Abstract
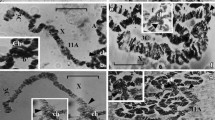
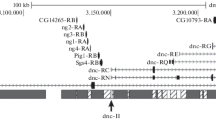
A detailed cytogenetic study of male-viable and lethal deficiencies affecting the w-spl interval in Drosophila melanogaster has revealed the existence of genetic duplication such that, for example, the consequences of the loss of salivary chromosome band 3C3 are essentially compensated for by the presence of band 3C5-6, and vice versa. Although each of the duplicate elements possesses rst + and vt + activity, rst and vt phenotypes appear in males when 3C3 and part, but not all, of 3C5-6 are deleted. The degree of rst and vt expression can be correlated with the amount of material lost from 3C5-6. Deletions removing the entire 3C3-6 interval are male lethal. Despite the duplicate elements, at least one EMS-induced, presumptive point mutation expressing only rst is known; two others express both rst and vt. No loci other than rst and vt occur between W and spl. Band 3C2 appears to be associated with the w locus, which probably extends into the interband space between 3C1 and 3C2. The w locus is not involved in the rst-vt duplication in the 3C3-6 region. — The cytogenetic characteristics of the 3C region—a high coefficient of crossing over, frequent induced chromosome breakage, ectopic pairing, constriction, and an extended replication period—can be correlated with the fact that in 3C a relatively long stretch of DNA, nearly 2% of the entire X chromosome, is highly compacted into but few adjacent bands. These characteristics do not necessarily represent special properties of intercalary heterochromatin; they can be interpreted as reflecting the properties of any similarly organized euchromatic region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcos-Terán, L., Beermann, W.: Changes of DNA replication behavior associated with intragenic changes of the white region in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma (Berl.) 25, 377–391 (1968).
Beermann, W.: Riesenchromosomen. Protoplasmatologia VI/C, S. 1–161. Wien: Springer 1962.
Beermann, W.: Gene action at the level of the chromosome. In: Heritage from Mendel (R. A. Brink, ed.), p. 179–201. Madison: Univ. of Wisconsin Press 1967.
Bridges, C. B.: Salivary chromosome maps. J. Hered. 26, 60–64 (1935).
Bridges, C. B.: Correspondences between linkage maps and salivary chromosome structure, as illustrated in the tip of chromosome 2R of Drosophila melanogaster. Cytologia (Tokyo) Fujii Jubilee Vol. p. 745–755 (1937).
Bridges, G. B.: A revised map of the salivary gland X-chromsome of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Hered. 29, 11–13 (1938).
Emmens, C. W.: Salivary gland cytology of roughest 3 inversion and reinversion, and roughest 2. J. Genet. 34, 191–202 (1937).
Fahmy, O. G., Fahmy, M. J.: New mutants: Report of O. G. and Myrtle J. Fahmy. Dros. Inf. Ser. 32, 67–78 (1958).
Fahmy, O. G., Fahmy, M. J.: New mutants: Reports of O. G. and M. J. Fahmy. Dros. Inf. Ser. 33, 82–94 (1959).
Fahmy, O. G., Fahmy, M. J.: New mutants: Report of O. G. and M. J. Fahmy. Dros. Inf. Ser. 34, 49 (1960).
Gans-David, M.: Étude génétique et physiologique du mutant zeste de Drosophila melanogaster. Bull. biol. France Belg. (Suppl.) 38, 1–90 (1953).
Gersh, E. S.: A new locus in the white-Notch region of the Drosophila melanogaster X chromosome. Genetics 51, 477–480 (1965).
Green, M. M.: Putative non-reciprocal crossing over in Drosophila melanogaster. Z. Vererbungsl. 90, 375–384 (1959).
Green, M. M.: Unequal crossing over and the genetical organization of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Z. Vererbungsl. 94, 200–214 (1963).
Green, M. M.: The genetics of a mutable gene at the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 56, 467–482 (1967).
Grüneberg, H.: The position effect provided by a spontaneous reinversion of the X chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Gen. 34, 169–189 (1937).
Hannah, A.: Localization and function of heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Advanc. Genet. 4, 87–125 (1951).
Hochman, B.: Analysis of chromosome 4 in Drosophila melanogaster. II. Ethyl methanesulfonate induced lethals. Genetics 67, 235–252 (1971).
Judd, B. H.: Analysis of products from regularly occurring asymmetrical exchange in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 46, 1687–1697 (1961).
Judd, B. H.: The structure of intralocus duplication and deficiency chromosomes produced by recombination in Drosophila melanogaster, with evidence for polarized pairing. Genetics 49, 253–265 (1964).
Kaufmann, B. P.: Organization of the chromosome. I. Break distribution and chromosome recombination in Drosophila melanogaster. J. exp. Zool. 102, 293–320 (1946).
Lefevre, G., Jr.: Tests for deficiencies in the vicinity of the white locus. Dros. Inf. Ser. 43, 141 (1968).
Lefevre, G., Jr.: The eccentricity of vermilion deficiencies in Drosophila melano gaster. Genetics 63, 589–600 (1969).
Lefevre, G., Jr.: Salivary chromosome bands and the frequency of crossing over in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 67, 497–513 (1971).
Lefevre, G., Jr., Moore, L. B.: Recombination in regions adjacent to deletions in the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 58, 557–571 (1968).
Lefevre, G., Jr., Wilkins, M. D.: Cytogenetic studies on the white locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 53, 175–187 (1966).
Lindsley, D. L., Grell, E. H.: Genetic variations of Drosophila melanogaster. Carnegie Instn. Washington Publ. 627 (1968).
Panshin, I. B.: A viable homozygous deficiency in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature (Lond.) 142, 837 (1938).
Panshin, I. B.: Cytogenetic analysis of the homology of genes in reversed linear repeats. C. R. (Doklady) Sci. URSS 30, 57–60 (1941).
Plaut, W.: On ordered DNA replication in polytene chromosomes. Genetics (Suppl.) 61, 239–244 (1969).
Plaut, W., Nash, D., Fanning, D.: Ordered replication of DNA in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. J. molec. Biol. 16, 85–93 (1966).
Redfield, H.: Recombination increase due to heterologous inversions and the relation to cytological length. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 41, 1084–1091 (1955).
Ritossa, F. M., Atwood, K. C., Lindsley, D. L., Spiegelman, S.: On the chromosomal distribution of DNA complementary to ribosomal and soluble RNA. Nat. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 23, 449–472 (1966).
Rudkin, G. T.: The relative mutabilities of DNA regions of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 52, 665–681 (1965).
Shannon, M. P., Kaufman, T. C., Judd, B. H.: Lethal patterns of mutations in the zeste-white region of Drosophila melanogaster. (Abstr.) Genetics (Suppl.) 64, s58 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was aided by research grants from the U. S. Public Health Service (GM 13631) to G. Lefevre, Jr. and the National Science Foundation (GB 27599) to M. M. Green.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lefevre, G., Green, M.M. Genetic duplication in the white-split interval of the X chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster . Chromosoma 36, 391–412 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336795
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336795