Abstract
In eight groups of healthy male athletes, aged 19–44 years, serum urea, alpha-amino nitrogen and free tyrosine were determined before and after physical exercise of different duration. Exercise was competitional running, skiing, march or bicycle ergometer work, its duration between 15 and 765 min. The results were compared with previous data from this laboratory and those of other authors.
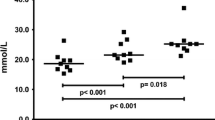
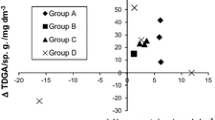
After about 60–70 min of exertion, there is a significant fall in serum amino nitrogen and a rise in urea and free tyrosine; the magnitude of these changes correlated well to the duration of exercise. Likewise, there is a significant correlation between increase in serum urea and decrease in amino nitrogen. The observed changes strongly suggest an increased breakdown of nitrogen-containing compounds during prolonged exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborg, G., Felig, Ph., Hagenfeldt, L., Hendler, R., Wahren, J.: Substrate turnover during prolonged exercise in man. J. clin. Invest. 53, 1080–1090 (1974)
Altman, P., Dittmer, D.: Excretion products in sweat. In: Biology data book, 2nd ed., Vol. III, p. 1493. Bethesda: Feder. Amer. Soc. for Exper. Biol. 1974
Ambrose, J. A.: Fluorometric measurement of tyrosine in serum and plasma. Clin. Chem. 20, 505–510 (1974)
Ambrose, J. A., Sullivan, P., Ingerson, A., Brown, R. L.: Fluorometric determination of tyrosine. Clin. Chem. 15, 611–620 (1969)
Astrand, P. O., Rodahl, K.: Textbook of work physiology. New York: McGraw-Hill 1970
Berg, A., Keul, J.: Der Einflu\ von anabolen Substanzen auf das Verhalten der freien SerumaminosÄuren von Normalpersonen und Schwerathleten in Ruhe und bei Körperarbeit. österr. J. Sportmed. 3, 11–18 (1974)
Bergström, J., Hermansen, L., Hultman, E., Saltin, B.: Diet, muscle glycogen and physical performance. Acta physiol. scand. 71, 140–150 (1967)
Binnewies, S. M.: Zu Problemen biochemischer VerÄnderungen wÄhrend der MuskeltÄtigkeit. Z. ges. Hyg. 14, 657–669 (1968)
Buse, M., Biggers, S. F., Friderich, K., Buse, J.: Oxidation of branched-chain amino acids by isolated hearts and diaphragms of the rat. J. biol. Chem. 247, 8085–8092 (1972)
Carlsten, A., HÄggendal, J., Hallgren, B., Jagenburg, R., Svanborg, A.: Effects of ganglionic blocking drugs on blood glucose, free fatty acids and catecholamines at exercise in man. Acta physiol. scand. 64, 439–447 (1965)
Carlsten, A., Hallgren, B., Jagenburg, R., Svanborg, A., Werkö, L.: Arterial concentrations of free fatty acids and free amino acids in healthy human individuals at rest and at different work loads. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 14, 185–191 (1962)
Cerny, F.: Protein metabolism during two hours of ergometer exercise. In: Metabolic effects of prolonged exercise (H. Howald, J. R. Poortmans, eds.), Sympos. Magglingen 1973. Basel: BirkhÄuser 1975
Chailley-Bert, P., Plas, F., Pallardy, G.: Le métabolisme protidique pendant l'effort musculaire prolongé. Presse méd. 70, 705–707 (1962)
Costill, D. L., Sparks, K., Gregor, R., Turner, C.: Muscle glycogen utilization during exhaustive running. J. appl. Physiol. 31, 353–356 (1971)
Felig, Ph.: The glucose-alanine cycle. Metabolism 22, 179–207 (1973)
Felig, Ph., Wahren, J.: Amino acid metabolism in exercising man. J. clin. Invest. 50, 2703–2714 (1971a)
Felig, Ph., Wahren, J.: Interrelationship between amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism during exercise: The glucose-alanine cycle. In: Muscle metabolism during exercise (B. Pernow, B. Saltin, eds.), pp. 205–214. New York-London: Plenum Press 1971b
Goldberg, A. L.: Amino acid catabolism in muscle. In: Muscle biology, Vol. I (R. Cassens, ed.), pp. 102–105. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. 1972
Gontzea, J., Schutzescu, P.: Stickstoffverluste mit dem Schwei\ bei Muskelarbeit. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 20, 90–110 (1963)
Haralambie, G.: L'élimination de la tyrosine pendant l'effort physique. Méd. éduc. phys. Sport 39, 325–331 (1964)
Haralambie, G., Keul, J.: Beziehungen zwischen Proteinstoffwechsel und körperlichen Belastungen. Med. Welt 22, 1977–1980 (1971)
Hultman, E., Nilsson, L.: Liver glycogen as a glucose supplying source during exercise. In: Limiting factors of physical performance (J. Keul, ed.), pp. 179–189. Stuttgart: Thieme 1973
Keul, J.: Der Einflu\ von Kalium-Magnesiumaspartat bei langwÄhrenden körperlichen Belastungen. In: Biochemische Eigenschaften und Möglichkeiten der klinischen Anwendung von Kalium-Magnesiumaspartat (R. Beer, U. Finsterer, eds.), pp. 21–27. Aulendorf: Editio Cantor 1971
Keul, J., Doll, E., Keppler, D.: Energy metabolism of human muscle. Basel-New York: Karger 1972
Keul, J., Haralambie, G.: Die Wirkung von Kohlenhydraten auf die LeistungsfÄhigkeit und die energieliefernden Substrate im Blut bei langwÄhrender Körperarbeit. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 98, 1806–1811 (1973)
Keul, J., Haralambie, G., Arnold, T., Schumann, W.: Heart rate and energy-yielding substrates in blood during long-lasting running. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 32, 279–289 (1974)
Keul, J., Haralambie, G., Fleischmann, W., Schick, G.: Der Einflu\ von Intervallarbeit auf die arteriellen und femoralvenösen AminosÄurespiegel. Sportarzt u. Sportmed. 22, 1–3 (1971)
Lenkova, R. I., Usik, S. V., Yakovlev, N. N.: Changes of urea content in the blood and tissues during muscular activity in relation to adaption of the organism. Sechenov physiol. J. U.S.S.R. 49, 1097–1101 (1973)
Lowenstein, J.: Ammonia production in muscle and other tissues: the purine nucleotide cycle. Physiol. Rev. 52, 382–414 (1972)
Magazanik, A., Shapiro, Y., Meytes, D., Meytes, I.: Enzyme blood levels and water balance during a marathon race. J. appl. Physiol. 36, 214–217 (1974)
Maron, M. B., Horvath, St., Wilkerson, J. E.: Acute blood biochemical alterations in response to marathon running. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 34, 173–181 (1975)
Poortmans, J., Siest, G., Galteau, M.-M., Houot, O.: Distribution of plasma amino acids in humans during submaximal prolonged exercise. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 32, 143–147 (1974)
Randle, P., England, P., Denton, R.: Control of the tricarboxylate cycle and its interactions with glycolysis during acetate utilization in rat heart. Biochem. J. 117, 677–695 (1970)
Rapp, R. D.: Determination of serum amino acid. Clin. Chem. 9, 27–30 (1963)
Rasch, P., Wilson, I. D.: In: Exercise physiology (H. B. Falls, ed.), Chapt. IV, pp. 129–151. New York-London: Academic Press 1968
Refsum, H. E., Strömme, S.: Urea and creatinine production and excretion in urine during and after prolonged heavy exercise. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 33, 247–254 (1974)
Refsum, H. E., Strömme, S.: Relationship between urine flow, glomerular filtration and urine solute concentrations during prolonged heavy exercise. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 35, 775–780 (1975)
Richterich, R.: Klinische Chemie. Theorie und Praxis, 2. Aufl. Frankfurt (Main): Akad. Verlagsges. 1968
Rogozkin, V.: Nitrogen metabolism in muscular activity of different duration. Ukr. Biochim. Jurn. 31, 489–494 (1959)
Ulmeanu, Fl.-C., Partheniu, Al., Haralambie, G.: Rapports entre la variation de la tyrosinémie et certaines modifications de l'excitabilité neuromusculaire, determinées par un effort dosé chez le sportif. In: Biochemistry of exercise (J. R. Poortmans, ed.), pp. 347–352. Basel-New York: Karger 1969
Viru, A., Körge, P.: Metabolic processes and adrenocortical activity during marathon races. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 29, 173–183 (1971)
Wahren, J., Felig, Ph., Hendler, R., Ahlborg, G.: Glucose and amino acid metabolism during recovery after exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 34, 838–845 (1973)
Williams, J. N., Schurr, P., Elvehjem, C.: The influence of chilling and exercise on free amino acid concentrations in rat tissues. J. biol. Chem. 182, 55–59 (1950)
Wurtman, R. J., Chou, Ch., Rose, Chr.: Daily rhythm in tyrosine concentrations in human plasma: persistence on low-protein diets. Science 158, 660–663 (1967)
Wurtman, R. J., Rose, Chr., Chou, Ch., Larin, F.: Daily rhythms in the concentrations of various amino acids in human plasma. New Engl. J. Med. 279, 171–175 (1968)
Young, V.: The role of skeletal and cardiac muscle in the regulation of cardiac metabolism. In: Mammalian protein metabolism, Vol. IV (H. N. Munro, ed.), p. 586. New York-London: Academic Press 1970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haralambie, G., Berg, A. Serum urea and amino nitrogen changes with exercise duration. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 36, 39–48 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421632
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421632