Summary
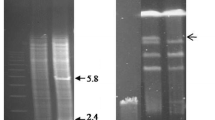
The isopenicillin N synthetase (IPNS) gene has been isolated from wild-type Penicillium chrysogenum and used as a probe to detect the equivalent gene on Southern blots of genomic DNA from a mutant producing high levels of penicillin. The IPNS gene in this strain is contained within a region of DNA of wild-type restriction pattern that extends for at least 39 kb and is present at between 8 and 16 copies. The steady state level of IPNS mRNA in the mutant producing high levels of penicillin is between 32-and 64-fold of that of the wild type, suggesting that the rate of transcription of some or all of the copies has been increased. In addition we have also shown that both the IPNS mRNA and enzyme is present throughout the growth phase in both strains under the culture conditions used. IPNS enzyme activity is greatly increased in the strain with the high penicillin titre.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballance DJ, Turner G (1985) Development of a high-frequency transforming vector for Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 36:321–331
Ballance DJ, Buxton FP, Turner G (1983) Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans by the orotidine-5′-phosphate decarboxylase gene of Neurospora crassa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 112:284–289
Beri R, Turner G (1987) Transformation of Penicillium chrysogenum with the Aspergillus nidulans amdS gene as a dominant selective marker. Curr Genet 11:639–641
Bull JH, Smith DJ, Turner G (1988) Transformation of Penicillium chrysogenum with a dominant selectable marker. Curr Genet 13:377–382
Brownlee KA, Loraine PK, Stephens J (1949) The biological assay of penicillin by a modified plate method. J Gen Microbiol 3:347–382
Carr LG, Skatrud PL, Scheetz ME, Queener SW, Ingolia TD (1986) Cloning and expression of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Penicillium chrysogenum. Gene 48:257–266
Jaklitsch WM, Hampel W, Rohr M, Kubicek CP (1986) α-Aminoadipate pool concentration and penicillin biosynthesis in strains of Penicillium chrysogenum. Can J Microbiol 32:473–480
Kolar M, Punt PJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Schwab H (1988) Transformation of Penicillium chrysogenum using dominant selection markers and expression of an Escherichia coli lacZ fusion gene. Gene 62:127–134
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Nuesch J, Heim J, Treichler HJ (1987) The biosynthesis sulphur containing β-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol 41:51–75
Pirt SJ (1987) Microbial physiology in the penicillin fermentation. Trends Biotechnol 5:69–72
Ramon D, Carramolino L, Patino C, Sanchez F, Penalva MA (1987) Cloning and characterisation of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene mediating the formation of the β-lactam ring in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 57:171–181
Ramos FR, Lopez-Nieto MJ, Martin JF (1985) Isopenicillin N synthetase of Penicillium chrysogenum, an enzyme that converts δ-(l-α-aminoadipyl)-l-cysteinyl-d-valine to isopenicillin N. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27:380–387
Raper KB, Alexander DF, Coghill RD (1944) Natural variation and penicillin production in Penicillium notatum and allied species. J Bacteriol 48:639–659
Rowlands RT (1984) Industrial strain improvement: mutagenesis and random screening procedures. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 6:3–10
Samson SM, Belagaje R, Blankenship DT, Chapman JL, Perry D, Skatrud PL, Vanfrank RM, Abraham EP, Baldwin JE, Queener SW, Ingolia TD (1985) Isolation, sequence determination and expression in Escherichia coli of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Cephalosporium acremonium. Nature 318:191–194
Skatrud PL, Fisher DC, Ingolia TD, Queener SW (1986) Improved transformation of Cephalosporium acremonium. In: Alacevic M, Hranueli D, Toman Z (eds) Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on the Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms. Pliva, Zagreb, Yugoslavia, pp 111–119
Timberlake WE (1986) Isolation of stage- and cell-specific genes from fungi. In: Bailey J (ed) Biology and molecular biology of plant pathogen interactions NATO ASI Series, Series H: Cell Biology, vol I, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 343–357
Turner G, Ballance DJ (1986) Cloning vectors for Aspergillus nidulans based on ans1, a chromosomal fragment enhancing transformation frequency. In: Alacevic M, Hranueli D, Toman Z (eds) Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on the Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms. Pliva, Zagreb, Yugoslavia, pp 121–127
Wernars K, Goosen T, Wennekes LMJ, Visser J, Bos CJ, van den Broek HWJ, van Gorcom RFM, van den Hodel CAMJJ, Pouwels PH (1985) Gene amplification in Aspergillus nidulans by transformation with vectors containing the amdS gene. Curr Genet 9:361–368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C.P. Hollenberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, D.J., Bull, J.H., Edwards, J. et al. Amplification of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene in a strain of Penicillium chrysogenum producing high levels of penicillin. Mol Gen Genet 216, 492–497 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334395
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334395