Abstract
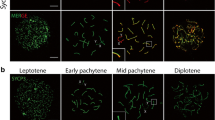
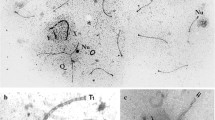
A method is presented for the sequential analysis of male meiosis using hydroxyurea (HU). HU produces a gap in the spermatogenic line. The front of surviving cells behind the gap was examined day by day using silverstained whole mount spreads on glass slides. With this method it was possible to study the development and behaviour of the synaptonemal complex (SC) in mouse spermatocytes by the light microscope. At zygotene no unpaired axial elements could be seen. Unpaired axial elements were found to be specific for the diplotene stage. The axes of the XY pair could be recognized from late zygotene up to diplotene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Counce, S.J., Meyer, G.F.: Differentiation of the synaptonemal complex and the kinetochore in Locusta spermatocytes studied by whole mount electron microscopy. Chromosoma (Berl.) 44, 231–253 (1973)
Dresser, M.E., Moses, M.J.: Silver-staining of synaptonemal complexes in surface spreads for light and electron microscopy. Exp. Cell Res. 121, 416–419 (1979)
Dresser, M.E., Moses, M.J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus). IV. Light and electron microscopy of synapsis and nucleolar development by silver-staining. Chromosoma (Berl.) 76, 1–22 (1980)
Holm, P.B., Rasmussen, S.W.: Three-dimensional reconstructions of meiotic chromosome in human spermatocytes. Chromosomes today 6, 83–93 (1977)
Jhanwar, S.C., Chaganti, R.S.K.: Silver-stained synaptonemal complexes of human pachytene bivalents studied by light microscopy. Hum. Genet. 54, 405–408 (1980)
Moens, P.B.: The fine structure of meiotic chromosome polarization and pairing in Locusta migratoria spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 28, 1–25 (1969)
Monesi, V.: Autoradiographic study of DNA synthesis and the cell cycle in spermatogonia and spermatocytes of mouse testis using tritiated thymidine. J. Cell Biol. 14, 1–18 (1962)
Moses, M.J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus). I. Morphology of the autosomal complement in spread preparations. Chromosoma (Berl.) 69, 99–125 (1977a)
Moses, M.J.: Microspreading and the synaptonemal complex in cytogenetic studies. Chromosomes today 6, 71–82 (1977b)
Oakberg, E.F.: A description of spermiogenesis in the mouse and its use in analysis of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium and germ cell renewal. Amer. J. Anat. 99, 391–413 (1956a)
Oakberg, E.F.: Duration of spermatogenesis in the mouse and timing of stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. Amer. J. Anat. 99, 507–516 (1956b)
Oud, J.L.: The sequence of changes in chromosome morphology during meiotic prophase I. (Abstract of the workshop on chromosomal aspects of male sterility in mammals). Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 27, 209–210 (1980)
Oud, J.L., Jong, J.H. de, Rooij, D.G. de: A sequential analysis of meiosis in the male mouse using a restricted spermatocyte population obtained by a hydroxyurea/triaziquone treatment. Chromosoma (Berl.) 71, 237–248 (1979)
Oud, J.L., Reutlinger, A.H.H.: Chromosome behaviour during early meiotic prophase of mouse primary spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 81, 569–578 (1981)
Pathak, S., Lau, Y.F., Drwinga, H.L.: Observations on the synaptonemal complex in Armenian hamster spermatocytes by light microscopy. Chromosoma (Berl.) 73, 53–60 (1979)
Sheridan, W.F., Barnett, R.J.: Cytochemical studies on chromosome ultrastructure. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 27, 216–229 (1969)
Solari, A.J.: The morphology and ultrastructure of the sex vesicle in the mouse. Exp. Cell Res. 36, 160–168 (1964)
Solari, A.J.: The spatial relationship of the X and Y chromosomes during meiotic prophase in mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 29, 217–236 (1970)
Solari, A.J., Counce, S.J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in Melanoplus differentialis. J. Cell Sci. 26, 229–250 (1977)
Tres, L.L.: Extensive pairing of the XY bivalent in mouse spermatocytes as visualized by whole-mount electron microscopy. J. Cell Sci 25, 1–15 (1977)
Tres, L.L.: Side-by-side pairing of the XY bivalent in spermatocytes and the ubiquity of the H-Y locus. Arch. Androl. 2, 101–108 (1979)
Westergaard, M., Wettstein, D. von: The synaptinemal complex. Ann. Rev. Genet. 6, 71–110 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dietrich, A.J.J., Mulder, R.J.P. A light microscopic study of the development and behaviour of the synaptonemal complex in spermatocytes of the mouse. Chromosoma 83, 409–418 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327362
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327362