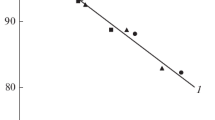
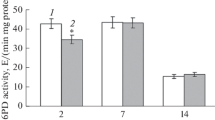
Abstract
The inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, isocitrate lyase and cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase in Candida maltosa was found to occur after the addition of glucose to starved cells. The concentration of cyclic AMP and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate increased drastically within 30 s when glucose was added to the intact cells of this yeast. From these results it was concluded that catabolite inactivation, with participation of cyclic AMP and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, is an important control mechanism of the gluconeogenetic sequence in the n-alkane-assimilating yeast Candida maltosa, as described for Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Entian K-D, Droell L, Mecke D (1983) Studies on rapid reversible and non-reversible inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and malate dehydrogenase in wild-type and glycolytic block mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 134: 187–192
Entian K-D, Froehlich K-U, Mecke D (1984) Regulation of enzymes and isoenzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 798:181–186
Ferguson JJ, Boll M, Holzer H (1967) Yeast malate dehydrogenase: enzyme inactivation and catabolite repression. Eur J Biochem 1:21–25
Francois J, Van Schaftingen E, Hers H-G (1984) The mechanism by which glucose increases fructose-2,6-bisphosphate concentrations in Sacharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 145:187–193
Funaguma T, Toyoda Y, Sy J (1985) Catabolite inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and cytoplasmatic malate dehydrogenase in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 130: 467–471
Funayama S, Gancedo JM, Gancedo C (1980) Turnover of yeast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in different metabolic conditions. Eur J Biochem 109:61–66
Gancedo C (1971) Inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by glucose in yeast. J Bacteriol 107:401–405
Gancedo JM, Gancedo C (1971) Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, phosphofructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from fermenting and non-fermenting yeasts. Arch Microbiol 76:132–138
Gancedo JM, Mazon MJ, Gancedo C (1982) Inactivation and phosphorylation of yeast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Biochem Soc Transact 10:326–327
Gancedo C, Schwerzmann N (1976) Inactivation by glucose of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 109:221–225
Gilman AG (1970) A protein binding assay for adenosine 3′, 5′-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 67:305–312
Hildebrandt W, Durner K, Weide H (1972) Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Aktivitätsbestimmung einiger Hefestämme nach Wachstum auf n-Alkanen. Z Allg Mikrobiol 12:15–18
Hofmann KH, Schauer F (1988) Utilization of phenol by hydrocarbon assimilating yeasts. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 54: 179–188
Hofmann KH, Vogt U (1987) Induction of phenol assimilation in chemostat cultures of Candida maltosa L4. J Basic Microbiol 27:441–447
Holzer H (1976) Catabolite inactivation in yeast. Trends Biochem Sci 1:178–181
Kretschmer M, Schellenberger W, Otto A, Kessler R, Hofmann E (1987) Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase and 6-phosphofructo-2 kinase are separable in yeast. Biochem J 246:755–759
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T 4. Nature (Lond) 227:680–685
Lenz A-G, Holzer H (1980) Rapid reversible inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by glucose. FEBS Lett 109:271–274
Lopez-Boado YS, Herrero P, Fernandez T, Fernandez R, Moreno F (1988) Glucose-stimulated phosphorylation of yeast isocitrate lyase in vivo. J Gen Microbiol 134:2499–2505
Lopez-Boado YS, Herrero P, Gascon S, Moreno F (1987) Catabolite inactivation of isocitrate lyase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 147:231–234
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AC, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mach H, Hecker M, Mach F (1984) Evidence for the presence of cyclic adenosine monophosphate in Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 22:27–30
Neeff J, Haegele E, Nauhaus J, Heer H, Mecke D (1978) Evidence for catabolite degradation in the glucose dependent inactivation of yeast cytoplasmatic malate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem 87:489–495
Pohlig G, Holzer H (1985) Phosphorylation and inactivation of yeast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase from yeast. J Biol Chem 260:13818–13823
Purwin C, Leidig F, Holzer H (1982) Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 107:1482–1489
Tortora P, Birtel M, Lenz A, Holzer H (1981) Glucose dependent inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 100:688–695
Toyoda Y, Sy Y (1985) Catabolite inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in Kluyveromyces fragilis. Curr Microbiol 12:241–244
Van der Plaat JB, Van Solingen P (1974) Cyclic 3′, 5′-adenosine monophosphate stimulates trehalose degradation in baker's yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 56:580–587
Van Schaftingen E, Hers H-G (1983) Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate in relation with the resumption of metabolic activity in slices of Jerusalem artichoke tubers. FEBS Lett 164:195–200
Witt J, Kronau R, Holzer H (1966) Isoenzyme der Malatdehydrogenase und ihre Regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 128:63–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polnisch, E., Hofmann, K. Cyclic AMP, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate and catabolite inactivation of enzymes in the hydrocarbon-assimilating yeast Candida maltosa . Arch. Microbiol. 152, 269–272 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409662
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409662