Abstract
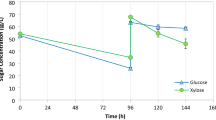
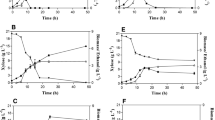
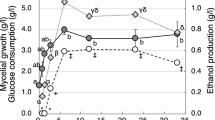
The xylose in an enzymatic hydrolysate of steam-exploded rice straw was not consumed by Pichia stipitis until the glucose was almost exhausted. A diauxic lag of 2 to 3 h in both cell growth and ethanol production occurred as metabolism switched from glucose to xylose utilization. Ethanol production was maximal [6 g ethano/l from 15 g reducing sugars/l (78% theoretical yield)] at an aeration rate of 0.2 vol/vol. min.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DuPreezJ.C. 1994 Process parameters and environmental factors affecting Dxxx-xylose fermentation by yeasts. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 16, 944–956.
DuPreezJ.C., BoschM. & PriorB.A. 1986 Xylose fermentation by Candida shehatae and Pichia stipitis: effects of pH, temperature and substrate concentration. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 8, 360–364.
Hahn-HagerdalB., JeppssonH., SkoogK. & PriorB.A. 1994 Biochemistry and physiology of xylose fermentation by yeasts. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 16, 933–943.
JeffriesT.W. & KurtzmanC.P. 1994 Strain selection, taxonomy, and genetics of xylose-fermenting yeasts. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 16, 922–932.
JurasekL. 1979 Enzymic hydrolysis of pretreated aspen wood. Developments in Industrial Microbiology 20, 177–183.
Lohmeier-VogelE., SkoogK., VogelH. & Hahn-HagerdalB. 1989 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study of the effect of azide on xylose fermentation by Candida tropicalis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 55, 1974–1980.
Mes-HartreeM., HoganC.M. & SaddlerJ.N. 1984 The enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of agricultural residues to ethanol. Biotechnology and Bioengineering Symposium 14, 397–405.
NakamuraY., MoniruzzamanM., NagaoM., SawadaT. & MotoiM. 1991 Modification of rice straw by steam explosion and enzymatic saccharification of steam-exploded products. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 17, 504–510.
SliningerP.J., BolenP.L. & KurtzmanC.P. 1987 Pachysolen tannophilus: properties and process considerations for ethanol production from Dxxx-xylose. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 9, 5–15.
Additional information
The author was with the Department of Chemical Engineering, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa 920, Japan, but is now with the Engineering Biosciences Research Center, Cater-Mattil Hall, The Texas A&M University System, College Station, Texas 77843-2476, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moniruzzaman, M. Alcohol fermentation of enzymatic hydrolysate of exploded rice straw by Pichia stipitis . World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology 11, 646–648 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361008