Abstract
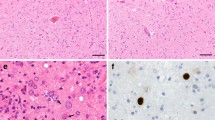
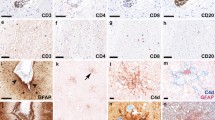
Nuclear p53 immunoreactivity is demonstrated in infected oligodendroglia, as well as in a proportion of reactive and bizarre astrocytes, in seven progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) biopsies. This likely represents binding to, and prolongation of the half-life of, wild-type p53 protein by JC virus T-antigen. Other possible mechanisms are considered. The same cells show proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) positivity, as do a proportion of morphologically normal oligodendroglia and astrocytes, reflecting proliferating populations of these glial sub-types. It is possible that functional inactivation of p53 in nonlytically infected astrocytes may allow neoplastic astrocyte clones to emerge. However, p 53 and PCNA immunoreactivity per se cannot be regarded as indicative of neoplasia in PML, and caution must be exercised in the interpretation of such nuclear staining profiles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksamit AJ, Sever JL, Major EO (1986) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: JC virus detection by in situ hybridisation compared with immunohistochemistry. Neurology 36: 499–504
Aksamit AJ, Gendelman HE, Orenstein JM, Pezeshkpour GH (1990) AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Neurology 40: 1073–1078
Astrom KE, Mancall EL, Richardson EP (1958) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Brain 81: 93–111
Baker TS, Rayment I (1987) Animal virus structure. In: Nermut MV, Steven AC (eds) Perspectives in modern virology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Berger JR, Kaszovitz B, Post MJD, Dickinson G (1987) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Ann Intern Med 107: 78–87
Berges RR, Furuya Y, Remington L, English HF, Jacks T, Isaacs JT (1993) Cell proliferation, DNA repair and p53 function are not required for programmed death of prostatic glandular cells induced by androgen ablation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 8910–8914
Bollag B, Chuke W-F, Frisque RJ (1989) Hybrid genomes of the polyomaviruses JC virus, BK virus and Simian virus HO: identification of sequences important for efficient transformation. J Virol 63: 863–872
Bravo R, MacDonald-Bravo H (1987) Existence of two populations of cyclin-proliferating cell nuclear antigens during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol 105: 1549–1554
Bravo R, Frank R, Blundell PA, MacDonald-Bravo H (1987) Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-δ. Nature 326: 515–517
Budka H, Shah KV (1983) Papovavirus antigens in paraffin sections of PML brains. Prog Clin Biol Res 105: 299–309
Castaigne P, Roudot P, Escourolle R, Ribadeau-Dumar J-L, Cathala F, Hauw J-J (1974) Leucoencéphalopathie multifocale progressive et “gliomes” multiple. Rev Neurol (Paris) 130: 379–392
Clarke AR, Purdie CA, Harrison DJ, Morris RG, Bird CC, Hooper ML, Wyllie AH (1993) Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature 362: 849–852
Frisque RJ, White FA (1992) The molecular biology of JC virus, causative agent of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. In: Roose RP (ed) Molecular neurovirology. Humana Press Inc., Totowa
Gannon JV, Greaves R, Iggo R, Lane DP (1990) Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J 9: 1595–1602
Ghatak NR (1992) Occurrence of oligodendrocytes within astrocytes in demyelinating lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 51: 40–46
Hedley-White ET, Smith BP, Tyler HR, Peterson WP (1966) Multifocal leukoencephalopathy with remission and five year survival. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 25: 107–116
Henson J, Saffer J, Furneaux M (1992) The transcription factor Sp1 binds to JC virus promoter and is selectively expressed in glial cells in the brain. Ann Neurol 32: 72–77
Iggo R, Gatter K, Bartek J, Lane D, Harris AC (1990) Increased expression of mutant p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet 335: 675–679
Kern SE, Kinzler KW, Bruskin A, Jarosz D, Friedman P, Prives C, Vogelstein B (1991) Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science 252: 1708–1711
Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB (1992) Wildtype p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 7491–7495
Lane DP (1992) p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 358: 15–16
Lane DP, Crawford LV (1979) T-antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature 278: 261–263
London WT, Houff SA, Madden DL, Fuccillo DA, Gravell M, Wallen WC, Palmer AE, Sever JL, Padgett BL, Walker DL, Zu Rhein GM, Ohashi T (1978) Brain tumors inowl monkeys inoculated with human polyomarivus (JC virus). Science 201: 1246–1249
Louis DN, Von Deimling A, Chung RY, Rubio M-P, Whaley JM, Eibl RH, Ohgaki H, Otmar DVM, Wiestler OD, Thor AD, Seizinger BR (1993) Comparative study of p53 gene and protein alterations in human astrocytic tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52: 31–38
Mack DH, Vartikar J, Pipas JM, Laimins LA (1993) Specific repression of TATA-mediated but not initiator-mediated transcription by wild-type p53. Nature 363: 281–283
Martinez J, Georgoff I, Martinez J, Levine AJ (1991) Cellular localisation and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev 5: 151–159
Mázló M, Tariska J (1982) Are astrocytes infected in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)? Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 56: 45–51
Nagashima K, Matsuda M, Ikeda K, Kimura-Kuroda J, Yasui K, Mori IV (1986) Induction of brain tumors experimentally by the JC virus. Prog Neuropathol 6: 145–163
Oren M, Maltzman W, Levine AJ (1981) Post translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol 1: 101–110
Pender MP, Nguyen KB, McCombe PA, Kerr JFR (1991) Apoptosis in the nervous system in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci 104: 81–87
Prayoonwiwat N, Rodriguez M (1993) The potential for oligodendrocyte proliferation during demyelinating disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52: 55–63
Price RW, Nielsen S, Horten B, Rubino M, Padgett B, Walker D (1983) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a burnt out case. Ann Neurol 13: 485–490
Reich NC, Levine AJ (1984) Growth regulation of a cellular tumor antigen, p53, in transformed cells. Nature 308: 199–201
Revesz T, Alsanjari N, Darling JL, Scaravilli F, Lane DP, Thomas DGT (1993) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): expression in samples of human astrocytic gliomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 19: 152–158
Richardson EP (1961) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med 265: 815–823
Richardson EP, Webster H (1983) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: its pathological features. In: Sever JL, Madden DL (eds) Polyoma viruses and human neurological disease. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 191–203
Sangalang VE, Embil JA (1984) Emergency of papovavirus in long-term cultures of astrocytes from progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43: 553–567
Scaravilli F, Ellis DS, Tovey G, Harcourt-Webster JN, Guiloff RJ, Sinclair E (1989) Unusual development of polyoma virus in the brains of two patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 15: 407–418
Scaravilli F, Gray F, Mikol J, Sinclair E (1993) Pathology of the nervous system. In: Scaravilli F (ed) The Neuropathology of HIV infection. Springer, London, pp 99–169
Sima AAF, Finkelstein SD, McLachlan DR (1983) Multiple malignant astrocytomas in a patient with spontaneous progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 14: 183–188
Small JA, Khoury G, Howley PM, Scangos GA (1986) Early regions of JC virus and BK virus induce distinct and tissue-specific tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 8288–8292
Small JA, Scangos GA, Cork L, Jay G, Khoury G (1986) The early region of human papovavirus JC induces dysmyelination in transgenic mice. Cell 46: 13–18
Start RD, Cross SS, Clelland C Silcocks PB, Rogers K, Smith JHF (1992) Delay in fixation does not affect the immunoreactivity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). J Pathol 168: 197–199
Theile M, Grabowski G (1990) Mutagenic activity of BKV and JCV in human and other mammalian cells. Arch Virol 113: 221–233
Trapp BD, Small JA, Pulley M, Khoury G, Scangos GA (1988) Dysmyelimation in transgenic mice containing JC virus early region. Ann Neurol 23: 38–48
Waseem NH, Lane DP (1990) Monoclonal antibody analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Structural conservation and the detection of a nucleolar form. J Cell Sci 96: 121–129
Wegner M, Drolet DW, Rosenfeld MG (1993) Regulation of JC virus by the POU-domain transcription factor Tst-1: Implications for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 4743–4747
Wiley CA, Grafe M, Kennedy C, Nelson JA (1988) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and JC virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 76: 338–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lammie, G.A., Beckett, A., Courtney, R. et al. An immunohistochemical study of p53 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 88, 465–471 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389500
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389500