Summary
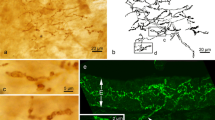
In the tracheal epithelium of adult rats “Brush Border Cells” are found arranged in pairs. Their special structures are narrowly placed and very regular microvilli, the axial filaments of which continue between a number of apical vesicles inside of the cell, without ending in a terminal web. The Golgi apparatus is situated supranuclear; the mitochondria are longitudinally oriented. Ribosomes are free or attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum. Furthermore there are single and aggregated granules of glycogen and lipid droplets.
Along their lateral surface the brush border cells contact initial nerve fibres which contain numerous vesicles, mitochondria, microtubuli and endoplasmatic reticulum.
In 14 day-old rats there are found initial nerve fibres in the undifferenciated epithelium. They contain numerous mitochondria with longitudinally oriented cristae. The dendritic branches partly envelope cells that are arranged in pairs like the brush border cells, and also show their typical cytoplasmatic structure. The brush border is missing, since these cells do not reach the free surface of the mucosa. Besides small mitochondria, filaments and numerous ribosomes they contain small accumulations of vesicles (synaptic vesicles) beneath the plasma membrane, on places which lie opposite of a thickened dendritic plasmalemma (postsynaptic membrane).
The morphological characteristics of the brush border cells allow to assume that they are chemoreceptors. They make contact with dendrites and form afferent synapses respectively epithelio-neural junctions.
Ciliated, goblet and replacement cells are innervated, too. They form contacts with telodendrites, that are efferent synapses or neuro-epithelial junctions and contain structures as they are widely spread in the autonomous nerve system.
Zusammenfassung
Im Epithel der Trachea der erwachsenen Ratte finden sich paarweise angeordnete „Bürstenzellen“. Ihre strukturellen Besonderheiten sind eng stehende, sehr gleichmäßige Mikrovilli, deren axiale Filamente sich zwischen zahlreichen apikalen Vesikeln innerhalb des Zellkörpers fortsetzen, ohne in einem Terminalgespinst zu enden. Der Golgi-Apparat liegt supranukleär; die Mitochondrien sind längs gerichtet. Außerdem liegen im Zellkörper freie oder an den Membranen des endoplasmatischen Retikulums adsorbierte Ribosomen, einzelne und aggregierte Glykogengranula sowie Fett in Tröpfchenform.
Die Bürstenzellen treten entlang ihrer seitlichen Oberfläche mit initialen Nervenfasern in Kontakt, die zahlreiche Vesikel, Mitochondrien, Mikrotubuli und endoplasmatisches Retikulum enthalten.
Bei 14 Tage alten Ratten finden sich im noch nicht ausdifferenzierten Epithel initiale Fasern mit einer größeren Anzahl dichter Mitochondrien, die meist längs orientierte Cristae zeigen. Die dendritischen Verzweigungen umhüllen teilweise Zellen, die wie die Bürstenzellen paarweise angeordnet sind und deren cytoplasmatische Struktur besitzen. Der Bürstensaum fehlt, da diese Zellen nicht die freie Oberfläche der Schleimhaut erreichen. Neben kleinen Mitochondrien, Filamenten und zahlreichen Ribosomen enthalten sie unter der Plasmamembran kleine Anhäufungen von Vesikeln (synaptische Vesikel), die gegenüber einer Verdickung (postsynaptische Membran) des dendritischen Plasmalemms liegen.
Die morphologische Charakteristika der Bürstenzellen lassen vermuten, daß sie Chemorezeptoren sind. Sie treten in Kontakt mit Dendriten und bilden afferente Synapsen bzw. epithelio-neurale Verbindungen.
Auch Flimmerzellen, Schleim- und Ersatzzellen sind reichlich innerviert. Sie weisen Kontakte mit Telodendriten auf, die efferente Synapsen oder neuro-epitheliale Verbindungen darstellen und Strukturen zeigen, wie sie im autonomen Nervensystem weit verbreitet sind.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Andres, K. H.: Über die Feinstruktur der Rezeptoren an Sinushaaren. Z. Zellforsch. 75, 339–365 (1966).
Austin, L., J. W. Chubb, and B. G. Livett: The subcellular localization of catecholamines in nerve terminals in smooth muscle tissue. J. Neurochem. 14, 473–478 (1967).
Barajas, L.: The innervation of the juxtaglomerular apparatus. An electron microscopic study of the innervation of the glomerular arterioles. Lab. Invest. 13, 916–929 (1964).
Bargmann, W., u. A. Knoop: Elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen an der Neurohypophyse. Z. Zellforsch. 46, 242–251 (1957).
— E. Lindner u. K. H. Andres: Über Synapsen an endokrinen Epithelzellen und die Definition sekretorischer Neurone. Untersuchungen am Zwischenlappen der Katzenhypophyse. Z. Zellforsch. 77, 282–298 (1967).
Bencosme, S. A.: Studies on the terminal autonomic nervous system with special reference to the pancreatic islets. Lab. Invest. 8, 629–646 (1959).
Bensch, K. G., G. B. Gordon, and L. R. Miller: Studies on the bronchial counterpart of the Kultschitzky (argentaffin) cell and innervation of bronchial glands. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 12, 668–686 (1965).
Birbeck, M. S. C., and E. H. Mercer: Cytology of cells which synthesize protein. Nature (Lond.) 189, 558–560 (1961).
Bloom, F. E., and R. J. Barrnett: Fine structural localization of noradrenaline in vesicles of autonomic nerve endings. Nature (Lond.) 210, 599–601 (1966).
Bodian, D.: The generalized vertebrate neuron. Science 137, 323–326 (1962).
Brandt, P. W.: A consideration of the extraneous coats of the plasma membrane. Circulation 26, 1075–1091 (1962).
Brettschneider, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an der Nasenschleimhaut. Anat. Anz. 105, 194–204 (1958).
—: Ultrastruktur der visceralen Rezeptoren und afferenten Nerven. Acta neuroveg. (Wien) 28, 37–102 (1966).
Burnstock, G., and N. C. R. Merrillees: Structural and experimental studies on autonomic nerve endings in smooth muscle. In: Pharmacology of smooth muscle, ed. by E. Bülbring, A. Kavarikova and I. Seferna, p. 1–17. London: Pergamon Press 1964.
Cauna, N., and L. L. Ross: The fine structure of Meissners touch corpuscles of human fingers. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 8, 467–482 (1960).
Cireli, E.: Elektronenmikroskopische Analyse der prä- und postnatalen Differenzierung des Epithels der oberen Luftwege der Ratte. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 74, 132–178 (1966).
Cordier, R.: Sensory cells. In: The cell, ed. by J. Brachet and A. E. Mirsky, vol. VI, p. 331–386. New York and London: Academic Press 1964.
Coupland, R. E.: Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the rat adrenal medulla. I. The ultrastructure and organization of chromaffin cells in the normal adrenal medulla. J. Anat. (Lond.) 99, 231–254 (1965a).
—: Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the rat adrenal medulla. II. Normal innervation. J. Anat. (Lond.) 99, 255–272 (1965b).
—, and D. Hopwood: The mechanism of the differential staining reaction for adrenaline- and noradrenaline-storing granules in tissues fixed in glutaraldehyde. J. Anat. (Lond.) 100, 227–243 (1966).
De Duve, C., and R. Wattiaux: Functions of lysosomes. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 28, 435–492 (1966).
De Lorenzo, A. J.: Electron microscopic observations on the taste buds of the rabbit. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 143–150 (1958).
—: Studies on the ultrastructure and histophysiology of cell membranes nerve fibers and synaptic junctions in chemoreceptors. In: Olfaction and taste, ed. by Y. Zotterman, p. 5–17. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1963.
De Robertis, E.: Ultrastructure and cytochemistry of the synaptic region. Science 156, 907–914 (1967).
—, and S. H. Bennett: Some features of the submicroscopic morphology of synapses in frog and earthworm. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 47–58 (1955).
Dirksen, E. R., and T. T. Crocker: Centriole replication in differentiating ciliated cells of mammalian respiratory epithelium. An electron microscopic study. J. Microscopic 5, 629–644 (1966).
Dowell, W. C. T.: Die Entwicklung geeigneter Folien für elektronenmikroskopische Präparatträger großen Durchlaßbereiches und ihre Verwendung zur Untersuchung von Kristallen. Optik 21, 47–58 (1964).
Drochmans, P.: Morphologie du glycogène. Etude au microscope électronique de colorations négatives du glycogène particulaire. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 6, 141–163 (1962).
Ekholm, R., and T. Zelander: Nerve tissue in the mouse thyroid gland. Proc. European Reg. Conf. Electr. Micr., Delft 2, 827–830 (1960).
Elfvin, L.-G.: The fine structure of the cell surface of chromaffin cells in the rat adrenal medulla. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 12, 263–286 (1965).
Engström, H., and C. Rytzner: The structure of taste buds. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) 46, 364–367 (1956).
Fahimi, H. D., et P. Drochmans:Essais de standardisation de la fixation au glutaraldéhyde. I. Purification et détermination de la concentration du glutaraldéhyde. II. Influence des concentrations en aldéhyde et de l'osmolalité. J. Microscopic 4, 725–736; 737–748 (1965).
Farbman, A. J.: Electron microscope study of the developing taste bud in rat fungiform papilla. Develop. Biol. 11, 110–135 (1965a).
—: Fine structure of the taste bud. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 12, 328–350 (1965b).
Fawcett, D. W.: Physiologically significant specializations of the cell surface. Circulation 26, 1106–1125 (1962).
—: Surface specializations of absorbing cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 13, 75–91 (1965).
Feyrter, F.: Über die peripheren endokrinen (parakrinen) Drüsen des Menschen, 2. Aufl. Wien u. Düsseldorf: Wilhelm Maudrich 1953.
Fisher, A. W. F.: The intrinsic innervation of the trachea. J. Anat. (Lond.) 98, 117–124 (1964).
Fröhlich, E.: Die „helle Zelle“ der Bronchialschleimhaut und ihre Beziehungen zum Problem der Chemoreceptoren. Frankfurt. Z. Path. 60, 517–559 (1949).
Gordon, G. B., L. R. Miller, and K. G. Bensch: Fixation of tissue culture cells for ultrastructural cytochemistry. Exp. Cell Res. 31, 440–443 (1963).
Gray, E. G., and K. G. Watkins: Electron microscopy of taste buds of the rat. Z. Zellforsch. 66, 583–595 (1965).
—, and R. W. Guillery: Synaptic morphology in normal and degenerating nervous system. Int. Rev. Cytol. 19, 111–182 (1966).
Grillo, M. A.: Electron microscopy of sympathetic tissues. Pharmacol. Rev. 18, 387–399 (1966).
—, and S. L. Palay: Granule-containing vesicles in the autonomic nervous system. Proc. Fifth Int. Congr. Electr. Micr. 1962, vol. 2, p. U-1.
Gruner, J.-E.: La structure fine du fuseau neuromusculaire humain. Rev. neurol. 104, 490–507 (1961).
Hager, H., u. W. L. Tafuri: Elektronenoptischer Nachweis sog. neurosekretorischer Elementargranula in marklosen Nervenfasern des Plexus myentericus (Auerbach) des Meerschweinchens. Naturwissenschaften 46, 332–333 (1959).
Hartmann, J. F.: Electron microscopy of mitochondria in the central nervous system. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol., Suppl. 2, 375–378 (1956).
Hay, E. D.: The fine structure of nerves in the epidermis of regenerating Salamander limbs. Exp. Cell Res. 19, 299–317 (1960).
Hökfelt, T.: Electron microscopic observations on nerve terminals in the intrinsic muscles of the albino rat iris. Acta physiol. scand. 67, 255–256 (1966).
Honjin, R.: On the ganglia and nerves of the lower respiratory tract of the mouse. J. Morph. 95, 263–287 (1954).
Howatson, A. F., and A. W. Ham: Electron microscope study of sections of two rat liver tumors. Cancer Res. 15, 62–69 (1955).
Ito, S.: The enteric surface coat on cat intestinal microvilli. J. Cell Biol. 27, 475–491 (1965).
Karnovsky, M. J.: Simple methods for “staining with lead” at high pH in electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 11, 729–732 (1961).
Kaye, G. J.: Studies on the cornea. III. The fine structure of the frog cornea and the uptake and transport of colloidal particles by the cornea in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 15, 241–258 (1962).
Konradova, V.: The ultrastructure of the tracheal epithelium in rabbit. Folia morph. (Prag) 14, 210–214 (1966).
Lacy, P. E.: Electron microscopy of the normal islets of Langerhans. Studies in the dog, rabbit, guinea pig and rat. Diabetes 6, 498–507 (1957).
Leeson, T. S.: The development of the trachea in the rabbit, with particular reference to its fine structure. Anat. Anz. 110, 214–223 (1961).
Legg, P. G.: The fine structure and innervation of the beta and delta cells in the islet of Langerhans of the cat. Z. Zellforsch. 80, 307–321 (1967).
Luft, J. H.: Microscopic structure of the electric organ of the electric eel. Anat. Rec. 121, 440 (1955).
Merrillees, N. C. R.: The fine structure of muscle spindles in the lumbrical muscles of the rat. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 725–742 (1960).
— Some observations on the fine structure of a Golgi tendon organ of a rat. In: Symposium on muscle receptors, ed. by D. Barker, p. 199–206. Hongkong: Hongkong University Press 1962.
— G. Burnstock, and M. E. Holman: Correlation of fine structure and physiology of the innervation of smooth muscle in the guinea pig vas deferens. J. Cell Biol. 19, 529–550 (1963).
Messerklinger, W.: Die Schleimhaut der oberen Luftwege im Blickfeld neuerer Forschung. Arch. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 173, 1–104 (1958).
Millington, P. F., and J. B. Finean: Electron microscope studies of the structure of the microvilli on principal epithelial cells of rat jejunum after treatment in hypo- and hypertonic saline. J. Cell Biol. 14, 125–139 (1962).
Moppert, J.: Zur Ultrastruktur der phaeochromen Zellen im Nebennierenmark der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 74, 32–44 (1966).
Munger, B. L.: The ultrastructural morphology of epidermal innervation in the opossum nose. Anat. Rec. 145, 264 (1963).
—: The intraepidermal innervation of the snout skin of the opossum. A light and electron microscope study, with observations on the nature of Merkels Tastzellen. J. Cell Biol. 26, 79–97 (1965).
Murray, R. G., and A. Murray: The fine structure of the taste buds of rhesus and cynomolgus monkeys. Anat. Rec. 138, 211–218 (1960).
Nemetschek-Gansler, H., u. H. Ferner: Über die Ultrastruktur der Geschmacksknospen. Z. Zellforsch. 63, 155–178 (1964).
Novikoff, A. B.: Lysosomes and related particles. In: The cell, ed. by J. Brachet and A. E. Mirsky, vol. II, p. 423–488. New York and London: Academic Press 1963.
Orfanos, C.: Elektronenmikroskopischer Nachweis epithelio-neuraler Verbindungen (Mechano-Receptoren) am Haarfollikelepithel des Menschen. Arch. klin. exp. Derm. 228, 421–429 (1967).
Osada, M.: Electron microscopical observations on the human tracheal epithelium with reference to the ciliated cells. Arch. histol. jap. 24, 91–111 (1963).
Overton, J., and J. Shoup: Fine structure of cell surface specializations in the maturing duodenal mucosa of the chick. J. Cell Biol. 21, 75–85 (1964).
Palade, G. E.: A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J. exp. Med. 95, 285–298 (1952).
—: Electron microscopic observations of interneuronal and neuromuscular synapses. Anat. Rec. 118, 335–336 (1954).
Palay, S. L.: Electron microscope study of the cytoplasm of neurons. Anat. Rec. 118, 336 (1954).
—: The fine structure of the neurohypophysis. In: Ultrastructure and cellular chemistry of neural tissue, ed. by H. Waelsch, p. 31–44. London: Cassell & Co., Ltd. 1957.
—: The morphology of synapses in the central nervous system. Exp. Cell Res., Suppl. 5, 275–293 (1958).
—, and L. J. Karlin: An electron microscopic study of the intestinal villus. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 5, 363–372 (1959).
—, and G. E. Palade: The fine structure of neurons. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 69–88 (1955).
Patrizi, G., and B. L. Munger: The ultrastructure and innervation of rat vibrissae. J. comp. Neurol. 126, 423–436 (1966).
Pease, D. C., and T. A. Quilliam: Electron microscopy of the Pacinian corpuscle. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 3, 331–342 (1957).
Ploschko, A.: Die Nervenendigungen und Ganglien der Respirationsorgane. Anat. Anz. 13, 12–22 (1897).
Rambourg, A., and C. P. Leblond: Electron microscope observations on the carbohydraterich cell coat present at the surface of cells in the rat. J. Cell Biol. 32, 27–53 (1967).
Reale, E., u. L. Luciano: Die Anwendung der Dowell'schen Präparatträger in der Histologie. J. Microscopie 4, 405–408 (1965).
Revel, J. P., L. Napolitano, and D. W. Fawcett: Identification of glycogen in electron micrographs of thin tissue sections. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 8, 575–589 (1960).
Rhodin, J. A. G.: Le tractus epithelial respiratoire, son ultra-structure et sa fonction. Bronches 7, 14–23 (1957).
—: Ultrastructure of the tracheal ciliated mucosa in rat and man. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis) 68, 964–974 (1959).
—: The ciliated cell. Ultrastructure and function of the human tracheal mucosa. Amer. Rev. resp. Dis. 93, 1–15 (1966).
—, and T. Dalhamn: The ultrastructure of the epithelial cells in the trachea of the albino rat. J. appl. Phys. 25, 1463 (1954).
—: Electron microscopy of the tracheal ciliated mucosa in rat. Z. Zellforsch. 44, 345–412 (1956).
Richardson, K. C.: The fine structure of the albino rabbit iris with special reference to the identification of adrenergic and cholinergic nerves and nerve endings in its intrinsic muscles. Amer. J. Anat. 114, 173–205 (1964).
—: Electron microscopic identification of autonomic nerve endings. Nature (Lond.) 210, 756 (1966).
Robertson, D. R.: The ultimobranchial body in Rana pipiens. III. Sympathetic innervation of the secretory parenchyma. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 328–340 (1967).
Robertson, J. D.: Preliminary observations on the ultrastructure of a frog muscle spindle. Proc. Stockholm Conf. Electr. Micr. 1956, p. 197–200.
—: Electron microscopy of the motor end-plate and the neuromuscolar spindle. Amer. J. phys. Med. 39, 1–43 (1960).
Robinson, P. M., and C. Bell: The localization of acetylcholinesterase at the autonomic neuromuscular junction. J. Cell Biol. 33, 93–102 (1967).
Ross, L. L.: Peripheral nervous tissue. In: Electron microscopic anatomy, ed. by S. M. Kurtz, p. 341–367. New York and London: Academic Press 1964.
Ruska, C.: Die Zellstrukturen des Dünndarmepithels in ihrer Abhängigkeit von der physikalisch-chemischen Beschaffenheit des Darminhalts. I. Wasser und Natriumchlorid. Z. Zellforsch. 52, 748–777 (1960).
Ruska, H.: Microscopie électronique des cellules libres dans la ≪lamina propria≫ de l'intestin de la souris. 7e Congr. Internat. de Gastro-Entérologie, Symp. Micr. électronique et path. digestive. Bruxelles 1964, p. 125–134.
Sabatini, D. D., K. Bensch, and R. J. Barrnett: Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J. Cell Biol. 17, 19–58 (1963).
Scalzi, H. A.: The cytoarchitecture of gustatory receptors from the rabbit foliate papillae. Z. Zellforsch. 80, 413–435 (1967).
Silva, D. G.: The fine structure of multivesicular cells with large microvilli in the epithelium of the mouse colon. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 16, 693–705 (1966).
—: The ultrastructure of crystal-containing cells in the colonic epithelium of mice. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 18, 127–141 (1967).
Spoendlin, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am respiratorischen Epithel der oberen Luftwege. Pract. oto-rhino-laryng. (Basel) 21, 484–498 (1959).
Stahl, M.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen über die vegetative Innervation der Bauchspeicheldrüse. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 70, 62–102 (1963).
Stockinger, L.: Die Ultrastruktur des Flimmerepithels des Nasenseptums der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 59, 443–466 (1963).
Stöhr, P.: Mikroskopische Anatomie des vegetativen Nervensystems. In: Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen, herausgeg. von W. Bargmann, V. Teil, Ergänzung zu Bd. IV/1. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1957.
Szentagothai, J.: The structure of the autonomic interneuronal synapse. Acta neuroveg. (Wien) 26, 338–359 (1964).
Taxi, J.: Etude de certaines synapses interneuronales du système nerveux autonome. Acta neuroveg. (Wien) 26, 360–372 (1964).
—: Contribution à l'étude des connexions des neurones moteurs du système nerveux autonome. Ann. Sci. natur., Zool, Sér. XII, 7, 413–674 (1965).
Thaemert, J. C.: Ultrastructural interrelationships of nerve processes and smooth muscle cells in three dimensions. J. Cell Biol. 28, 37–49 (1966).
—: Ultrastructure of cardiac muscle and nerve contiguities. J. Cell Biol. 29, 156–162 (1966).
Tranzer, J. P., and H. Thoenen: Significance of “empty vesicles” in postganglionic sympathetic nerve terminals. Experientia (Basel) 23, 123–124 (1967).
Trujillo-Cenóz, O.: Electron microscope study of the rabbit gustatory bud. Z. Zellforsch. 46, 272–280 (1957).
—: Electron microscope observations on chemo- and mechano-receptor cells of fishes. Z. Zellforsch. 54, 654–676 (1961).
Watson, J. H., and G. L. Brinkman: Electron microscopy of the epithelial cells of normal and bronchitic human bronchus. Amer. Rev. resp. Dis. 90, 851–866 (1964).
Watson, M. L.: Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 475–478 (1958).
Whitear, M.: An electron microscope study of the cornea of the mice, with special reference to the innervation. J. Anat. (Lond.) 94, 387–409 (1960).
Whittaker, V. P.: Catecholamine storage particles in the central nervous system. Pharmacol. Rev. 18, 401–412 (1966).
Wolfe, D. E., J. Axelrod, L. T. Potter, and K. C. Richardson: Localization of norepinephrine in adrenergic axons by light- and electronmicroscopic autoradiography. Fifth Int. Congr. Electr. Micr. Philadelphia 1962, vol. 2, p. L-12.
— L. T. Potter, K. C. Richardson, and J. Axelrod: Localizing tritiated norepinephrine in sympathetic axons by electron microscopic autoradiography. Science 138, 440–441 (1962).
Yamada, E.: The fine structure of the gall bladder epithelium of the mouse. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 445–458 (1955).
Zetterqvist, H.: The ultrastructural organization of the columnar absorbing cells of the mouse jejunum. Thesis Aktiebolaget Godvil Stockholm 1956.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luciano, L., Reale, E. & Ruska, H. Über eine „chemorezeptive“ Sinneszelle in der Trachea der Ratte. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 85, 350–375 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328847
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328847