Abstract
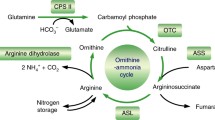
The catabolic products of arginine metabolism were observed in Aphanocapsa 6308, a unicellular cyanobacterium, by thin layer chromatography of growth media, by limiting growth conditions, and by enzymatic analysis. Of the organic, nitrogenous compounds examined, only arginine supported growth in CO2-free media. The excretion of ornithine at a concentration level greater than citrulline suggested the existence in Aphanocapsa 6308 of the arginine dihydrolase pathway which produced ornithine, CO2, NH4, + adenosine 5′-triphosphate. Its existence was confirmed by enzymatic analysis. Although cells could not grow on urea as a sole carbon source a very active urease and subsequently an arginase were also demonstrated, indicating that Aphanocapsa can metabolize arginine via the arginase pathway. The level of enzymes for both pathways indicates a lack of genetic control. It is suggested that the arginase pathway provides only nitrogen for the cells whereas the arginine dihydrolase pathway provides not only nitrogen, but also CO2 and adenosine 5′-triphosphate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCCP:
-
carbonylcyanide mchlorophenyl hydrazone
- DCMU:
-
3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethyl urea
- CGP:
-
cyanophycin granule protein
- PS II:
-
photosystem II
- PSI:
-
photosystem I
- TLC:
-
thin layer chromatography
- TCA:
-
trichloroacetic acid
- DPM:
-
disintegrations per min
References
Allen, M. M.: Simple conditions for growth of unicellular blue-green algae on plates. J. Phycol 4, 1–4 (1968)
Allen, M. M., Hutchison, F., Weathers, P. J.: Nitrogen limitation and cyanophycin granule formation in Aphanocapsa 6308. American Society for Microbiology, Abstracts, p. 171 (1977)
Berns, D. S., Holohan, P., Scott, E.: Urease activity in blue-green algae. Science 152, 1077–1078 (1966)
Blakemore, R. P., Canale-Parola, E.: Arginine catabolism by Treponema denticola. J. Bacteriol. 128, 616–622 (1976)
Brown, G. W., Cohen, P. P.: Comparative biochemistry of urea synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 234, 1769–1774 (1959)
Carr, N. G., Hood, W., Pearce, J.: Control and intermediary metabolism in blue-green algae. Prog. Photosyn. Res. 3, 1565–1569 (1969)
Goldschmidt, M. C., Lockhart, B. M.: Rapid methods for determining decarboxylase activity: arginine decarboxylase. Appl. Microbiol. 22, 350–357 (1971)
Goldschmidt, M. C., Lockhart, B. M., Perry, K.: Rapid methods for determining decarboxylase activity: ornithine and lysine decarboxylase. Appl. Microbiol. 22, 344–349 (1971)
Hoare, D. S., Hoare, L.: Feedback regulation of arginine biosynthesis in blue-green algae and photosynthetic bacteria. J. Bacteriol 92, 375–379 (1966)
Hood, W., Carr, N. G.: Apparent lack of control by repression of arginine metabolism in blue-green algae. J. Bacteriol. 107, 365–367 (1971)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, A. L., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Roberts, R. B., Abelson, P. H., Cowie, D. B., Bolton, E. J., Britten, R. J.: Studies of biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Carnegie Insf. Washington Publ. (1963)
Schimke, R. T., Berlin, C. M., Sweeney, E. W., Carroll, W. R.: The generation of energy by the arginine dihydrolase pathway in Mycoplasma hominis 07. J. Biol. Chem. 241, 2228–2236 (1966)
Sperry, J. F., Wilkins, T. D.: Arginine, a growth-limiting factor for Eubacterium lentum. J. Bacteriol. 127, 780–784 (1976)
Stalon, V., Ramos, F., Pierard, A., Wiame, J. M.: The occurrence of a catabolic and anabolic ornithine carbamyltransferase in Pseudomonas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 139, 91–97 (1967)
Stanier, R.: Autotrophy and heterotrophy. In: The biology of the blue-green algae (N. G. Carr, B. A. Whitton, eds.), pp. 501–518. Berkeley-Los Angeles: Univ. of Calif. Press 1973
Townsend, R.: Arginine metabolism by Spiroplasma citri. J. Gen. Microbiol. 94, 417–420 (1976)
Zolog, W., Ottow, J. C. G.: Improved thin-layer technique for detection of arginine dihydrolase among the Pseudomonas species. Appl. Microbiol. 26, 1001–1003 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weathers, P.J., Chee, H.L. & Allen, M.M. Arginine catabolism in Aphanocapsa 6308. Arch. Microbiol. 118, 1–6 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406066
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406066