Abstract
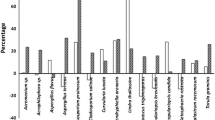
Gravimetric analyses of cellulose (Solka Floc) utilization by representative marine Ascomycetes, including Lulworthia floridana, Lindra sp., Torpedospora sp. and Halosphaeria mediosetigera, have shown noteworthy activity based on loss of weight of cellulose by the various fungi. Particularly striking activity is evidenced by L. floridana and Torpedospora sp., with >50% cellulose degradation after 3 weeks of fungal growth. Comparable studies with the deuteromycete, Dendryphiella salina, showed >50% loss within 6 days. Dissimilar responses by various L. floridana isolates are noted. Intensive degradative activity at pH's of 6 to 8 is common along with negligible amounts of cellulase (Cx units). Adsorption of the enzyme to the mycelia or to the cellulose particles in the medium is suggested. Earlier laboratory analyses of fungal degradation of Manila cordage compare favorably with present gravimetric studies and support field observations on the significance of fungal infestation of wood, particularly that incited by the Lulworthia floridana group.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bull, A. T.: The enzymatic degradation of β-glucans. Int. Biodeterioration. Bull. 3, 3–12 (1967).
Halliwell, G.: Measurement of cellulase and factors affecting its activity. In: Advances in enzymic hydrolysis of cellulose and related materials, pp 71–92. Ed. by E. T. Reese. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1963.
Mandels, M. and E. T. Reese: Induction of cellulase in Trichoderma viride as influenced by carbon sources and metals. J. Bact. 73, 269–278 (1957).
Meyers, S. P.: Variability in growth and reproduction of the marine fungus Lulworthia floridana. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 13, 436–443 (1966).
—, B. Peindle, K. M. Kamp and J. V. Levi: Degradation of Manila cordage by marine fungi: Analysis of breaking strength tests. Tappi 46, 164A-167A (1963).
— and E. S. Reynolds: Cellulolytic activity of marine fungi. Degradation of lignocellulose material. Tappi 43, 534–538 (1960).
— and E. S. Reynolds: Cellulolytic activity of lignicolous marine Ascomycetes and Deuteromycetes. Devs ind. Microbiol. 1, 157–168 (1960).
— Degradation of lignocellulose material by marine fungi. In: Symposium on marine microbiology, pp 315–328. Ed. by C. H. Oppenheimer. Springfield, Ill.: C. C. Thomas 1963.
— and J. Simms: Thalassiomycetes VI. Comparative growth studies of Lindra thalassiae and lignicolous ascomycete species. Can. J. Bot. 43, 379–392 (1965).
Rautela, G. S. and E. B. Cowling: Simple cultural tests for relative cellulolytic activity of fungi. Appl. Microbiol. 14, 892–898 (1966).
Sguros, P. L., S. P. Meyers and J. Simms: Role of marine fungi in the biochemistry of the oceans. I. Establishment of quantitative technique for cultivation, growth measurement and production of inocula. Mycologia 54, 521–535 (1962).
Sumner, J. B. and G. F. Somers: Chemistry and methods of enzymes, 415 pp. New York: Academic Press 1947.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. L. Voss, Miami
This work was supported by Grant GM 12482 from the National Institute of Health and Office of Naval Research Contract No. 137-792 to the Institute of Marine Sciences, University of Miami. Contribution No. 950 from the Institute of Marine Sciences, University of Miami.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyers, S.P., Scott, E. Cellulose degradation by Lulworthia floridana and other lignicolous marine fungi. Marine Biol. 2, 41–46 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351636
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351636