Summary
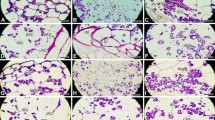
The two-cell-layered endosperm of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) is characterized by thick cell walls and dense cytoplasm. The periodic-acid-Schiff's(PAS)-positive cell wall forms numerous peg-like projections which extend into the cytoplasm. The dense cytoplasm contains organelles of protein and lipid storage. The protein bodies are numerous and appear to be interconnected by narrow extensions of their envelopes. Spherosomes are also numerous; they occupy a peripheral position in the cytoplasm. Other organelles typical of plant cells (nuclei with prominent nucleoli, mitochondria, microbodies, dictyosomes and various vesicles) are also found in the ground cytoplasm of the endosperm cell. Germination of the seeds began after 14 h imbibition in light, and by 24 h 35–40% of the seeds had germinated. The cell walls of endosperm from seeds germinated in light for 12–15 h were extensively broken down as shown by the decrease in PAS staining of the wall. Cell-wall breakdown increased with the duration of imbibition, with the exception of the wall adjacent to the integument which showed no evidence of digestion. The structural complexity of the endosperm cell wall is correlated with the role this tissue plays in restricting embryo growth. Cell-wall breakdown is correlated with radicle protrusion, although a causal relationship between these two events is not proved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brothwick, H. A., Hendricks, S. B., Parker, H., Toole, E. H., Toole, V. K.: A reversibl photoreaction controlling seed germination. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 38, 662–666 (1952)
Borthwick, H. A., Hendricks, S. B., Toole, E. H., Toole, V. K.: Action of light in lettuce seed germination. Bot. Gaz. 115, 205–225 (1954)
Borthwick, H. A., Robbins, W. W.: Lettuce seed and its germination. Hilgardia 3, 275–304 (1928)
Evenari, M.: The germination of lettuce seeds. I. Light, temperature and coumarin as germination factors. Palestine J. Bot. 5, 138–169 (1952)
Evenari, M.: Light and seed dormancy. In: Encycl. Plant Physiol., vol. XV, pt. 2, p. 808–847, ed. A. Lang. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1965
Evenari, M., Neumann, G.: The germination of lettuce seed. II. The influence of fruit coat, seed coat, and endosperm on germination. Bull. Res. Coun. Israel 2, 15–17 (1952)
Fisher, D. B.: Protein staining of ribboned Epon sections for light microscopy. Histochemie 16, 92–96 (1968)
Frey-Wyssling, A., Mühlethaler, K.: Ultrastructural plant cytology. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1965
Gunning, B. E. S., Pate, J. S., Briarty, L. G.: Specialized “transfer cells” in minor veins of leaves and their possible significance in phloem translocation. J. Cell Biol. 37, C7-C12 (1968)
Ikuma, H., Thimann, K. V.: The photosensitive site in lettuce seeds. Science 130, 568–569 (1959)
Ikuma, H., Thimann, K. V.: The role of seed coats in germination of photosensitive lettuce seeds. Plant Cell Physiol. 4, 169–185 (1963)
Jones, R. L., Price, J. M.: Gibberellic acid and the fine structure of barley aleurone cells III. Vacuolation of the aleurone cell during the phase of ribonuclease release. Planta (Berl.) 94, 191–202 (1970)
Koller, D., Mayer, A. M., Poljakoff-Mayber, A., Klein, S.: Seed germination. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 13, 437–464 (1963)
Nabors, M. W., Lang, A.: The growth physics and water relations of red-light-induced germination in lettuce seeds. I. Embryos germinating in osmoticum. Planta (Berl.) 101, 1–25 (1971a)
Nabors, M. W., Lang, A.: The growth physics and water relations of red-light-induced germination in lettuce seeds. II. Embryos germinating in water. Planta (Berl.) 101, 26–42 (1971b)
Pate, J. S., Gunning, B. E. S., Briarty, L. G.: Ultrastructure and functioning of the transport system of the leguminous root nodule. Planta (Berl.) 85, 11–34 (1969)
Poljakoff-Mayber, A., Blumenthal-Goldschmidt, S., Evenari, M.: The growth substances content of germinating lettuce seeds. Physiol. Plantarum 10, 14–19 (1957)
Scheibe, J., Lang, A.: Lettuce seed germination: Evidence for a reversible light induced increase in growth potential and for phytochrome mediation of the low temperature effect. Plant Physiol. 40, 485–492 (1965)
Scheibe, J., Lang, A.: Lettuce seed germination: A phytochrome-mediated increase in the growth rate of lettuce seed radicles. Planta (Berl.) 72, 348–354 (1967)
Taiz, L., Jones, R. L.: Gibberellic acid, β-1,3-glucanase and the cell walls of barley aleurone layers. Planta (Berl.) 92, 73–84 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, R.L. The structure of the lettuce endosperm. Planta 121, 133–146 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388752
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388752