Summary
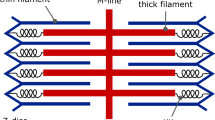
The structure of the Z disc has been studied in thin sections of striated muscle fibers from a wide variety of vertebrates. A common organization is found in all muscles examined. The disc shows a regular pattern made up of dense lines which seem to connect the actin filaments from adjacent sarcomeres. The lines are sometimes disposed to form a regular zigzag configuration; in other orientations with respect to the plane of the section the morphology is confused and, in still other images, the dense lines continuous with the actin filaments seem to go straight through the Z disc. In cross section this structure corresponds to a square pattern of considerable regularity. The intersections in the square pattern mark the location in the plane of the section of the actin filaments from adjacent sarcomeres. Dense lines form the edges of the squares and appear to represent condensations of Z-disc material, i.e., the lines in the zigzag. The possible origin of the structure as a product of the stretching of a membrane is discussed, together with functional interpretations of the Z disc.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Amici, G. B.: Sulla fibra muscolare. II. Tempo-Giornale Italiano di Medicina, Chirurgia e Scienze affini, Anno I, vol. III, p. 328 (1858).
Andersson-Cedergren, E.: Ultrastructure of motor end plate and sarcoplasmic components of mouse skeletal muscle fibers. J. Ultrastruct. Res., Suppl. 1, 1–191 (1959).
Ahsley, C. A., K. R. Porter, D. E. Philpott and G. M. Hass: Observations by electron microscopy on contraction of skeletal myofibrils induced with adenosinetriphosphate. J. exp. Med. 94, 9–20 (1951).
Barer, R.: The structure of the striated muscle fiber. Biol. Rev. 23, 159–200 (1948).
Bennett, H. S.: Modern concept of structure of striated muscle. Amer. J. phys. Med. 34, 46–67 (1955).
: An electron microscope study of sectioned breast muscle of the domestic fowl. Amer. J. Anat. 93, 61–106 (1953).
Boga, L. v.: Beitrag zur Kenntnis des Muskelgewebes von Trichopterenlarven. Eine mikroskopische Studie des feineren Baues des Insektenkörpers. Z. Zellforsch. 27, 568–602 (1937).
Bowman, W.: On the minute structure and movements of voluntary muscle. Phil. Trans. B 130, 457–502 (1840).
Dobie, W. M.: Observations on the minute structure and mode of contraction of voluntary muscle fibers. Ann. and Mag. Natur.-History 3, (Ser. II), 109–119 (1849).
Draper, M. H., and A. J. Hodge: Studies on muscle with the electron microscope. I. The ultrastructure of toad striated muscle. Aust. J. exp. Biol. med. Sci. 27, 46–51 (1949).
: Electron induced microincineration with the electron microscope. I. Distribution of residual mineral content in vertebrate striated muscle. Aust. J. exp. Biol. med. Sci. 28, 549–557 (1950).
Enderlein, G.: Beitrag zur Kenntnis des Baues der quergestreiften Muskeln bei den Insekten. Arch. mikr. Anat. 55, 144–150 (1899).
Guba, F., M. Goramwolgyi and E. Ernst: On the electron microscopic structure of the Z lines. IV. Int. Conf. E. M. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960, vol. III, p. 324.
Hanson, J., and H. E. Huxley: Structural basis of the cross striations in muscle. Nature (Lond.) 172, 530–532 (1953).
Heidenhain, M.: Struktur der kontraktilen Materie. Ergebn. d. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 8, 1–111 (1898).
: Plasma und Zelle. In: Handbuch der Anatomie des Menschen, Bd. 8/2, S. 613. K. von Bardeleben (ed), Jena: Gustav Fischer 1911.
Hodge, A. D.: The fine structure of striated muscle. A comparison of insect flight muscle with vertebrate and invertebrate skeletal muscle. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2 (Suppl.), 131–142 (1956).
Huxley, A. F., and R. E. Taylor: Function of Krause's membrane. Nature (Lond.) 176, 1068 (1955).
Huxley, H. E.: The double array of filaments in cross striated muscle. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 3, 613–648 (1957).
Karnovsky, M. J.: Simple methods for “staining with lead” at highpH in electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 11, 729–732 (1961).
Knappeis, G. G., and F. Carlsen: The ultrastructure of the Z disc in skeletal muscle. J. Cell Biol. 13, 323–335 (1962).
Kölliker, A.: Zur Kenntnis der quergestreiften Muskelfasern. Z. wiss. Zool. 47, 689–710 (1888).
Lowy, J., and J. Hanson: Ultrastructure of invertebrate smooth muscles. Physiol. Rev. 42 (Suppl. 5), 34–42 (1962).
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Moscona, A.: Cell suspensions from organ rudiments of chick embryos. Exp. Cell Res. 3, 535–539 (1952).
Palade, G. E.: A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J. exp. Med. 95, 285–298 (1952).
- The fixation of tissues for electron microcsopy. Proc. 3rd. Int. Conf. for E. M., London 1954. J. roy. micr. Soc. 417 (1956).
Peachey, L. D.: Structure of the longitudinal body muscles of Amphioxus. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 10 (Suppl. 4), 159–176 (1961).
Porter, K. R.: The sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells of Amblystoma larvae. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2 (Suppl.), 163–170 (1956).
: The properties and effects of osmium tetroxide as a tissue fixative with special reference to its use for electron microscopy. Exp. Cell Res. 4, 127–141 (1953).
Sabatini, D. D., K. G. Bensch and R. J. Barrnett: Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J. Cell Biol. 17, 19–58 (1963).
Schäfer, E. A.: On the minute structure of the muscle-columns or sarcostyles which form the wing muscles of insects. Proc. roy. Soc. (Edinb.) 49, 280–286 (1891).
Schipiloff, C., und A. Danielevsky: Über die Natur der anisotropen Substanzen des quergestreiften Muskels und ihre sämtliche Vertheilung im Muskelbündel. Hoppe Seylers Z. physiol. Chem. 5, 349–358 (1881).
Scott, G. H., and D. M. Packer: An electron microscope study of magnesium and calcium in striated muscle. Anat. Rec. 74, 31–43 (1939).
Sjöstrand, F. S., and E. Andersson-Cedergren: The ultrastructure of the skeletal muscle myofilaments at various stages of shortening. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1, 74–108 (1957).
Spiro, D.: The ultrastructure of striated muscle at various sarcomere lengths. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2 (Suppl.), 157–162 (1957).
Veratti, E.: Ricerche sulla fine struttura della fibra muscolare striata. Mem. Ist. Lomb. Cl. Sc. nat. 19, 87–133 (1901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Postdoctoral fellow under USPHS Training Grant 2 G-707 to K. R. Porter.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franzini-Armstrong, C., Porter, K.R. The Z disc of skeletal muscle fibrils. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 61, 661–672 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342617
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342617