Abstract
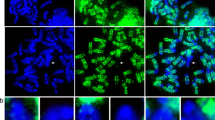
With simultaneous immunofluorescence and fluorescent in situ hybridization, we have determined the organization of native and heterologous DNA sequences relative to the cores of meiotic prophase chromosomes. The normal chromatin organization is demonstrated with probes of mouse sequences: a cosmid probe that identities unique sequences and a 720 kb yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) probe that recognizes a specific region of the chromatin domain. The heterologous DNA consists of a 1.8 Mb insertion of 40 tandem head-to-tail phage λ LIZ vectors and of 11.4 Mb of bacterial/mouse DNA repeats. The lengthy λ insert is unusual in that it is not contained in the chromatin domain of chromosome 4 and in that it fails to form direct attachments to the chromosome core. The ends are attached indirectly, probably by means of the flanking mouse sequences. At late stages of meiotic prophase, while the terminal attachments remain the same, the λ DNA becomes highly compacted. Apparently, higher order condensation and core attachment are independent processes. The condensed inserts relax precociously at metaphase I. In the mouse heterozygous for the insert, the two sister inserts are usually merged, as are all four inserts in the homozygous mouse. Evidently chromatin loops with identical sequences can become associated during meiotic prophase. Mouse sequences within a heterologous DNA insert (repeats of bacterial plasmid pBR322 with a mouse β-globin insert) were observed to restore some degree of core attachment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobson M, Pearlman RE, Karaiskakis A, Spyropoulos B, Moens PB (1994) Synaptonemal complex proteins: occurrence and epitope mapping. J Cell Sci 107 (in press)
Feng GS, Shen R, Heng HHQ, Tsui LC, Kazlauskas A, Pawson TG (1994) Receptor-binding, tyrosine phosphorylation and chromosome localization of the mouse SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. Oncogene 9:1545–1550
Heng HHQ, Tsui LC (1993) Modes of DAPI banding and simultaneous in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 102:325–332
Heng HHQ, Tsui LC (1994) FISH detection on DAPI banded chromosomes. In: Choo KHA (ed) In situ hybridization protocols, vol. 20. Humana Press, New Jersey (in press)
Heng HHQ, Squires J, Tsui LC (1992) High resolution mapping of mammalian genes by in situ hybridization to free chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9505–9513
Heng HHQ, Shi XM, Scherer SW, Andrulis IL, Tsui LC (1994) Refined localization of the asparagine synthetase gene locus (ASNS) to chromosome 1, region q21.3, and characterization of the somatic cell hybrid line 4AF/106/KO15. Cytogenet Cell Genet 66:135–138
Kohler SW, Provost GS, Fjeck A, Kretz PL, Bullock WO, Putman DL, Sorge JA, Short JM (1991) Analysis of spontaneous and induced mutations in transgenic mice using a λ ZAP/lacI shuttle vector. Environ Mol Mutagen 18:316–321
Lo CW (1986) Localization of low abundance DNA sequences in tissue sections by in situ hybridization. J Cell Sci 81:143–162
Lo CW, Coulling M, Kirby C (1987) Tracking of mouse cell lineage using microinjected DNA sequences: Analyses using genomic Southern blotting and tissue-section in situ hybridization. Differentiation 35:37–44
McManus J, Perry P, Sumner AT, Wright DM, Thomson EJ, Allshire RC, Hastie ND, Bickmore WA (1994) Unusual chromosome structure of fission yeast DNA in mouse cells. J Cell Sci 107:469–486
Moens PB, Pearlman RE (1989) Satellite DNA I in chromatin loops of rat pachytene chromosomes and in spermatids. Chromosoma 98:287–294
Moens PB, Pearlman RE (1990a) Telomere and centromere DNA are associated with the cores of meiotic prophase chromosomes. Chromosoma 100:8–14
Moens PB, Pearlman RE (1990b) In situ DNA sequence mapping with surface-spread mouse pachytene chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 53:219–200
Moens PB, Pearlman RE (1988) Chromatin organization at meiosis. Bioessays 9:151–153
Moens PB, Spyropoulos B, Dobson M, Karaiskakis A, Pearlman RE (1992) Searching for synaptonemal complex proteins and their genes. Dev Genet 13:435–439
Murti JR, Bumbulis M, Schimenti JC (1994) Gene conversion between unfinked sequences in the germline of mice. Genetics 137:837–843
Pearlman RE, Tsao N, Moens PB (1991) Synaptonemal complexes from DNase-treated rat pachytene chromosomes contain (GT)n and LINE sequences, but no MARs/SARs. Genetics 130:865–872
Radman M, Wagner R (1993) Mismatch recognition in chromosomal interactions and speciation. Chromosoma 102:369–373
Scherer SW, Tompkins BJF, Tsui LC (1992) A human chromosome 7-specific genomic DNA library in yeast artificial chromosomes. Mammalian Genome 3:179–181
Short JM, Provost GS, Kretz PL, Dycaico MJ (1992) Overview of the Big Blue in vivo mutagenesis assay. mammalian Mutagenicity Study group communication, vol. 6. Proceedings from Japanese Environmental Mutagen Society, pp 74–89
Spyropoulos B, Moens PB (1994) In situ hybridization on meiotic prophase chromosomes. In: Choo KHA (ed) In situ hybridization protocols, vol. 20. Humana Press, New Jersey, in press
Thomson AT, Sloter D (1989) Chimeras between parthenogenic or androgenic blastomeres and normal embryos: allocation of the inner cell mass and trophectoderm. Dev Biol 131:580–583
Tres LL, Kierszenbaum AL (1981) Meiotic chromosomes of mouse spermatocytes: identification of bivalents, lampbrush organization, and transcription activities. In: Jagiello G, Vogel HJ (eds) Bioregulation of reproduction. Academic Press, New York, pp 229–255
Weith A, Traut W (1980) Synaptonemal complexes with associated chromatin in a moth Ephestia kuehniella Z. Chromosoma 78:275–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heng, H.H.Q., Tsui, LC. & Moens, P.B. Organization of heterologous DNA inserts on the mouse meiotic chromosome core. Chromosoma 103, 401–407 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362284
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362284