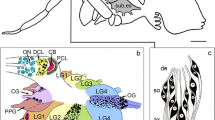
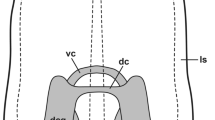
Abstract
In this study, immunohistochemistry on Vibracut sections is used to demonstrate anti-histamine immunoreactivity in the brain of the spider, Cupiennius salei (Keys.) (Ctenidae). We describe a system of histamine-immunoreactive neurons within the central nervous system that consists of six omnisegmental neurons. These histamine-immunoreactive neurons form two subgroups: a dorsal system with two cells per hemisphere and a ventral system with only one cell per hemisphere. The cells have extended arborizations in the motor and sensory areas of all neuromeres in the suboesophageal ganglionic mass. We have also found histamine immunoreactivity in the photoreceptors of C. salei and suggest that histamine is a neurotransmitter of photoreceptors in all arthropods, since it is also known to occur in the photoreceptors of the other main arthropod taxa (Merostomata, Crustacea, and Insecta).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ache BW, McClintock T (1990) The lobster olfactory receptor cell as a neurobiological model: the action of histamine. In: Wiese K, Krenz WD, Tautz J, Reichert H, Malloney B (eds) Frontiers in crustacean neurobiology. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 33–90
Anton S, Barth FG (1993) Central nervous projection patterns of the trichobothria and other cuticular sensilla in the wandering spider Cupiennius salei (Arachnida, Araneae). Zoomorphology 113:21
Babu KS, Barth FG (1984) Neuroanatomy of the central nervous system of the wandering spider, Cupiennius salei (Arachnida, Araneida). Zoomorphology 104:344–359
Babu KS, Barth FG (1989) Central nervous projections of mechanoreceptors in the spider Cupiennius salei Keys. Cell Tissue Res 258:69–82
Babu KS, Barth FG, Strausfeld NJ (1985) Intersegmental sensory tracts and contralateral motor neurons in the leg ganglia of the spider Cupiennius salei Keys. Cell Tissue Res 241:53–57
Battelle BA, Calman BG, Andrews AW, Grieco FD, Mleziva MB, Callaway JC, Stuart AE (1991) Histamine: a putative afferent neurotransmitter in Limulus eyes. J Comp Neurol 305:527–542
Baux G, Fossier P, Tauc L (1990) Histamine and FLRFamide regulate acetylcholine release at an identified synapse in Aplysia in opposite ways. J Physiol (Lond) 429:247–255
Bayer TA, McClintock T, Grünert U, Ache BW (1989) Histamine induced modulation of olfactory receptor neurons in two species of lobsters, Panulirus argus and Homarus americanus. J Exp Biol 145:133–146
Callaway JC, Stuart AE (1989) Biochemical and physiological evidence that histamine is the transmitter of barnacle photoreceptors. Vis Neurosci 3:311–325
Claiborne BJ, Selverston AI (1984) Histamine as a transmitter in the stomatogastric nervous system of the spiny lobster. J Neurosci 4:708–721
Duelli P (1980) The neuronal organization of the posterior lateral eyes of jumping spiders (Salticidae). Zool Jb Anat 103:17–40
Eckweiler W, Seyfarth EA (1988) Tactile hairs and the adjustment of body height in wandering spiders: behavior, leg reflexes, and afferent projections in the leg ganglia. J Comp Physiol [A] 162:611–621
Eckweiler W, Hammer K, Seyfarth EA (1989) Long, smooth hair sensilla on the spider leg coxa: sensory physiology, central projection pattern, and proprioceptive function (Arachnida, Araneida). Zoomorphology 109:97–102
Elias MS, Evans PD (1983) Histamine in the insect nervous system: distribution, synthesis and metabolism. J Neurochem 41:562–568
Elias MS, Evans PD (1984) Autoradiographic localization of 3H-histamine accumulation in the visual system of the locust. Cell Tissue Res 238:105–112
Elste A, Koester J, Shapiro E, Panula P, Schwartz JH (1990) Identification of histaminergic neurons in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 64:736–744
Gronenberg W (1989) Anatomical and physiological observations on the organization of mechanoreceptors and local interneurons in the central nervous system of the wandering spider Cupiennius salei. Cell Tissue Res 258:163–175
Gronenberg W (1990) The organization of plurisegmental mechanosensitive interneurons in the central nervous system of the wandering spider Cupiennius salei. Cell Tissue Res 260:49–61
Gupta AP (1987) Evolutionary trends in the central and mushroom bodies of the arthropod brain. A dilemma. In: AP Gupta (ed) Arthropod brain. Wiley, New York Singapore, pp 27–42
Hanström B (1928) Vergleichende Anatomie des Nervensystems der wirbellosen Tiere unter Berücksichtigung seiner Funktion. Springer, Berlin
Hardie RC (1987) Is histamine a neurotransmitter in insect photoreceptors? J Comp Physiol [A] 161:201–213
Hardie RC (1989) A histamine-activated chloride channel involved in neurotransmission at a photoreceptor synapse. Nature 339:704–706
Holmgren N (1916) Zur vergleichenden Anatomie des Gehirns von Polychaeten, Onychophoren, Xiphosuren, Arachniden, Crustaceen, Myriapoden und Insekten. Kungl Svenska Vetenskapskad Handlingar 56:1–290
Homberg U, Hildebrand JG (1991) Histamine-immunoreactive neurons in the midbrain and suboesophageal ganglion of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 307:647–657
Hough LB (1988) Cellular localization and possible functions for brain histamine: recent progress. Prog Neurobiol 30:469–505
Itowi N, Yamatodani A, Kiyono S, Hiraiwa ML, Wada H (1991) Effect of histamine depletion on the circadian amplitude of the sleep-wakefulness cycle. Physiol Behav 49:643–641
Kravitz EA (1988) Hormonal control of behavior: amines and the biasing of behavioral output in lobster. Science 241:1775–1781
Lin JT, Toh Y, Mizunami M, Tateda H (1990) Putative neurotransmitter in the ocellar neuropil of American cockroaches. Zool Sci 7:593–603
McCaman RE, Weinreich D (1985) Histaminergic synaptic transmission in the cerebral ganglion of Aplysia. Neurophysiology 53:1016–1037
McClintock T, Ache BW (1989) Histamine directly gates a chloride channel in lobster olfactory receptor neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8137–8141
Melamed J, Trujillo-Cenoz O (1966) The fine structure of the visual system of Lycosa (Araneae: Lycosidae). Part I. Retina and optic nerve. Z Zellforsch 74:12–31
Milde JJ, Seyfarth EA (1988) Tactile hairs and leg reflexes in wandering spiders: physiological and anatomical correlates of reflex activity in the leg ganglia. J Comp Physiol [A] 162:623–631
Mulloney B, Hall WM (1991) Neurons with histamine-like immunoreactivity in the segmental and stomatogastric nervous system of the crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus and the lobster Homarus americanus. Cell Tissue Res 266:197–207
Nässel DR, Holmquist MH, Hardie RC, Håkanson R, Sundler F (1988) Histamine like immunoreactivity in photoreceptors of the compound eyes and ocelli of the flies Calliphora erythrocephala and Musca domestica. Cell Tissue Res 253:639–646
Nässel DR, Pirvola U, Panula P (1990) Histamine-like immunoreactive neurons innervating putative neurohaemal areas and central neuropil in the thoraco-abdominal ganglia of the flies Drosophila and Calliphora. J Comp Neurol 297:525–536
Oberdorfer MD (1977) The neural organization of the first optic ganglion of the principal eyes of jumping spiders (Salticidae). J Comp Neurol 174:95–118
Orona E, Battelle BA, Ache BW (1990) Immunohistochemical and biochemical evidence for the putative inhibitory neurotransmitters histamine and GABA in lobster olfactory lobes. J Comp Neurol 294:633–646
Panula P, Häppölä O, Airaksinen MS, Auvinen MS, Virkamäki A (1988) Carbodiimide as a tissue fixative in histamine immunohistochemistry and its application to developmental biology. J Histochem Cytochem 36:259–269
Pasztor VM, Bush BMH (1987) Peripheral modulation of mechanosensitivity in primary afferent neurons. Nature 326:793–795
Pirvola U, Tuomisto L, Yamatodani A, Panula P (1988) Distribution of histamine in the cockroach brain and visual system: an immunocytochemical and biochemical study. J Comp Neurol 276:514–526
Pollack I, Hofbauer A (1991) Histamine-like immunoreactivity in the visual system and brain of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res 266:391–396
Schlemermeyer E, Schütte M, Ammermüller J (1989) Immunohistochemical and electrophysiological evidence that locust ocellar photoreceptors contain and release histamine. Neurosci Lett 99:73–78
Schmid A, Sperk G, Reiter H (1992) Quantitative determination of neuroactive substances in the CNS of the spider Cupiennius salei Keys. Comp Biochem Physiol (C) 102:447–450
Simmons PJ, Hardie RC (1988) Evidence that histamine is a neurotransmitter of photo-receptors in the locust ocellus. J Exp Biol 138:205–219
Skiebe P, Corrette BJ, Wiese K (1990) Evidence that histamine is the inhibitory transmitter of the auditory interneuron ON1 of crickets. Neurosci Lett 116:361–366
Strausfeld NJ, Barth FG (1993) Two visual systems in one brain: neuropils serving the secondary eyes of the spider Cupiennius salei. J Comp Neurol 328:43–62
Strausfeld NJ, Weltzien P, Barth FG (1993) Two visual systems in one brain: neuropils serving the principal eyes of the spider Cupiennius salei. J Comp Neurol 328:63–75
Trujillo-Cenoz O, Melamed J (1967) The fine structure of the visual system of Lycosa (Araneae: Lycosidae) Part II. Primary visual centers. Z Zellforsch 76:377–388
Wada H, Inagaki N, Yamatodani A, Watanabe T (1991) Is the histaminergic neuron system a regulatory center for whole-brain activity? Trends Neurosci 14:415–418
Weinreich D (1977) Synaptic responses mediated by identified histamine-containing neurons. Nature 267:854–856
Weinreich D, Weiner C, McCaman R (1975) Endogenous levels of histamine in single neurons isolated from CNS of Aplysia californica. Brain Res 84:341–345
Wikgren M, Reuter M, Gustafsson MKS, Lindroos P (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of histamine in flatworms. Cell Tissue Res 260:479–484
Yamashita S, Tateda H (1981) Efferent neural control in the eyes of orb weaving spiders. J Comp Physiol [A] 143:477–483
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmid, A., Duncker, M. Histamine immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the spider Cupiennius salei . Cell Tissue Res 273, 533–545 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333707
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333707