Abstract
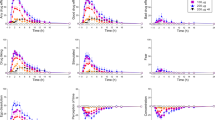
Deprenyl has previously been reported to be a selective monoamine oxidase (MAO) type B inhibitor, which is associated with little or no enhancement of the pressor effects of tyramine. Employing an intravenous steady-state tyramine infusion technique, the effects of different doses of deprenyl and, for comparison, the mixed inhibitor tranlcypromine on the pressor response to tyramine were studied in 11 depressed patients. After 3 weeks of treatment, deprenyl produced dose-proportionate increases in tyramine sensitivity at all three doses (10, 30, and 60 mg/day) when compared to placebo baseline tyramine responses. While only a modest (3.7-fold) increase in tyramine sensitivity was found with the 10 mg/day deprenyl dose, the increase in tyramine sensitivity at the 60 mg/day dose of deprenyl (22-fold) approached that found with tranylcypromine. Reductions in plasma 3-methoxy,4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG), used as a possible index of in vivo MAO-A inhibition, were highly correlated with increases in tyramine pressor sensitivity (r=0.82). The data suggest that deprenyl acts as a relatively selective MAO-B inhibitor at low doses, but that this selectivity is lost at higher doses, resulting in a significant “crossover” inhibition of MAO-A and increased tyramine pressor sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asatoor AM, Levi AJ, Milne MD (1963) Tranylcypromine and cheese. Lancet II:733–734
Bieck PR, Antonin KH (1982) Monoamine oxidase inhibition by tranylcypromine: assessment in normal volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22:301–308
Birkmayer W, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1982) (-) Deprenyl in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Clin Neuropharmacol Ther 5:195–230
Blackwell B (1963) Hypertensive crisis due to monoamine-oxidase inhibitors. Lancet II:849–851
Byck R (1975) Drugs and the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In: Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, McMillan, New York, pp 152–160
Cohen RM, Campbell IC, Yamaguchi I, Pickar D, Kopin IJ, Murphy DL (1982) Cardiovascular changes in response to selective monoamine oxidase inhibition in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 80:155–160
Dollery CT, Brown MJ, Davies DS, Lewis PJ, Strolin-Benedetti M (1983) Oral absorption and concentration-effect relationship of tyramine with and without cimoxatone, a type-A specific inhibitor of monoamine oxidase. Clin Pharmacol Ther 34:651–662
Eisler T, Teravainen H, Nelson R, Krebs H, Weise V, Lake CR, Ebert MH, Whetzel H, Murphy DL, Kopin IJ, Calne DB (1981) Deprenyl in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 31:19–23
Elsworth JD, Glover V, Reynolds GP, Sandler M, Lees AJ, Phuapradit P, Shaw KM, Stern KM, Kumar P (1978) Deprenyl administration in man: A selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor without the “cheese effect”. Psychopharmacology 57:33–38
Fuentes JA, Neff NH (1975) Selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs as aids in evaluating the role of type-A and B enzymes. Neuropharmacology 14:819–825
Garcha G, Imrie PR, Marley E, Thomas DV (1979) Effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) on pretreatment on the fate of intraduodenally instilled [14C]-tyramine. Br J Pharmacol 78:454–455
Garrick NA, Murphy DL (1980) Species differences in the deamination of dopamine and other substrates for monoamine oxidase in brain. Psychopharmacology 72:27–33
Ghose K, Turner P, Coppen A (1975) Intravenous tyramine pressor response in depression. Lancet I:1317–1318
Glover V, Sandler M, Owen F, Riley GJ (1977) Dopamine is a monoamine oxidase B substrate in man. Nature 265:80–81
Glover V, Pycock CJ, Sandler M (1983) Tyramine-induced noradrenaline release from rat brain slices: Prevention by (_)-deprenyl. Br J Pharmacol 80:141–148
Hall DWR, Logan BW (1969) Further studies on the inhibition of monoamine oxidase by M and B 9302 (clorgyline). II. Comparison of M and B 9302 inhibition with that of iproniazid. Biochem Pharmacol 18:1955–1959
Horwitz D, Lovenberg W, Engelman K, Sjoerdsma A (1964) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tyramine, and cheese. JAMA 190:1108–1110
Houslay MD, Tipton KF, Youdim MBH (1976) Mutliple forms of monoamine oxidase, fact and artifact. Life Sci 19:467–468
Jimerson DC, Markey SP, Oliver JA, Kopin IJ (1981) Simultaneous measurement of plasma 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenolethylene glycol and 3,4-dihydroxy phenylethylene glycol by gaschromatography-mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectrom 8:256–259
Knoll J, Ecsery Z, Keleman K, Nievel J, Knoll B (1965) Phenylisopropylmethyl propinylamine (E-250), a new spectrum psychic energizer. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 155:154–164
Knoll J, Ecsery Z, Magyar K, Satory E (1978) Novel (-)deprenylderived selective inhibitors of B-type monoamine oxidase. The relation of structure to their action. Biochem Pharmacol 27:1739–1747
Lader MH, Sakalis G, Tansella M (1970) Interactions between sympathomimetic amines and a new monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Psychopharmacologia 18:118–123
Lees AJ, Shaw KM, Kohout L, Stern GM, Elsworth JD, Sandler M, Youdim MGH (1977) Deprenyl in Parkinson's disease. Lancet II:791–795
Lipper S, Murphy DL, Slater S, Buchsbaum MS: Comparative behavioral effects of clorgyline and pargyline in man: A preliminary report. Psychopharmacology 62:123–128
Mann JJ, Gershon S (1980) l-Deprenyl, a selective monoamine oxidase type-B inhibitor in endogenous depression. Life Sci 26:877–882
Mann JJ, Frances A, Kaplan RD, Kocsis J, Peselow ED, Gershon S (1982) The relative efficacy of 1-deprenyl, a selective monoamine oxidase type B inhibitor, in endogenous and non-endogenous depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol 54–57
Marley E, Blackwell R (1970) Interactions of monoamine oxidase inhibitors, amines and foodstuffs. In: Garattini S, Goldin A, Hawking F, Kopin I (eds) Advances in pharmacology and chemotherapy. Academic, New York, pp 184–239
Mendelewicz J, Youdim MBH (1978) Antidepressant potentiation of 5-hydroxy-tryptophan by 1-deprenyl, an MAO “type B” inhibitor. J Neural Transm 43:279–286
Mendelewicz J, Youdim MBH (1983) l-Deprenyl, a selective monoamine oxidase type-B inhibitor, in the treatment of depression: a double blind evaluation. Br J Psychiatry 142:508–511
Mendis N, Pare CMB, Sandler M, Glover V, Stern GM (1981) Is the failure of (-)deprenyl, a selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor, to alleviate depression related to freedom from the cheese effect? Psychopharmacology 73:87–90
Murphy DL (1978) Substrate-selective monoamine oxidases: Inhibitor, tissue, species and functional differences. Biochem Pharmacol 27:1889–1893
Murphy DL, Wright C, Buchsbaum M, Costa J, Nichols A, Wyatt R (1976) Platelet and plasma amine activities in 650 normals: Sex and age differences and stability over time. Biochem Med 16:254–265
Pickar D, Cohen RM, Murphy DL (1979) Tyramine infusions in bipolar illness: Behavioral effects and longitudinal changes in pressor sensitivity. Am J Psychiatry 136:1460–1463
Pickar D, Cohen RM, Jimerson DC, Murphy DL (1981a) Tyramine infusions and selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor treatment. I. Changes in pressor sensitivity. Psychopharmacology 74:4–7
Pickar D, Cohen RM, Jimerson DC, Lake CR, Murphy DL (1981b) Tyramine infusions and selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor treatment. II. Interrelationship among pressor sensitivity changes, platelet MAO inhibition and plasma MHPG reduction. Psychopharmacology 74:8–12
Sandler M, Glover V, Ashford A, Stern GM (1978) Absence of “cheese effect” during deprenyl therapy: Some recent studies. J Neural Transm 43:209–215
Sandler M, Glover V, Ashford A, Esmail A (1980) The inhibition of tyramine oxidation and the tyramine hypertensive response (“cheese effect”) may be independent phenomena. J Neural Transm 48:241–247
Sen NP (1969) Analysis and significance of tyramine in foods. J Food Sci 34:22–26
Simpson G, White K, Pi E, Razani J, Sloane B (1983) Monoamine oxidase inhibition and tyramine sensitivity in l-deprenyl-treated subjects. Psychopharmacol Bull 19:340–342
Stern GM, Lees AJ, Sandler M (1978) Recent observations on the clinical pharmacology of (-)deprenyl. J Neural Transm 43:245–251
Varga E, Tringer L (1967) Clinical trial of a new type promptly acting psychoenergetic agent (Phenylisopropyl methyl-propinyl-HCl, “E-250”). Acta Med Acad Sci Hung 23:289–295
Waldmeier PC, Felner AE (1978) Deprenil: Loss of selectivity for inhibition of B-type MAO after repeated treatment. Biochem Pharmacol 27:801–802
Youdim MBH (1977) Tyramine and psychiatric disorders. In: Usdin E, Hamberg DA, Barchas JD (eds) Neuroregulators and psychiatric disorders. Oxford University, New York, pp 57–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunderland, T., Mueller, E.A., Cohen, R.M. et al. Tyramine pressor sensitivity changes during deprenyl treatment. Psychopharmacology 86, 432–437 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427904
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427904