Abstract
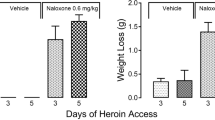
Four schedules of subcutaneous morphine pellet implantation were developed to render rats rapidly physically dependent on morphine. The schedules included implantation of four morphine pellets over a 3-day period (schedule 1), six morphine pellets over a 3-day period (schedule 2), six pellets over a 7-day period (schedule 3), and ten pellets over a 10-day period (schedule 4). Each morphine pellet contained 75 mg of morphine base. The degree of morphine dependence was quantitated by determining the median effective dose (ED50) of naloxone required to induce the stereotyped jumping response. Hypothermia and weight loss, during abrupt and naloxone-induced withdrawal, were also measured. Rats on schedule 4 exhibited a high degree of dependence on morphine as evidenced by an extremely low naloxone ED50 for the precipitated withdrawal jumping response, whereas schedules 1 and 2 produced a low degree of dependence as shown by high naloxone ED50's. Further evidence for a high degree of physical dependence on morphine is schedule 4 rats was indicated by their greater loss in body weight and greater hypothermic response after abrupt and after naloxone precipitated withdrawal compared with these responses in the rats in the other three schedules. A correlation was found to exist between naloxone ED50 for the jumping response, body weight loss, and hypothermia observed during naloxone-induced withdrawal in morphine-dependent rats. These studies suggest that the implantation of four morphine pellets in the rat produces a mild degree of dependence and that caution should be exercised when making generalized conclusions about the biochemical correlations involved when four or less number of pellets, each containing 75 mg of morphine base, are used to induce morphine dependence in the rat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akera, T., Brody, T. M.: The addiction cycle to narcotics in the rat and its relation to catecholamines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 17, 675–688 (1968)
Algeri, S., Costa, E.: Physical dependence on morphine fails to increase turnover rate in rat brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 20, 877–884 (1971)
Bläsig, J., Herz, A., Gramsch, C.: Effect of depletion of brain catecholamines during the development of morphine dependence on precipitated withdrawal in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 286, 325–336 (1975)
Bläsig, J., Herz, A., Reinhold, K., Zieglgansberger, S.: Development of physical dependence on morphine in respect to time and dosage and quantification of the precipitated withdrawal syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 33, 19–38 (1973)
Cicero, T. J., Meyer, E. R.: Morphine pellet implantation in rats: Quantitative assessment of tolerance and dependence. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 184, 404–408 (1973)
Colasanti, B., Kirchman, A., Khazan, N.: Changes in the electroencephalogram and REM sleep time during morphine abstinence in pellet-implanted rats. Res. Comm. Chem. Path. Pharmacol. 12, 163–172 (1975)
Collier, H. O. J., Francis, D. L., Schneider, C.: Modification of morphine withdrawal by drugs interacting with humoral mechanisms: some contradictions and their interpretation. Nature (Lond.) 237, 220–223 (1972)
Domino, E. F., Wilson, A.: Effect of narcotic analgesic agonists and antagonists on rat brain acetylcholine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 184, 18–32 (1973)
Francis, D. L., Schneider, C.: Jumping after naloxone precipitated withdrawal of chronic morphine in the rat. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 41, 424P-425P (1971)
Gibson, R. D., Tingstad, J. E.: Formulation of a morphine implantation pellet suitable for tolerance-physical dependence studies in mice. J. pharm. Sci. 59, 426–427 (1971)
Hosoya, E.: Some withdrawal symptoms of rats to morphine. Pharmacologist 1, 77 (1959)
Hui, K. S., Roberts, M. B.: An improved implantation pellet for rapid induction of morphine dependence in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 27, 569–573 (1975)
Iwamoto, E. T., Ho, I. K., Way, E. L.: Elevation of brain dopamine during naloxone-precipitated withdrawal in morphine dependent mice and rats. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 187, 558–567 (1973)
Litchfield, J. T., Wilcoxon, F. A.: A simplified method of evaluation dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 96, 99–113 (1949)
Marshall, I., Grahame-Smith, D. G.: Evidence against a role of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine in the development of physical dependence upon morphine in mice. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 179, 634–641 (1971)
Maruyama, Y., Takemori, A. E.: The role of dopamine and nor-epinephrine in the naloxone-induced abstinence of morphine dependent mice. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 185, 602–608 (1973)
Numan, R., Smith, N., Lal, H.: A versatile procedure for rapid induction of narcotic addiction in the rat utilizing intravenous injections. Physiol. Psychol. 3, 261–262 (1975)
Oka, T., Nozaki, M., Hosoya, E.: Effects of P-chlorophenylalanine and cholinergic antagonists on body temperature changes induced by the administration of morphine to the non-tolerant and morphine-tolerant rats. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 180, 136–143 (1972)
Shen, F. H., Loh, H. H., Way, E. L.: Brain serotonin turnover in morphine tolerant and dependent mice. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 175, 427–434 (1970)
Stolerman, I. P., Kumar, R.: Preferences for morphine in rats: Validation of an experimental model of dependence. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 217–223 (1970)
Way, E. L., Loh, H. H., Shen, F. H.: Simultaneous quantitative assessment of morphine tolerance and physical dependence. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 167, 1–8 (1969)
Wei, E., Loh, H. H., Way, E. L.: Quantitative aspects of precipitated abstinence in morphine-dependent rats. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 184, 398–403 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhargava, H.N. Rapid induction and quantitation of morphine dependence in the rat by pellet implantation. Psychopharmacology 52, 55–62 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426600
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426600