Abstract
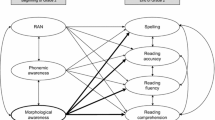
The present report with three inter-related studies examined the effects of morphological complexity on reading proficiency in 103 fourth graders, 88 fifth graders and 107 sixth graders trichotomized into below average, average and above average readers. The reaction time paradigm and the developmental framework with three age groups provided more sensitive and stable results for inferring mental processes in accessing the lexicon. Study 1 on lexical decision with visually presented words and non-words with different morphemic boundaries suggests that words can be accessed in a decomposed state as morphemes by children. Study 2 and the complementary Study 3 requiring the vocalization of derived or base forms of words primed by target items in sentence frames indicate that words might be accessed in full forms. Further, the depth of derivational morphology and of base morphology with correlated phonological changes affect reading proficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, S. R. 1982. Where's morphology? Linguistic Inquiry, 13, 571–612.
Aronoff, M. 1976. Word formation in generative grammer. Linguistic Inquiry Monograph 1, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Balota, D. A. and Chumbley, J. I. 1984. Are lexical decisions a good measure of lexical access? The role of word frequency in the neglected decision stage. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 10, 340–357.
Burani, C., Salmaso, D. and Caramazza, A. 1984. Morphological structure and lexical access. Visible Language, 18, 342–352.
Butterworth, B. 1983. Lexical representation. In B., Butterworth (ed.), Language production Vol. 2: Development, writing and other language processes (pp. 257–294). London: Academic Press.
Caramazza, A., Miceli, G., Silveri, M. C. and Laudanna, A. 1985. Reading mechanisms and the organization of the lexicon: Evidence from acquired dyslexia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 2, 81–114.
Carlisle, J. F. 1988. Knowledge of derivational morphology and spelling ability in fourth, sixth, and eighth graders. Applied Psycholinguistics, 9, 247–266.
Carroll, J. B., Davies, P. and Richman, B. 1971. The American heritage word frequency book. Boston, MA: Houghton-Mifflin.
Cutler, A. 1980. Errors of stress and intonation. In V. A., Fromkin (ed.), Errors in linguistic performance: Slips of the tongue, ear, pen, and hand (pp. 67–80). New York: Academic Press.
Cutler, A. 1983. Lexical complexity and sentence processing. In G. B., Flores D'Arcais and R. J., Jarvella (eds), The process of language understanding (pp. 43–79). New York: John Wiley.
Cutler, A., Norris, D. and Williams, J. N. 1987. A note on the role of phonological expectations in speech segmentation. Journal of Memory and Language, 26, 480–487.
Elliott, C. D., Murray, D. J. and Pearson, L. S. 1978. British Ability Scales: Manual 3: Directions for administration and scoring and Manual 4: Tables of abilities and norms. Windsor, Berks: NFER.
Fischer, F. W., Shankweiler, D. and Liberman, I. Y. 1985. Spelling proficiency and sensitivity to word structure. Journal of Memory and Language, 24, 423–441.
Freyd, P. and Baron, J. 1982. Individual differences in acquisition of derivational morphology. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 21, 282–295.
Henderson, L. 1985. Toward a psychology of morphemes. In A. W., Ellis (ed.), Progress in the psychology of language (Vol. 1, pp. 15–72). London: Erlbaum.
Henderson, L., Coltheart, M., Cutler, A. and Vincent, N. (eds). 1988. Linguistic and psychological approaches to morphology [Special issue]. Linguistics, 26(4).
Jarvella, R. J. and Snodgrass, J. G. 1974. Seeing ring in rang and retain in retention: On recognizing stem morphemes in printed words. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 13, 590–598.
King, E. M. (ed.). 1982. Canadian Tests of Basic Skills: Multilevel edition/Levels 9–12/Forms 5 and 6. Toronto: Nelson.
Kiparsky, P. 1982. Lexical morphology and phonology. In The Linguistic Society of Korea (ed.), Linguistics in the morning calm: Selected papers from SICOL—1981 (pp. 3–91). Seoul, Korea: Hanshin Publishing.
Lima, S. D. and Pollatsek, A. 1983. Lexical access via an orthographic code? The Basic Orthographic Syllabic Structure (BOSS) reconsidered. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 22, 310–332.
Luszcz, M. A., Bungey, J. and Geffen, G. 1984. Orthographic-morphemic factors in reading: A developmental study. Australian Journal of Psychology, 36, 355–365.
Mackay, D. G. 1978. Derivational rules and the internal lexicon. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 17, 61–71.
Manelis, L. and Tharp, D. A. 1977. The processing of affixed words. Memory and Cognition, 5, 690–695.
Matthews, P. H. 1974. Morphology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Morton, J. 1979. Word recognition. In J., Morton and J. C., Marshall (eds), Psycholinguistics 2: Structures and Processes (pp. 107–156). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Murrell, G. and Morton, J. 1974. Word recognition and morphemic structure. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 102, 963–968.
Rubin, G. S., Becker, C. A. and Freeman, R. H. 1979. Morphological structure and its effect on visual word recognition. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 18, 757–767.
Santee, J. L. and Egeth, H. E. 1982. Do reaction time and accuracy measure the same aspects of letter recognition? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 8, 489–501.
Smith, P. T., Meredith, T., Pattison, H. M. and Sterling, C. 1984. The representation of internal word structure in English. In L., Henderson (ed.), Orthographies and reading: Perspectives from cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and linguistics (pp. 103–120). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Stemberger, J. P. 1985. The lexicon in a model of language production. New York: Garland Publishing, Inc.
Taft, M. 1979. Lexical access via an orthographic code: The Basic Orthographic Syllabic Structure (BOSS). Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 18, 21–39.
Taft, M. 1985. The decoding of words in lexical access: A review of the morphographic approach. In D., Besner, T. G., Waller and G. E., Mackinnon (eds), Reading Research: Advances in theory and practice (Vol. 5, pp. 83–123). New York: Academic Press.
Taft, M. 1987. Morphographic processing: The BOSS re-emerges. In M., Coltheart (eds), Attention and performance XII: The psychology of reading (pp. 265–279). London: Erlbaum.
Taft, M. and Forster, K. I. 1976. Lexical storage and retrieval of polymorphemic and polysyllabic words. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 15, 607–620.
Templeton, S., and Scarborough-Franks, L. 1985. The spelling's the thing: Knowledge of derivational morphology in orthography and phonology among older students. Applied Psycholinguistics, 6, 371–390.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leong, C.K. The effects of morphological structure on reading proficiency—A developmental study. Read Writ 1, 357–379 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386267
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386267