Abstract
Key message
This study revealed different catalytic efficiencies of cyanobacterial argininosuccinate lyases in non-nitrogen-fixing and nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, demonstrating that l-arginine inhibition of l-argininosuccinate lyase is conserved among enzymes of three cyanobacterial orders.
Abstract
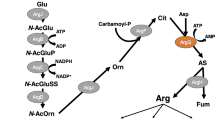
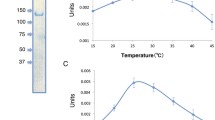
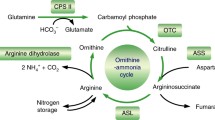
Arginine is a nitrogen-rich amino acid that uses a nitrogen reservoir, and its biosynthesis is strictly controlled by feedback inhibition. Argininosuccinate lyase (EC 4.3.2.1) is the final enzyme in arginine biosynthesis that catalyzes the conversion of argininosuccinate to l-arginine and fumarate. Cyanobacteria synthesize intracellular cyanophycin, which is a nitrogen reservoir composed of aspartate and arginine. Arginine is an important source of nitrogen for cyanobacteria. We expressed and purified argininosuccinate lyases, ArgHs, from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Nostoc sp. PCC 7120, and Arthrospira platensis NIES-39. The catalytic efficiency of the Nostoc sp. PCC 7120 ArgH was 2.8-fold higher than those of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Arthrospira platensis NIES-39. All three ArgHs were inhibited in the presence of arginine, and their inhibitory effects were lowered at pH 7.0, compared to those at pH 8.0. These results indicate that arginine inhibition of ArgH is widely conserved among the three cyanobacterial orders. The current results demonstrate the conserved regulation of enzymes in the cyanobacterial aspartase/fumarase superfamily.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Allen MM (1988) Cyanophycin—inclusions. Methods Enzymo 167:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(88)67022-4
Belkin S, Boussiba S (1991) Resistance of Spirulina platensis to ammonia at high pH values. Plant Cell Physiol 32:953–958. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078182
Bhaumik P, Koski MK, Bergmann U, Wierenga RK (2004) Structure determination and refinement at 2.44 Å resolution of argininosuccinate lyase from Escherichia coli. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60:1964–1970. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444904021912
Burnat M, Picossi S, Valladares A, Herrero A, Flores E (2019) Catabolic pathway of arginine in Anabaena involves a novel bifunctional enzyme that produces proline from arginine. Mol Microbiol 111:883–897. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14203
Cao YL, Li GL, Wang KT, Zhang HY, Li LF (2011) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of argininosuccinate lyase from Streptococcus mutans. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67:682–684. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309111011377
Chen LM, Omiya T, Hata S, Izui K (2002) Molecular characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from a thermophilic cyanobacterium, Synechococcus vulcanus with unusual allosteric properties. Plant Cell Physiol 43:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcf019
Chen X, Chen J, Zhang W, Wang H, Liu X, Zhou W, Yang H, Rao Z (2019) Crystal structure and biochemical study on argininosuccinate lyase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 510:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.01.061
Esteves-Ferreira AA, Cavalcanti JHF, Vaz MGMV, Alvarenga LV, Nunes-Nesi A, Araújo WL (2017) Cyanobacterial nitrogenases: phylogenetic diversity, regulation and functional predictions. Genet Mol Biol 40:261–275. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2016-0050
Farrell K, Overton S (1987) Characterization of argininosuccinate lyase (EC 4.3.2.1) from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochem J 242:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2420261
Flores E, Herrero A (2010) Compartmentalized function through cell differentiation in filamentous cyanobacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2242
Forchhammer K (2004) Global carbon/nitrogen control by PII signal transduction in cyanobacteria: from signals to targets. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:319–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2003.11.001
Forchhammer K, Selim KA (2020) Carbon/nitrogen homeostasis control in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 44:33–53. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuz025
Gupta M, Carr NG (1981) Enzyme activities related to cyanophycin metabolism in heterocysts and vegetative cells of Anabaena spp. J Gen Microbiol 125:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-125-1-17
Herrero A, Muro-Pastor AM, Flores E (2001) Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol 183:411–425. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.2.411-425.2001
Hoare DS, Hoare SL (1966) Feedback regulation of arginine biosynthesis in blue-green algae and photosynthetic bacteria. J Bacteriol 92:375–379. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.92.2.375-379.1966
Iijima H, Watanabe A, Sukigara H, Shirai T, Kondo A, Osanai T (2020) Simultaneous increases in the levels of compatible solutes by cost-effective cultivation of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biotechnol Bioeng 117:1649–1660. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27324
Inabe K, Miichi A, Matsuda M, Yoshida T, Kato Y, Hidese R, Kondo A, Hasunuma T (2021) Nitrogen availability affects the metabolic profile in cyanobacteria. Metabolites 11:867. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120867
Ito S, Koyama N, Osanai T (2019) Citrate synthase from Synechocystis is a distinct class of bacterial citrate synthase. Sci Rep 9:6038. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42659-z
Ito S, Hakamada T, Ogino T, Osanai T (2021) Reconstitution of oxaloacetate metabolism in the tricarboxylic acid cycle in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: discovery of important factors that directly affect the conversion of oxaloacetate. Plant J 105:1449–1458. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15120
Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani H, Tanaka A, Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Miyajima N, Hirosawa M, Sugiura M, Sasamoto S, Kimura T, Hosouchi T, Matsuno A, Muraki A, Nakazaki N, Naruo K, Okumura S, Shimpo S, Takeuchi C, Wada T, Watanabe A, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Tabata S (1996) Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions. DNA Res 3:109–136. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/3.3.109
Katayama N, Takeya M, Osanai T (2019) Biochemical characterisation of fumarase C from a unicellular cyanobacterium demonstrating its substrate affinity, altered by an amino acid substitution. Sci Rep 9:10629. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47025-7
Ke S, Haselkorn R (2013) The Sakaguchi reaction product quenches phycobilisome fluorescence, allowing determination of the arginine concentration in cells of Anabaena strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol 195:25–28. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01512-12
Krehenbrink M, Oppermann-Sanio FB, Steinbüchel A (2002) Evaluation of non-cyanobacterial genome sequences for occurrence of genes encoding proteins homologous to cyanophycin synthetase and cloning of an active cyanophycin synthetase from Acinetobacter sp. strain DSM 587. Arch Microbiol 177:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-001-0396-9
Lawrence BA, Polse J, DePina A, Allen MM, Kolodny NH (1997) 31P NMR identification of metabolites and pH determination in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6308. Curr Microbiol 34:280–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900182
Maheswaran M, Ziegler K, Lockau W, Hagemann M, Forchhammer K (2006) PII-regulated arginine synthesis controls accumulation of cyanophycin in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 188:2730–2734. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.188.7.2730-2734.2006
Mishra A, Surolia A (2017) Biochemical characterization of argininosuccinate lyase from M. tuberculosis: significance of a c-terminal cysteine in catalysis and thermal stability. IUBMB Life 69:896–907. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1683
Montesinos ML, Herrero A, Flores E (1997) Amino acid transport in taxonomically diverse cyanobacteria and identification of two genes encoding elements of a neutral amino acid permease putatively involved in recapture of leaked hydrophobic amino acids. J Bacteriol 179:853–862. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.3.853-862.1997
Muro-Pastor MI, Reyes JC, Florencio FJ (2005) Ammonium assimilation in cyanobacteria. Photosynth Res 83:135–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-004-2082-7
Nakamura S, Fu N, Kondo K, Wakabayashi KI, Hisabori T, Sugiura K (2021) A luminescent Nanoluc-GFP fusion protein enables readout of cellular pH in photosynthetic organisms. J Biol Chem 296:100134. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.016847
Oliver NJ, Rabinovitch-Deere CA, Carroll AL, Nozzi NE, Case AE, Atsumi S (2016) Cyanobacterial metabolic engineering for biofuel and chemical production. Curr Opin Chem Biol 35:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.08.023
Puthan Veetil V, Fibriansah G, Raj H, Thunnissen AM, Poelarends GJ (2012) Aspartase/fumarase superfamily: a common catalytic strategy involving general base-catalyzed formation of a highly stabilized aci-carboxylate intermediate. Biochemistry 51:4237–4243. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi300430j
Rae BD et al (2013) Cyanobacterial carboxysomes: microcompartments that facilitate CO2 fixation. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 23:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1159/000351342
Schirrmeister BE, de Vos JM, Antonelli A, Bagheri HC (2013) Evolution of multicellularity coincided with increased diversification of cyanobacteria and the Great Oxidation Event. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:1791–1796. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209927110
Sherman DM, Tucker D, Sherman LA (2000) Heterocyst development and localization of cyanophycin in N2-fixing cultures of Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 (Cyanobacteria). J Phycol 36:932–941. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.2000.99132.x
Troshina O, Jansson E, Lindblad P (1997) Ornithine cycle in Nostoc PCC 73102: presence of an in vitro functional argininosuccinate lyase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 152:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb10411.x
Turner MA, Simpson A, McInnes RR, Howell PL (1997) Human argininosuccinate lyase: a structural basis for intragenic complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9063–9068. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.17.9063
Watzer B, Engelbrecht A, Hauf W, Stahl M, Maldener I, Forchhammer K (2015) Metabolic pathway engineering using the central signal processor PII. Microb Cell Fact 14:192. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0384-4
Watzer B, Spät P, Neumann N, Koch M, Sobotka R, Macek B, Hennrich O, Forchhammer K (2019) The signal transduction protein PII controls ammonium, nitrate and urea uptake in cyanobacteria. Front Microbiol 10:1428. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01428
Wolk CP, Austin SM, Bortins J, Galonsky A (1974) Autoradiographic localization of 13N after fixation of 13N-labeled nitrogen gas by a heterocyst-forming blue-green alga. J Cell Biol 61:440–453. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.61.2.440
Xu Y, Labedan B, Glansdorff N (2007) Surprising arginine biosynthesis: a reappraisal of the enzymology and evolution of the pathway in microorganisms. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 71:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00032-06
Zeth K, Fokina O, Forchhammer K (2014) Structural basis and target-specific modulation of ADP sensing by the Synechococcus elongatus PII signaling protein. J Biol Chem 289:8960–8972. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.536557
Zhang H, Liu Y, Nie X, Liu L, Hua Q, Zhao GP, Yang C (2018) The cyanobacterial ornithine-ammonia cycle involves an arginine dihydrolase. Nat Chem Biol 14:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0038-z
Ziegler K, Deutzmann R, Lockau W (2002) Cyanophycin synthetase-like enzymes of non-cyanobacterial eubacteria: characterization of the polymer produced by a recombinant synthetase of Desulfitobacterium hafniense. Z Naturforsch 57:522–529. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2002-5-621
Funding
This work was supported by the following grants to NK: JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows (Grant Number 21J20651), JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (Grant Number 20H02905), and JST-ALCA of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (Grant Number JPMJAL1306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NK designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. TO analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katayama, N., Osanai, T. Arginine inhibition of the argininosuccinate lyases is conserved among three orders in cyanobacteria. Plant Mol Biol 110, 13–22 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01280-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01280-x