Summary
-
1.
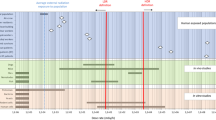
Chinese hamster fibroblast cell cultures were exposed to the alkylating mutagen, Trenimon, for 8 and 24 hrs; human fibroblast and lymphocyte cultures for 24 hrs. The dose range tested in each experiment comprised the entire span from concentrations causing aberration frequencies close to control levels up to those causing mitotic inhibition.
-
2.
In all test systems a clear dose-response relationship was observed. The curves for different degrees of chromosome damage (1–2 aberrations; multiple aberrations; pulverized chromosomes) showed a similar pattern in all systems.
-
3.
In Chinese hamster fibroblasts a 24 hrs exposure proved to be much more effective than an 8 hrs exposure: for a level of 50% damaged cells the drug concentration had to be increased 60-fold in the 8 hrs test. Practically no pulverized metaphases were produced in the 8 hrs experiment whereas over 70% pulverized mitoses appear after a 24 hrs exposure to the highest tolerable concentrations.
-
4.
Major differences in the sensitivities of the three different test materials were found. The Chinese hamster fibroblasts proved to be most susceptible, but also showed the highest rate of spontaneous chromosome breakage. Human lymphocytes were the least sensitive. The differences found in drug sensitivity at the 50% damage level were about 15-fold between Chinese hamster and human fibroblasts and 70-fold between human fibroblasts and human lymphocytes.
-
5.
Compared to the in vivo bone marrow system which responds to a very narrow dose range only (16x), the 24 hrs fibroblast system responded with a complete pattern of dose-response curves within a 32,000-fold difference between the highest and lowest test concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boller, K., Schmid, W.: Chemische Mutagenese beim Säuger. In vivo-Untersuchungen am Knochenmark des Chinesischen Hamsters. Korrelation zwischen zytogenetischen und hämatologischen Befunden. Humangenetik 11, 35–54 (1970).
Cohen, M. M., Shaw, M. W.: Effects of mitomycin C on human chromosomes. J. Cell Biol. 23, 386–395 (1964).
— Marinello, M. J., Back, N.: Chromosomal damage in human leukocytes induced by lysergic acid diethylamide. Science 155, 1417–1419 (1967).
— Hirschhorn, K., Frosch, W. A.: Cytogenetic effects of tranquillizing drugs in vivo and in vitro. J. Amer. med. Ass. 207, 2425–2426 (1969).
Gabridge, M. G., Reedy, R.J., Legator, M. S.: A host mediated microbial assay for detecting mutagenic compounds. Bact. Proc. 61 (1968).
Gebhart, E.: Chromosomenaberrationen durch Myleran in menschlichen Leukocyten in vitro. Humangenetik 7, 126–136 (1969).
Hampel, K. E.: Über die Wirkung von Cytostatica auf die Chromosomen des Menschen. Intern. J. clin. Pharmacol. 14, 322–371 (1968).
Irwin, S., Egozcue, J.: Chromosomal abnormalities in leukocytes from LSD-25 users. Science 157, 313–314 (1967).
Kato, R.: Chromosome breakage induced by a carcinogenic hydrocarbon in Chinese hamster cells and human leukocytes in vitro. Hereditas (Lund) 59, 120–141 (1968).
Kihlman, B. A.: The action of chemicals on dividing cells. Englewood Cliffs (N.J.): Prentice Hall Inc. 1966.
Loughman, W. D., Sargent, T. W., Israelstom, D. W.: Leukocytes of humans exposed to lysergic acid diethylamide: Lack of chromosomal damage. Science 158, 508–510 (1969).
Nichols, W. W., Heneen, W. K.: Chromosomal effects of arabinosylcytosine in a human diploid cell strain. Hereditas (Lund) 52, 402–410 (1964).
Röhrborn, G.: Die mutagene Wirkung von Trenimon bei der männlichen Maus. Humangenetik 1, 576–578 (1968).
— Vogel, F.: Mutationen durch chemische Einwirkung bei Säuger und Mensch. 2. Genetische Untersuchungen an der Maus. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 50, 2315–2321 (1967).
Schmid, W., Staiger, G. R.: Chromosome studies on bone marrow from Chinese hamsters treated with benzodiazepine tranquillizers and cyclophosphamide. Mutat. Res. 7, 99–108 (1969).
— Arakaki, D. T., Breslau, N. A., Culbertson, J. C.: Chemical mutagenesis. The Chinese hamster bone marrow as in vitro test system. I. Cytogenetic results on basic aspects of the methodology, obtained with alkylating agents. Humangenetik 11, 103–118 (1971).
Sparkes, R. S., Melnyk, J., Bozzetti, L. P.: Chromosomal effect in vitro of exposure to lysergic acid diethylamide. Science 160, 1343–1345 (1968).
Staiger, G. R.: Chlordiazepoxide and diazepam: absence of effects on the chromosomes of diploid human fibroblast cells. Mutat. Res. 7, 109–115 (1969).
Stenchever, M. A., Frankel, R. B.: Some effects of diazepam in human cells in vitro. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec. 103, 836–842 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With support by the Swiss National Foundation and F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Co. Ltd. Basle (Switzerland).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arakaki, D.T., Schmid, W. Chemical mutagenesis the Chinese hamster bone marrow as an in vivo test system. Hum Genet 11, 119–131 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393792
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393792