Abstract
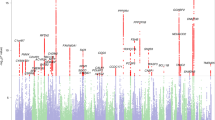
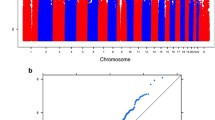
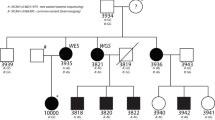
Genetic linkage analysis is a means of localizing genes to specific chromosomal regions. Localization of genes influencing specific reading disability (dyslexia) can lead to characterization of the phenotypic effects of each gene and to early diagnosis of children at risk. Previous studies using the family study LOD score method of linkage analysis have identified two chromosomal regions that may contain genes influencing dyslexia. The present study examines the sib pair method of linkage analysis, which has several advantages over the LOD score method. In particular, the mode of inheritance does not need to be specified and diagnosis of parents is not required, but it is a less powerful technique. Using the same population as the previous studies (with less than 200 sib pairs) and two different means of diagnosis of dyslexia, the sib pair analysis was able to detect the same suggested linkages as the LOD score method, plus a possible third region. This confirms that the sib pair method is an effective means of screening for linkage with reasonable sample sizes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeFries J. C., Fulker D. W., and LaBuda M. C. 1987. Evidence for a genetic aetiology in reading disability of twins. Nature, 329, 537–539.
DeFries J. C., Olson R. C., Pennington B. F., and Smith S. D. 1991 Colorado Reading Project: An Update. In Gray D., and Duane D. (Eds.), The reading brain: The biological basis of dyslexia. Parkton, MD: York Press.
Haseman J. K. and Elston R. C. 1972. The investigation of linkage between a quantitative trait and a marker locus. Behavior Genetics, 2, 3–19.
Housman D., Smith S. D., and Pauls D. 1985. Applications of Recombinant DNA to Neurogenetic Disorders. In Gray D. B. and Kavanagh J. F. (Eds.), Biobehavioral Measures of Dyslexia (pp. 155–162). Parkton, MD: York Press.
Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., and Ott J. 1985. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: Detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. American Journal of Human Genetics, 37, 482–498.
McKusick V. A. 1990. Mendelian Inheritance in Man: Catalogs of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal Recessive, and X-Linked Phenotypes, Ninth Edition. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
Morton N. E. 1955. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. American Journal of Human Genetics, 7, 277–328.
Ott J. 1974. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: Efficient computation of the likelihood for human studies. American Journal of Human Genetics, 26, 588–597.
Ott J. 1985. Analysis of human genetic linkage. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
Pennington, B. F., Gilgler, J., Pauls, D., Smith, S. A., Smith, S. D., and DeFries, J. C. (in review). Evidence for a major gene transmission of developmental dyslexia.
Pennington B. F., Smith S. D., McCabe L. L., Kimberling W. J., and Lubs H. A. 1984. Development continuities and discontinuities in a form of familial dyslexia. In Emde R. and Harman R. (Eds.), Continuities and Discontinuities in Development (pp. 123–151). New York: Plenum.
Smith S. D., Kimberling W. J., Pennington B. F., and Lubs H. A. 1983. Specific reading disability: Identification of an inherited form through linkage analysis. Science, 219, 1345–1347.
Smith, S. D., Kimberling, W. J., Shugart, Y. Y., Ing, P. S., and Pennington, B. F. 1989. Genetic linkage analysis of 20 families with specific reading disability, American Journal of Human Genetics, 45, A65. Presented to the American Society of Human Genetics, Baltimore, November 12, 1989.
Smith S. D., Pennington B. F., Kimberling W. J., and Ing P. S. 1990. Familial dyslexia: Use of genetic linkage data to define subtypes. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 29, 204–213.
Tran L. D., Elston R. C., Keat B. J. B., and Wilson A. F. 1989. Sib-Pair linkage program (SIBPAL) User's Guide. Part of the S.A.G.E. 89 Release 2.0 documentation, University of Louisiana Medical Center, New Orleans, LA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, S.D., Kimberling, W.J. & Pennington, B.F. Screening for multiple genes influencing dyslexia. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 3, 285–298 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00354963
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00354963