Abstract
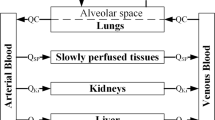
An improved pharmacokinetic model is described for inhalation of volatile xenobiotics from a closed gas phase system. This model is based on steady-state kinetics and covers metabolic elimination processes of either first-order, zero-order, or Michaelis-Menten characteristics. It is emphasized that the distribution of a volatile compound between gas phase and organism under steady-state conditions may be much different from a static equilibrium obtained in absence of metabolism, as it is observed after application of a metabolic inhibitor. A re-analysis of previous experimental data on dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of different haloethylenes reveals that, in general, the metabolic elimination processes of the rapidly equilibrating mono-haloethylenes (and vinylidene fluoride) can be resolved with excellent accuracy into sections of first-order and zero-order kinetics. Other compounds show a more smooth transition from first-order elimination (at lower atmospheric concentrations) into conditions of saturation (dichloroethylenes, trichloroethylene). The analyses are consistent with a recent concept of Andersen (1980) that metabolic elimination of inhaled xenobiotics is limited by either the capacity of metabolic enzymes or factors of transport to the metabolic sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen ME (1980) Physiological factors important in controlling the metabolism of inhaled gases and vapors. AFAMRL-TR-121, Air Force Aerospace Medical Research Laboratory, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio 45433 (ADA 086 341) Proc 10th Ann Conf Environ Toxicol, pp 118–134
Andersen ME, Gargas ML, Jones RA, Jenkins LJ (1980) Determination of the kinetic constants for metabolism of inhaled toxicants in vivo using gas uptake measurements. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 54: 100–116
Bolt HM, Kappus H, Buchter A, Bolt W (1976) Dispositon of 1,2-14C-vinyl chloride in the rat. Arch Toxicol 35: 153–162
Buchter A, Bolt HM, Filser JG, Goergens HW, Laib RJ, Bolt W (1978) Pharmakokinetik und Karzinogenese von Vinylchlorid; Arbeitsmedizinische Risikobeurteilung. Verh Dtsch Ges Arbeitsmedizin. (Gentner, Stuttgart) 18: 111–124
Buchter A, Filser JG, Peter H, Bolt HM (1980) Pharmacokinetics of vinyl chloride in the Rhesus monkey. Toxicology Lett 6: 33–36
Dietz, FK, Reitz RH, Watanabe PG, Gehring PJ (1981) Translation of pharmacokinetic/biochemical data into risk assessment. In: Snyder R, Parke DV, Kocsis JJ, Jollow DJ (eds) Second International Symposium on Biological Reactive Intermediates. Plenum Press, New York
Droz PO, Fernandez JG (1977) Effect of physical workload on retention and metabolism of inhaled organic solvents. A comparative theoretical approach and its applications with regards to exposure monitoring. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 38: 231–246
Ertle T, Henschler D, Müller G, Spassowski M (1972) Metabolism of trichloroethylene in man. I. The significance of trichloroethanol in long-term exposure conditions. Arch Toxicol 29: 171–188
Filser JG, Bolt HM (1979) Pharmacokinetics of halogenated ethylenes in rats. Arch Toxicol 42: 123–136
Gehring PJ, Watanabe PG, Park CN (1978) Resolution of dose-response toxicity data for chemicals requiring metabolic activation. Example — vinyl chloride. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 44: 581–591
Gehring PJ, Watanabe PG, Young JD (1977) The relevance of dose-dependent pharmacokinetics in assessment of carcinogenic hazard of chemicals. In: Hiatt HH, Watson JD, Winsten JA (eds) Origins of Human Cancer, vol 4. Cold Spring Harbor Conferences on Cell Proliferation. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, pp 187–203
Hallier E, Filser JG, Bolt HM (1981) Inhalation pharmacokinetics based on gas uptake studies. II. Pharmacokinetics of acetone. Arch Toxicol 47: 293–304
Kimmerle G, Eben A (1973) Metabolism, excretion and toxicology of trichloroethylene after inhalation. II. Experimental human exposure. Arch Toxicol 30: 127–138
Müller G, Spassowski M, Henschler D (1974) Metabolism of trichloroethylene in man. II. Pharmacokinetics of metabolites. Arch Toxicol 32: 283–295
Nomiyama K, Nomiyama H (1971) Metabolism of trichloroethylene in the human. Int Arch Arbeitsmed 28: 37–48
Pang KS, Rowland M (1977) Hepatic clearance of drugs. I. Theoretical considerations of a “well stirred” model and a “parallel tube” model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding, and the hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 5: 625–653
Pessayre D, Allemand H, Wandscheer JC, Descatoire V, Artigon JC, Benhamou JP (1979) Inhibition, activation, and induction of drug metabolizing enzymes by trichloroethylene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 49: 355–363
Pessayre D, Wandscheer JC, Descatoire V, Dolder A, Degott C, Benhamou JP (1980) Cumulative effects of repeated doses of compounds transformed into reactive metabolites. Biochem Pharmacol 29: 1041–1047
Smyth RD, Hottendorf GH (1980) Application of pharmacokinetics and biopharmaceutics in the design of toxicological studies. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 53: 179–195
Young JD, Braun WH, Gehring PJ (1978) Dose-dependent fate of 1,4-dioxane in rats. J Toxicol Environ Health 4: 709–726
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filser, J.G., Bolt, H.M. Inhalation pharmacokinetics based on gas uptake studies. Arch Toxicol 47, 279–292 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332394
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332394