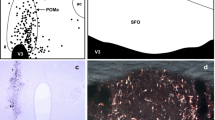
Abstract
Triple fluorescence labelling was employed to reveal the distribution of chemically identified neurons within the pontine laterodorsal tegmental nucleus and dorsal raphe nucleus which supply branching collateral input to the central nucleus of the amygdala and hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. The chemical identity of neurons in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus was revealed by immunocytochemical detection of choline-acetyltransferase or substance P; in the dorsal raphe nucleus, the chemical content of the neurons was revealed with antibody recognizing serotonin. The projections were defined by injections of two retrograde tracers, rhodamine-and fluorescein-labelled latex microspheres, in the central nucleus of the amygdala and paraventricular nucleus, respectively. Neurons projecting to both the central nucleus of the amygdala and the paraventricular nucleus were distributed primarily within the caudal extensions of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus and dorsal raphe nucleus. Approximately 11% and 7% of the labelled cells in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus and dorsal raphe nucleus projected via branching collaterals to the paraventricular nucleus and central nucleus of the amygdala. About half of these neurons in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus were cholinergic, and one-third were substance-P-ergic; in the dorsal raphe nucleus, approximately half of the neurons containing both retrograde tracers were serotonergic. These results indicate that pontine neurons may simultaneously transmit signals to the central nucleus of the amygdala and paraventricular nucleus and that several different neuroactive substances are found in the neurons participating in these pathways. This coordinated signalling may lead to synchronized responses of the central nucleus of the amygdala and paraventricular nucleus for the maintenance of homeostasis. Interactions between different neuroactive substances at the target site may serve to modulate the responses of individual neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrezik JA, Beitz AJ (1985) Reticular formation central grey and related tegmental nuclei. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, Sydney, pp 1–28
Beitz AJ, Shepard RD, Wells WE (1983) The periaqueductal grayraphe magnus projection contains somatostatin, neurotensin and serotonin but not cholecystokynin. Brain Res 261:132–137
Bittencourt JC, Benoit R, Sawchenko PE (1991) Distribution and origins of substance P-immunoreactive projections to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei: Partial overlap with ascending catecholaminergic projections. J Chem Neuroanat 4:63–78
Bolton RF, Cornwall J, Phillipson OT (1993) Collateral axons of cholinergic pontine neurones projecting to midline, mediodorsal and parafascicular thalamic nuclei in the rat. J Chem Neuroanat 6:101–114
Coote JH (1988) Organization of cardiovascular neurons in the spinal cord. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 110:147–285
Fallon JH, Cioffi P (1992) Distribution of monoamines within the amygdala. In: Aggleton JP (ed) The amygdala: Neurobiological aspects of emotion, memory, and mental dysfunction. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 97–114
Herbert H (1992) Evidence for projections from medullary nuclei onto serotonergic and dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 270:149–156
Herbert H, Saper CB (1992) Organization of medullary adrenergic and noradrenergic projections to the periaqueductal gray matter in the rat. J Comp Neurol 315:34–52
Jones BE, Cuello AC (1989) Afferents to the basal forebrain cholinergic cell area from pontomesencephalic-catecholamine, serotonin, and acetylcholine-neurons. Neuroscience 31:37–61
Kuhn DM, Wohf WA, Lovenberg W (1980) Review of the role of the central serotonergic neuronal system in blood pressure regulation. Hypertension 2:243–255
Leanza G, Pelliteri R, Russo A, Stanzani S (1991) Neurons in the raphe nuclei pontis and magnus have branching axons that project to the medial preoptic area and cervical spinal cord. A fluorescent retrograde double labelling study in the rat. Neurosci Lett 123:195–199
Levin MC, Cunningham ET, Sawchenko PE (1987) The organization of mesencephalic and pontine afferents to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in the rat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:1166
Li Y-Q, Jia H-G, Rao Z-R, Shi J-W (1990) Serotonin-, substance P- or leucine-enkephalin-containing neurons in the midbrain periaqueductal gray and nucleus raphe dorsalis send projection fibers to the central amygdaloid nucleus in the rat. Neurosci Lett 120:124–127
Lind W (1986) Bi-directional, chemically specified neural connections between the subfornical organ and the midbrain raphe system. Brain Res 384:250–261
Losier BJ, Semba K (1993) Dual projections of single cholinergic and aminergic brainstem neurons to the thalamus and basal forebrain in the rat. Brain Res 604:41–52
Melander T, Hökfelt T, Rökaeus A, Cuello AC, Oertel WH, Verhofstad A, Goldstein M (1986) Coexistence of galanin-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines, 5-hydroxytryptamine, GABA and neuropeptides in the rat CNS. J Neurosci 6:3640–3654
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Petrov T, Krukoff TL, Jhamandas JH (1992) The hypothalamic paraventricular and lateral parabranchial nuclei receive collaterals from raphe nucleus neurons: A combined double retrograde and immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 318:18–26
Petrov T, Krukoff TL, Jhamandas JH (1993) Branching projections of catecholaminergic brainstem neurons to the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus and the central nucleus of the amygdala in the rat. Brain Res 609:81–92
Saphier D, Feldman S (1989) Paraventricular nucleus neuronal responses following electrical stimulation of the midbrain dorsal raphe: evidence for cotransmission. Exp Brain Res 78:407–414
Sawchenko PE, Swanson LW, Steinbusch HWM, Verhofstad AAJ (1983) The distribution of cells of origin of serotonergic inputs to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the rat. Brain Res 277:355–360
Semba K, Reiner PB, McGeer EG, Fibiger HC (1988) Brainstem afferents to the magnocellular basal forebrain studied by axonal transport, immunohistochemistry, and electrophysiology in the rat. J Comp Neurol 267:433–453
Shiromani PJ, Floyd C, Velazquez-Moctezuma J (1990) Pontine cholinergic neurons simultaneously innervate two thalamic targets. Brain Res 532:317–322
Standaert DG, Saper CB, Rye DB, Wainer BH (1986) Colocalization of atriopeptin-like immunoreactivity with choline acetyl-transferase and substance P-like immunoreactivity in the pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei in the rat. Brain Res 382:163–168
Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1981) Neurotensin. In: Martin JB, Reichlin S, Bick KL (eds) Neurosecretion and brain peptides. Raven Press, New York, pp 87–106
Vanderhaeghen JJ, Lotstra F, De Mey J, Gilles C (1980) Immunocytochemical localization of cholecystokinin- and gastrin-like peptides in the brain and hypophysis of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1190–1194
Vertes RP (1991) A PHA-L analysis of ascending projections of the dorsal raphe nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 313:643–668
Weiss ML, Hatton GL (1990) Collateral input to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in the rat. II. Afferents from the ventral lateral medulla and nucleus tractus solitarius. Brain Res Bull 25:561–567
Wolf NJ, Butcher LL (1986) Cholinergic systems in the rat brain: III. Projections from the pontomesencephalic tegmentum to the thalamus, tectum, basal ganglia, and basal forebrain. Brain Res Bull 16:603–637
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrov, T., Krukoff, T.L. & Jhamandas, J.H. Chemically defined collateral projections from the pons to the central nucleus of the amygdala and hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in the rat. Cell Tissue Res 277, 289–295 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327776
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327776