Abstract
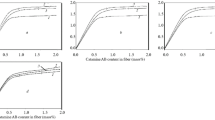
The influence of monomeric methylmethacrylate (MMA) on resting and compound action potential of the isolated desheathed sciatic nerve of the frog (sucrose gap method) was determined. Above 10 mM there was a dose-dependent decrease of the compound action potential and a hyperpolarization of the membrane which was augmented with increasing MMA concentrations (4.1 mV±0.2 S.E.M. after 50 mM MMA). The depolarization in low [Ca2+]0 solutions or with veratrine was reversed by MMA. The homologous ethyl, allyl and n-butyl esters were more effective than MMA, and the isobutyl ester less effective, whereas Na-methacrylate and methacrylamide showed no influence.
Voltage clamp experiments on the node of Ranvier indicated that 50 mM MMA led to a decrease of the Na+ and K+ currents.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde der Einfluß von monomerem Methylmethacrylat (MMA) auf das Ruhe- und Summenaktionspotential des isolierten entscheideten N. ischiadicus des Frosches (Saccharose-Trennwand-Methode) untersucht. Oberhalb von 10 mM trat eine dosisabhängige Abnahme des Summenaktionspotentials und eine Hyperpolarisation der Membran auf, die mit zunehmender MMA-Konzentration anstieg (4.1 mV±0.2 S.E.M. nach 50 mM MMA). Die durch niedrige [Ca2+]0 oder Veratrin hervorgerufene Depolarisation ließ sich durch MMA rückgängig machen. Die homologen Äthyl-, Allyl- und n-Butylester waren wirksamer als MMA, der Isobutylester weniger wirkungsvoll, während Na-Methacrylat und Methacrylsäureamid keinen Einfluß zeigten.
Voltage clamp Experimente am isolierten Ranvierschen Schnürring zeigten, daß 50 mM MMA zu einer Abnahme der Na+- und K+-Ströme führten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borchard, U., Erasmi, W.: Influence of the external K+-concentration on the electrical activity and the Na+-, K+-content of the retinal tissue. Pflügers Arch. 341, 297–304 (1973)
Deichmann, W. B.: Toxicity of methyl, ethyl and N-butyl methacrylate. J. industr. Hyg. 23, 343–351 (1941)
Drouin, H., Neumcke, B.: Specific and unspecific charges at the sodium channels of the nerve membrane. Pflügers Arch. 351, 207–229 (1974)
Fries, I. A., Fisher, A. A., Salvati, E. A.: Contact dermatitis in surgeons from methylmethacrylate bone cement. J. Bone Jt Surg. 57A, 547–549 (1975)
Hattingberg, V. H. M., Klaus, W., Lüllmann, H., Zepf, S.: Fuorimetrische Bestimmung von Mikromengen Calcium im Muskelgewebe. Experientia (Basel) 22, 253–258 (1966)
Hille, B., Woodhull, A. M., Shapiro, B. I.: Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Phil. Trans. B 270, 301–318 (1975)
Huxley, A. F., Stämpfli, R.: Direct determination of membrane potential and action potential in single myelinated nerve fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 112, 476–495 (1951)
Kutzner, F., Dittmann, E. Ch., Ohnsorge, J.: Restmonomerabgabe von abgehärtetem Knochenzement. Arch. orthop. Unfall-Chir. 79, 247–253 (1974a)
Kutzner, F., Dittmann, E. Ch., Ohnsorge, J.: Atemeffekte durch Knochenzement auf Methylmethacrylatbasis. Z. Orthop. 112, 1053–1062 (1974b)
McLaughlin, S.: Two different mechanisms by which the hydrophobic adsorption of ions to membranes produces an electrostatic potential. In: Electrical phenomena at the biological membrane level (E. Roux., ed.). Amsterdam-Oxford-New York: Elsevier 1977
Mohr, H. J.: Gewebsschädigung durch Polymethacrylsäuremethylester, eines für Plastiken, Prothesen und Zahnfüllungen gebräuchlichen Kunststoffes. Verh. dtsch. Ges. Path. 29, 212–215 (1956a)
Mohr, H. J.: Das Verhalten der Methacrylate zum Gewebe. J. med. Kosmet. 56, 235 (1956b)
Mohr, H. J.: Pathologische Anatomie und kausale Genese der durch selbstpolymerisierendes Methacrylat hervorgerufenen Gewebsveränderungen. Z. ges. exp. Med. 130, 41–69 (1958)
Neumcke, B., Fox, J. M., Drouin, H., Schwarz, W.: Kinetics of the slow variation of peak sodium current in the membrane of myelinated nerve following changes of holding potential or extracellular pH. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 426, 245–257 (1976)
Nonner, W.: A new voltage clamp method for Ranvier nodes. Pflügers Arch. 309, 176–192 (1969)
Sauerwein, E.: Zahnerhaltungskunde. Stuttgart: Thieme 1972
Seeman, P.: The membrane action of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol. Rev. 24, 583–655 (1972)
Schmidt, H., Stämpfli, R.: Die Depolarisation durch Calcium-Mangel und ihre Abhängigkeit von der Kalium-Konzentration. Helv. physiol. pharmacol. Acta 15, 200–211 (1957)
Spealman, C. R., Main, R. J., Haag, H. B., Larson, P. S.: Monomeric methylmethacrylate. Studies on toxicity. Industr. Med. 14, 292–298 (1945)
Spreter von Kreudenstein, T.: Kariestherapie mit schnellhärtendem Kunststoff. München: Hanser 1952
Stämpfli, R.: A new method for measuring membrane potentials with external electrodes. Experientia (Basel) 10, 508–509 (1954)
Stämpfli, R., Hille, B.: Electrophysiology of the frog peripheral myelinated nerve. In: Frog neurobiology (R. Llinas, W. Precht, eds.). Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Straub, R.: Die Wirkung von Veratridin und Ionen auf das Ruhepotential markhaltiger Nervenfasern des Frosches. Helv. physiol. pharmacol. Acta 14, 1–28 (1956)
Ulbricht, W.: The effect of veratridine on excitable membranes of nerve and muscle. Ergebn. Physiol. 61, 18–71 (1969)
White, S. H.: The lipid bilayer as a solvent for small hydrophobic molecules. Nature (Lond.) 262, 421–422 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Partly supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Bo 380/2 and SFB 38 “Membranforschung”)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böhling, H.G., Borchard, U. & Drouin, H. Monomeric methylmethacrylate (MMA) acts on the desheathed myelinated nerve and on the node of Ranvier. Arch. Toxicol. 38, 307–314 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352035
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352035