Abstract
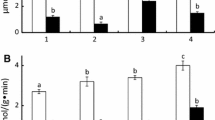
Acid and alkaline phosphatase activities have been partially characterized in Ruditapes philippinarum (Adams and Reeve, 1850). Two activity peaks at pH=4.5 and pH 10.5 were detected in the gill, digestive gland, mantle, siphon and foot. Acid phosphatase activity was higher than that of alkaline phosphatase. The highest activity for both enzymes was observed in the digestive gland and, in decreasing order, the gill, foot, siphon and mantle. Alkaline phosphatase activity was similar in the mantle, siphon and foot. K m values were determined for both enzymes in the gill and digestive gland. Hill coefficients were near 1, indicating no allosteric behaviour for either enzyme in the two organs. The optimum temperature was the same for acid phosphatase in both gill and digestive gland (50 °C), while for alkaline phosphatase it differed for these two organs (gill, 40 °C; digestive gland, 35 °C). The apparent activation energy was obtained from Arrhenius plots, and ranged from 8.61 kcal/mol for alkaline phosphatase in the gill, to 10.84 kcal/mol for acid phosphatase in the digestive gland. The effects of metals (1 mM conc) on both enzyme activities were assayed in vitro. Hg strongly inhibited the enzyme activities in the gill and digestive gland, probably because of its affinity for the sulphydryl group. Histochemically, acid phosphatase in the gill was located in a granular form throughout the gill cells, but was undetectable in the ciliate epithelium of the gill filaments. Alkaline phosphatase was located in the gill skeleton. Clam size and phosphatase activities were inversely related, probably reflecting a decrease in shell deposition with inereasing size. As a function of season, both enzymes were present in lowest amounts in winter, when undifferentiated sex cells were predominant in the germinative epithelium, and highest in summer, when ripe individuals of both sexes were more frequent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Belloc, F., Gallis, J. L. (1980). Fresh water adaptation in the euryhaline teleost, Chelon labrosus. III. Biochemical characterization and increase in the acid phosphatase activity in gill. Comp. Biochem. Physiol 65A: 433–437
Carpenè, E., Crisetig, G., Cortesi, P., Serrazanetti, G. (1979). Effetto del cadmio sull'attivitta' della fosfatasi alcalina (3.1.3.1) di Venus gallina. Boll. Soc. ital. Biol. sper. 55: 1210–1216
Chambers, J. E., McCorckle, F. M., Carrol, J. W., Heitz, J. R., Lewis, L., Yarbrough, J. D. (1975). Variation in enzyme activities of the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica) relative to size and season. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 51B: 145–150
Chuang, N. N. (1990). A heat-stable alkaline phosphatase from Penaeus japonicus Bate (Crustacea: Decapoda): a phosphatidylinositol-glycan anchored membrane protein. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 95B: 165–169
Curti, C., Pizauro, J. M., Rossinholi, G., Vugman, I., Mello de Oliveira, J. A., Leone, F. A. (1986). Isolation and kinetic properties of an alkaline phosphatase from rat bone matrix-induced cartilage. Cell. molec. Biol 32: 55–62
Cvancara, V., Conte, F. P. (1970). Gill alkaline phosphatase activity during salt water adaptation of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) Walbaum. Int. J. Biochem. 1: 597–604
Dixon, M., Webb, E. C. (1979). Enzymes. Academic Press, New York
Establier, R., Gutierrez, M., Blasco, J., Sarasquete, M. C., Bravo, E. (1984). Enzimas en organismos marinos. I. Fosfatasas del riñón de dorada, Sparus aurata, L. Investigación pesq. 48: 527–538
Fosset, M., Chappelet-Tordo, D., Lazdunski, M. (1974). Intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Physical properties and quaternary structure. Biochemistry 13: 1783–1791
González de Canales, M. L., Sarasquete, M. C. (1990). Enzimas hidrolíticas en el aparato digestivo de las almejas Ruditapes decussatus (Linnaeus, 1758) y Ruditapes philippinarum (Adams and Reeve, 1850), (Pelecipoda: Veneridae). Scientia mar. 54: 89–93
González de Canales, M. L., Sarasquete, M. C., Blasco, J., Gutiérrez, M. (1986). Caracteres fisicoquimicos de la fosfatasa alcalina del granulocito neutrófilo de Halobatrachus didactylus (Schneider, 1801) (Telostei, Halobatrachidae). Investigación pescq. 50: 265–269
Gutierrez, M., Establier, R., Blasco, J., Sarasquete, M. C. (1987). Phosphatases in the kidney of the aglomerular fish Halobatrachus didactylus (Schneider, 1801). Revue int. Océanogr. méd. 87–88: 161–169
Harkness, D. R. (1968). Studies on human placental alkaline phosphatase: kinetic studies. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 126: 513–523
Hiwada, K., Wachsmith, E. D. (1974) Catalytic properties of alkaline phosphatase from pig kidney. Biochem. J. 141: 283–291
Kato, T., Hara, A., Nakayama, T., Sawada, H., Hamatake, M., Matsumoto, Y. (1986). Purification and characterization of purple acid phosphatase from rat bone. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 83 B: 813–817
Krajnovic-Ozretic, M., Ozretic, B. (1982). Enzyme activity in prawns exposed to the water soluble fraction of “Ural” crude oil. Journées Étud. Pollut. mar. Méditerr. Cannes (C.I.E.S.M.) 6: 663–668
Lien, T., Knutsen, G. (1973). Synchronous cultures of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii properties and regulation of repressible phosphatases. Physiologia Pl. 28: 291–298
Lojda, Z., Gossrau, R., Schiebler, T. (1979). Enzyme histochemistry. A laboratory manual. Springer-Verlag, New York
Martoja, R., Martoja-Pierson, M. (1970). Técnicas de histología animal. Toray-Masson S. A., Barcelona
Møller, M., Myklestad, S., Haug, A. (1975). Alkaline and acid phosphatases of the marine diatoms Chaetocerosa affinis var. Willei (Gram.) Hustedt and Skeletonema costatum (Ger.) Cleve. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 19: 217–226
Pecreboom-Stegeman, J. H. J., Melet, J., Peereboom, J. W. C., Hooghwinkel, G. J. M. (1979). Influence of chronic Cd intoxication on the alkaline phosphatase activity of liver and kidney; biochemical, histochemical and histological investigations. Toxicology 14: 67–80
Plocke, D. J., Vallee, B. L. (1962). Interaction of alkaline phosphatase of E. coli with metal ions and chelating agents. Biochemistry 1: 1039–1043
Ram, R. N., Sathyanesan, A. G. (1985). Mercuric chloride, cythion and ammonium sulfate induced changes in the brain, liver and ovarian alkaline phosphatase content in the fish Channa puntactus. Envir. Ecol. 3: 263–268
Reddy, M. S., Ramana Rao, K. V. (1990). Methylparathion-induced alterations in the acethylcholinesterase and phosphatases in a penaeid prawn, Metapenaeus monoceros. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxic. 45: 350–357
Sarasquete, M. C., Gimeno, S., González de Canales, M. L. (1990). Cycle reproducteur de la palourde Ruditapes philippinarum (Adams & Reeve, 1850) de la côte Sud Ouest Atlantique (Espagne). Revue int. Océanogr. méd. 97: 90–99
Sastry, K. V., Sharma, K. (1979). In vitro inhibition of three phosphatases by mercuric chloride and their reversal by chelating agent EDTA. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxic. 23: 741–746
Schuel, H., Wilson, W. L., Wilson, J. R. (1975). Heterogenous distribution of “lysosomal” hydrolases of unfertilized eggs in yolk platelets isolated from zonal centrifugation. Devl. Biol 46: 404–412
Walter, K., Schütt, C. (1974). Acid and alkaline phosphatase in serum (two point method). In: Bergmeyer, H. U. (ed.) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Vol 2. Verlag Chemie & Academic Press, Weinheim
Westin, M. (1975). Phosphatase activity antigens in sea urchin eggs and embryos. J. exp. Zool. 192: 307–314
Whitmore, D. H., Goldberg, E. (1972a). Trout intestinal alkaline phosphatases. I. Some physical-chemical characteristics. J. exp. Zool. 182: 47–58
whitmore, D. H., Goldberg, E. (1972b). Trout intestinal alkaline phosphatases. II. The effect of temperature upon enzymatic activity in vitro and in vivo. J. exp. Zool. 182: 59–68
Yokota, Y. (1986). Purification and characterization of particulate acid phosphatases from eggs of Mediterranean sea urchins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol 84B: 255–260
Yora, T., Sakagishi, Y. (1986). Comparative biochemical study of alkaline phosphatase isozymes in fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 85 B: 649–658
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blasco, J., Puppo, J. & Sarasquete, M.C. Acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum . Marine Biology 115, 113–118 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349392
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349392