Summary
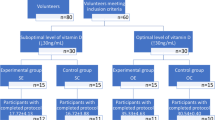
The effects of vitamin E (d-α-tocopherol) on serum enzyme levels after heavy exercise with trained and untrained muscles were studied in 26 subjects, aged 19–24, using a double blind experimental design. After a 6 week medication period (300 mg daily), the serum concentration of d-α-tocopherol had increased from 12.7–19.6 Μg/ml in the vitamin E group, while in the placebo group the value was unchanged. The subjects were then exposed to muscular work with either trained or untrained muscles. Serum concentrations of CK, ASAT and LD were measured prior to exercise and at different time intervals afterwards. In subjects exposed to exercise with trained muscles there was an insignificant elevation in serum enzymes and no indication of any difference between the two groups. Muscular work involving mainly untrained muscles caused a highly significant increase in serum CK activity. A significant elevation was also observed for ASAT and LD. No difference between the vitamin E and the placebo group was found. Isoenzyme studies showed that the rise in CK was due to an increase in the CK-MM fraction, indicating that striated muscle was the major site of enzyme release. It is concluded that vitamin E has no influence on the increase in serum enzyme levels following exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborg, B., Brohult, J.: Immediate and delayed metabolic reactions in well-trained subjects after prolonged physical exercise. Acta Med. Scand. 182, 41–54 (1967)
Anderson, T. W.: Vitamin E in angina pectoris. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 110, 401–406 (1974)
Boyd, A. M., Marks, J.: Treatment of intermittent claudication. A re-appraisal of the value of tocopherol. Angiology 14, 198–208 (1963)
Briggs, M., Briggs, M.: Are vitamin E supplements beneficial? Med. J. Aust. 1, 434–437 (1974)
Cheraskin, E., Ringsdorf, W. M., Jr.: Daily vitamin E consumption and reported cardiovascular findings. Nutr. Rep. Int. 2, 107–113 (1970)
Critz, J. B., Cunningham, D. A.: Plasma enzyme levels in man after different physical activities. J. Sports Med. 12, 143–149 (1972)
Cunningham, D. A., Critz, J. B.: Effect of hypoxia and physical activity on plasma enzyme levels in man. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. 30, 302–308 (1972)
Dinning, S., Day, L.: Vitamin E deficiency in the monkey. J. Exp. Med. 105, 395–402 (1957)
Dinning, S.: Vitamin E responsive anemia in monkeys and man. Nutr. Rev. 21, 289–291 (1963)
Farell, P. M., Bieri, J. G.: Megavitamin E supplementation in man. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 28, 1381–1386 (1975)
Fojt, E., Ekelund, L.-G., Hultman, E.: Enzyme activities in hepatic venous blood under strenuous physical exercise. Pfluegers Arch. 361, 287–296 (1976)
Fujii, T., Shimuzi, H.: Investigations on serum lipid components and serum vitamin E in iron deficiency anemia. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 19, 23–28 (1973)
Gallo-Torres, H. E.: Vitamin E in animal nutrition (Congress report). Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 42, 312–323 (1972)
Garcia, W.: Elevated creatine phosphokinase levels associated with large muscle mass. JAMA 228, 1395–1396 (1974)
Haeger, K.: The treatment of peripheral occlusive arterial disease with α-tocopherol as compared with vasodilatator agents and antiprothrombin (dicumarol). Vasc. Dis. 5, 199–213 (1968)
Hansen, Leland G., Warwick, Warren J.: A fluorometric micro method for serum tocopherol. Am. J. Clin. Path. 46, 133–137 (1966)
Haralambie, G.: Neuromuscular irritability and serum creatine phosphate kinase in athletes in training. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. 31, 279–288 (1973)
Hodges, R. E.: Vitamin E and coronary heart disease. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 62, 638–642 (1973)
Horwitt, M. K.: Vitamin E: a reexamination. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 29, 569–578 (1976)
Hunter, J. B., Critz, J. B.: Effect of training on plasma enzyme levels in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 31, 20–23 (1971)
Jager, F. C.: Long-term dose-response effects of vitamin E in rats. Nutr. Metab. 14, 1–7 (1972)
JAMA (editorial): Target for tocopherol. 217, 1545 (1971)
Kamimura, M.: Anti-inflammatory activity of vitamin E. J. Vitaminol. 18, 204–209 (1972)
Larsson, H., Haeger, K.: Plasma and muscle tocopherol contents during vitamin E therapy in arterial disease. Pharmacol. Clin. 1, 72–76 (1968)
Lawrence, J. P., Bower, R. C., Riehl, W. P., Smith, U. L.: Effects of α-tocopherol acetate on the swimming endurance of trained swimmers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 28, 205–208 (1975)
Magazanik, A., Shapiro, Y., Meytes, D., Meytes, I.: Enzyme blood levels and water balance during a marathon race. J. Appl. Physiol. 36, 214–217 (1974)
Misner, J. E., Massey, B. H., Williams, B. T.: The effect of physical training on the response of serum enzymes to exercise stress. Med. Sci. Sports 5, 86–88 (1973)
Nafstad, I., Tollersrud, S.: The vitamin E deficiency syndrome in pigs. Acta Vet. Scand. 11, 452–480 (1970)
Nagawa, T., Kita, H., Aoki, J., Maeshima, T., Hiozawa, K.: The effect of vitamin E on endurance. Asian Med. J. 11, 619–633 (1968)
Nail, P. P., Kayden, H. J. (editors): International conference on vitamin E and its role in cellular metabolism. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 203, 1–247 (1972)
Nuttall, F. Q., Jones, B.: Creatine kinase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase activity in serum: Kinetics of change with exercise and effect of physical conditioning. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 71, 847–854 (1968)
Oliver, I. T.: A spectrophotometric method for determination of creatine phosphokinase and myokinase. Biochem. J. 61, 116–122 (1955)
Rasch, P. J., Schwartz, P. L.: Effect of amateur wrestling on selected serum enzymes. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 12, 82–86 (1972)
Refsum, H. E., StrØmme, S. B., Tveit, B.: Changes in serum enzyme levels after 90 km crosscountry skiing. Acta Physiol. Scand. 84, 16A-17A (1972)
Roels, O. A.: Present knowledge of vitamin E. Nutr. Rev. 25, 33–37 (1967)
Rosalki, S. B.: An improved procedure for serum creatine phosphokinase determination. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 69, 696–705 (1967)
Rose, L. I., Bousser, J. E., Cooper, K. H.: Serum enzymes after marathon running. J. Appl. Physiol. 29, 355–357 (1970)
Sahayeva, Y. A., Yefremov, V. V.: Experience with vitamin E supplement for bicycle racers and skiers. USSR Acad. Med. Sci. 27, 78–82 (1972)
Scandinavian Enzyme Commission: Recommended methods for the determination of four enzymes in blood. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 33, 291–306 (1974)
Schwartz, P. L., Carroll, H. W., Douglas, J. S., Jr.: Exercise-induced changes in serum enzyme activities and their relationship to max VO2. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. 30, 20–33 (1971)
Sharman, I. M., Down, M. G., Norgan, N. G.: The effects of vitamin E on physiological function and athletic performance of trained swimmers. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 16, 215–225 (1976)
Shephard, R. V., Campbell, R., Pimm, P., Stuart, D., Wright, G. R.: Vitamin E, exercise and the recovery from physical activity. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 119–126 (1974)
Somer, H., Konttinen, A.: Demonstration of serum creatine phosphokinase and myokinase. Biochem. J. 61, 116–122 (1955)
Von Heinemann, G., Pabst, H., Schievelbein, H.: Die AktivitÄt der Creatinkinase und des Isoenzyms CK-MB im Serum von Hochleistungssportlern. Dtsch. Z. Sportmed. 29, 33–37 (1978)
Watt, T., Romet, T. T., McFarlane, I., McGuey, D., Allen, C., Goode, R. C.: Vitamin E and oxygen consumption. Lancet 1974 II, 354–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helgheim, I., Hetland, Ø., Nilsson, S. et al. The effects of vitamin E on serum enzyme levels following heavy exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 40, 283–289 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421520
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421520