptake inhibitor. Abstracts of the 7th World Congress of Psychiatry, Vienna (Austria), 11–16 July 1983, p 489, abstract P223
DaPrada M, Keller HH, Burkard WP, Schaffner R, Bonetti EP, Launay JM, Haefely W (1982) Some neuropharmacological effects of Ro 11-2465—a novel tricyclic antidepressant with potent inhibitory activity on the uptake of 5-HT. In Advances in biochemical psychopharmacology vol 31 (Typical and atypical antidepressants: Molecular mechanisms) pp 235–248
Desiles M, Rips R (1981) Use of potentiation of thyrotrophin releasing hormone (TRH)-induced hyperthermia as a test for screening antidepressants which active α-adrenoceptor systems. Br J Pharmacol 74:81–86
Doogan DP (1980) Fluvoxamine as an antidepressant drug. Neuropharmacology 19:1215–1216
Earley CJ, Leonard BE (1978) Isolation and assay of noradrenaline, dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and several, metabolites from brain tissue using disposable Bio-Rad columns packed with Sephadex G-10. J Pharmacol Methods 1:67–79
Fredricson Overø K (1982a) Kinetics of citalpram in test animals; drug exposure in safety studies. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 6:297–309
Fredricson Overø K (1982b) Kinetics of citalopram in man; plasma levels in patients. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 6:311–318
Gillespie JS, Maclaren A, Pollock D (1970) A method of stimulating different segments of the autonomic outflow from the spinal column to various organs in the pithed cat and rat. Br J Pharmacol 40:257–267
Gottlieb P, Wandall T, Fredricson Overø K (1980) Initial, clinical trial of a new, specific 5-HT reuptake inhibitor, citalopram (Lu 10-171). Acta Psychiatr Scand 62:236–244
Haefely W, Schaffner R, Burkard WP, Da Prada M, Keller HH, Pole P, Richards JG (1978) Ro 11-2465, a potent and selective inhibitor of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake. Abstracts of the 11th CINP Congress. Vienna (Austria), 9–14 July 1978, p 95
Horst WD, Spirt N (1974) A possible mechanism for the antidepressant activity of thyrotropin releasing hormone. Life Sci 15:1073–1082
Hyttel J (1977) Neurochemical characterization of a new potent and selective serotonin uptake inhibitor: Lu 10-171. Psychopharmacology 51:225–233
Hyttel J (1982) Citalopram-pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 6:277–295
Jones RB and Luscombe DK (1976) Plasma levels of clomipramine and its N-desmethyl metabolite following oral administration of clomipramine in man. Br J Pharmacol 57:430 P
Jones RB and Luscombe DK (1977) Plasma concentrations of clomipramine and its N-desmethyl metabolite in depressive patients following treatment with various dosage regimes of clomipramine. Postgrad Med J 53 (Suppl. 4):63–76
Keller HH, Burkard WP, Da Prada M (1980) Dopamine receptor blockade in rat brain after acute and subchronic treatment with tricyclic antidepressants. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol vol 24 (Long-term effects of neuroleptics) pp 175–179
Kragh-Sørensen P (1983) A controlled, double-blind multicentre trial comparing clomipramine and a new, highly selective 5-HT uptake inhibitor, citalopram (Lu 10-171). Abstracts of the 7th World Congress of Psychiatry, Vienna (Austrai), 11–16 July 1983, p 482, abstract P179
Lapin IP, Oxenkrug GF (1969) Intensification of the central serotoninergic processes as a possible determinant of the thymoleptic effect. Lancet I:132–136
Lindbrink P, Jonsson G, Fuxe K (1971) The effect of imipramine-like drugs and antihistamine drugs on uptake mechanisms in the central noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons. Neuropharmacology 10:521–536
Lindegaard Pedersen O, Kragh-Sørensen P, Bjerre M, Fredricson Overø K, Gram LF (1982) Citalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor: clinical antidepressive and long term effect — A phase II study. Psychopharmacology 77:199–204
Maître L, Baumann PA, Jaekel J, Waldmeier PC (1982) 5-HT uptake inhibotors: psychopharmacological and neurobiochemical criteria of selectivity. Adv Biochem Psychopharm 34 (Serotonin in biological psychiatry): 229–246
Maître L, Moser P, Baumann PA Waldmeier PC (1980) Amine uptake inhibitors: Criteria of selectivity. Acta Psychiatr Scand 61 (Suppl. 280):97–110
Maj J, Palider W, Baran L (1976) The effects of serotonergic and antiserotonergic drugs on the flexor reflex of spinal rat: a proposed model to evaluate the action on the central serotonin receptor. J Neural Transm 38:131–147
Maj J, Rogóz Z, Skuza G (1982a) Fluvoxamine, a new antidepressant drug, fails to show antiserotonin activity. Eur J Pharmacol 81:287–292
Maj J, Rogóz Z, Skuza G, Sowińska H (1983) The effect of selective inhibitors of noradrenaline and serotonin uptake on reserpine-and apomorphine-induced hypothermia in mice. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 35:49–57
Maj J, Stala L, Górka Z, Adamus A (1982b) Comparison of the pharmacological actions of desmethylclomipramine and clomipramine. Psychopharmacologyy 78:165–169
Mertens C (1983) A controlled double-blind clinical trial with a new highly selective 5-HT-re-uptake inhibitor, citalopram (Lu 10-171) versus mianserin in depressed patients. Abstracts of the 7th World Congress of Psychiatry, Vienna (Austria), 11–16 July 1983, p 441, abstract F924
Pawŀowski L, Górka Z, Rogóz Z, Skuza G Rawŀów A, Maj J (1983) Some acute and chronic effects of talsupram, a potent and selective, bicyclic inhibitor of the uptake of noradrenaline. Abstracts of the 5th International Catecholamine, Symposium, Göteborg (Sweden), 12–16 June 1983, Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr (Suppl) p 245, abstract 377
Pawŀowski L, Kwiatek H (1983a) The effect of highly selective inhibitors of the uptake of noradrenaline or 5-hydroxytryptamine on TRH-induced hyperthermia in mice. Psychopharmacology 81:48–53
Pawŀowski L, Kwiatek H (1983b) TRH-induced hyperthermia in mice: effect of NA and 5-HT uptake inhibitors. Abstracts of the 5th International Catecholamine Symposium, Göteborg (Sweden), 12–16 June 1983, Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr (Suppl.) p 235, abstract 378
Pawŀowski L, Kwiatek H, Górka Z (1981a) Is Ro 11-2465 (cyanimipramine) an antagonist of postsynaptic serotonin receptors? J Neural Transm 52:61–72
Pawŀowski L, Kwiatek H, Ruczyńska J (1980) A comparison of effects of zimelidine with those of other inhibitors of the serotonin (5-HT) uptake. Abstracts of the 12th CINP Congress, Göteborg (Sweden), 22–26 June 1980, Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol (Suppl.) p 277, abstract 516
Pawlowski L, Ruczyńska J, Górka Z (1981b) Citalopram: A new potent inhibitor of serotonin (5-HT) uptake with central 5-HT-mimetic properties. Psychopharmacology 74:161–165
Petersen EN, Olsson S-O, Squires RF (1977) Effects of 5-HT uptake inhibitors on the pressor response to 5-HT in the pithed rat. The significance of the 5-HT blocking property. Eur J Pharmacol 43:209–215
Przegaliński E, Siwanowicz J, Baran L, Bigajska K (1983) Antagonism by tricyclic antidepressants of reserpine-induced hypothermia in mice. Involvement of postsynaptic α2-adrenoceptors. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 35:309–317
Schildkraut JJ (1965) The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders: a review of supporting evidence. Am J Psychiatry 122:509–522
Schildkraut JJ, Kety SS (1967) Biogenic amines and emotion. Science 156:21–30
Slater IH, Rathbun RC, Kattau R (1979) Role of 5-hydroxytryptaminergic and adrenergic mechanism in antagonism of reserpine-induced hypothermia in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:108–110
Träskman L, Åsberg M, Bertilsson L, Cronholm B, Mellström B, Neckers LM, Sjöqvist F, Thorén P, Tybring G (1979) Plasma levels of chlorimipramine and its demethyl metabolite during treatment of depression. Clin Pharmacol Ther 26:600–610
van Praag HM (1974) Towards a biochemical typology of depression. Pharmacopsychiatry 7:281–292
Øfsti E (1982) Citalopram —a specific 5-HT-reuptake inhibitor-as an antidepressant drug: A phase II multicentre trial. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 6:327–335
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pawlowski, L., Nowak, G., Górka, Z. et al. Ro 11-2465 (cyan-imipramine), citalopram and their N-desmethyl metabolites: Effects on the uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline in vivo and related pharmacological activities. Psychopharmacology 86, 156–163 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431702
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431702