Summary
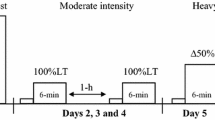
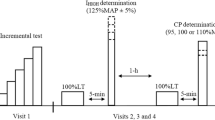
Fourteen Subjects (6 male, 8 female) participated in a training program upon a bicycle ergometer for 7 weeks. Group CT followed a continuous training regimen 4 days per week at 70% \(\dot V\)O2 max. Group IT trained by an interval method at 100% \(\dot V\)O2 max. The duration of each training session was assigned so that each subject would complete 10,000 kpm of work per session during the first week. Each subsequent week, the work load was increased 3000 kpm. Pretraining tests included \(\dot V\)O2 max, standard 7 min tests at 80% \(\dot V\)O2 and 90% \(\dot V\)O2, an endurance test at 90%, and an intense anaerobic work bout at 2400 kpm. Variables assessed were \(\dot V\)O2, HR, and blood lactic acid concentrations. The mean increase in \(\dot V\)O2 max was 5.1 ml/kg min (15%) for both groups with a corresponding increase in maximal lactate of 20 mg-%. The response to the post-training tests was nearly identical for both groups: submaximal heart rate at the same absolute work load declined 17 beats/min (CT) and 15 beats/min (IT), submaximal lactate levels declined significantly, endurance ride duration increased 26 min. Continuous and interval training at 70% and 100% \(\dot V\)O2 max respectively produce identical changes in heart rate response, blood lactic acid concentration and \(\dot V\)O2 max when the total work load is equated per training session.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benestad, A.: Trainability of old men. Acta med. scand. 178, 321–328 (1965)
Bryntesow, P., Sinning, W. E.: The effects of train-frequencies on the retention of cardiovascular fitness. Med. Sci. Sports. 5, 29–33 (1973)
Costill, D. L.: Metabolic responses during distance running. J. appl. Physiol. 28, 251–255 (1970)
Cotes, J. E., Meade, F.: Physical training in relation to the energy expenditure of walking and to factors controlling respiration during exercise. Ergonomics 2, 195–206 (1959)
Davies, C. T. M., Knibbs, A. V.: The training stimulus: The effect of intensity, duration and frequency of effort on maximum aerobic power output. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 29, 299–305 (1971)
Ekblom, B., Astrand, P. O., Saltin, B., Stenberg, J., Wallstrom, B.: Effect of training on circulatory response to exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 24, 518–528 (1968)
Faria, I. E.: Cardiovascular response to exercise as influenced by training of various intensities. Res. Quart. 41, 44–50 (1970)
Flint, M. M., Drinkwater, B. L., Horvath, S.: Effects of training on women's response to submaximal exercise. Med. Sci. Sports. 6, 89–94 (1974)
Fox, E. L., Bartels, R., Billings, C. E., Mathews, D. K., Bason, R., Webb, W. M.: Intensity and distance of interval training programs and changes in aerobic power. Med. Sci. Sports. 5, 18–22 (1974)
Karvonen, M. J., Kentala, E., Mustala, O.: The effects of training on heart rate. A longitudinal study. Ann. Med. exp. Fenn. 35, 307–315 (1957)
Kilbom, A.: Physical training in women. Scand, J. clin. Lab. Invest., Suppl. 119, 1–34 (1971)
Knuttgen, H. G., Nordesjo, L. O., Ollander, B., Saltin, B.: Physical conditioning through interval training with young male adults. Med. Sci. Sports. 5, 220–226 (1974)
Margaria, R., Cerretelli, P., Aghemo, P., Sossi, G.: Energy cost of running. J. appl. Physiol. 18, 367–370 (1963)
Pfleiderer, G., Dose, K.: Eine enzymatische Bestimmung der L(+) MilchsÄure mit MilchsÄuredehydrase. Biochem. Z. 326, 436–441 (1955)
Pollock, M. L., Cureton, T. K., Greninger, M. S.: Effects of frequency of training on work capacity, cardiovascular function and body composition of adult men. Med. Sci. Sports. 1, 70–74 (1969)
Roskamm, H.: Optimum patterns of exercise for healthy adults. Canad. med. Ass. J. 96, 895–898 (1967)
Saltin, B.: Physiological effects of physical conditioning. Med. Sci. Sports. 1, 50–56 (1969)
Saltin, B., Hartley, L., Kilbom, A., Astrand, I.: Physical training on sedentary middle-aged and older men. Oxygen uptake, heart rate and blood lactate concentrations at submaximal and maximal exercise. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 24, 323–334 (1969)
Sharkey, B. J.: Intensity and duration of training and the development of cardiorespiratory endurance. Med. Sci. Sports. 2, 197–202 (1970)
Sharkey, B. J., Hollman, J. P.: Cardiorespiratory adaptations to training at specified intensities. Res. Quart. 38, 398–704 (1967)
Shepard, R. J.: Intensity, duration and frequency of exercise as determinants of the response to a training regime. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 26, 272–278 (1968)
Sloan, A. W.: Estimation of body fat in young men. J. appl. Physiol. 23, 311–315 (1967)
Sloan, A. W., Burt, J. J., Blyth, C. S.: Estimation of body fat in young women. J. appl. Physiol. 17, 967–970 (1962)
Wilmore, J. H., Costill, D. L.: A semi-automated systems approach to the assessment of respiratory and metabolic parameters during exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 36, 618–620 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eddy, D.O., Sparks, K.L. & Adelizi, D.A. The effects of continuous and interval training in women and men. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 37, 83–92 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421694
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421694