Abstract
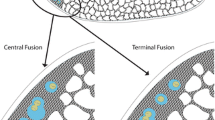
Somatic chromosomes of both sexes and chromosome behaviour during spermatogenesis were studied in the aphid Schoutedenia lutea (van der Goot). Four long but unequal chromosomes in females were interpreted as X chromosomes (X1X1X2X2) with one member of an autosome pair attached to one X1, and the other member to one X2, so that the four long chromosomes were actually X1+A, X1, X2+A, X2. Males (normally XO in aphids) received X chromosomes corresponding in relative length to the two longest (X1+A, X2+A) in females. During spermatogenesis parallel pairing occurred in prophase 1 and the X1 and X2 chromosomes became associated via their autosomal segments. In anaphase I, the autosomal segment became detached from one of the X chromosomes and entered the non-viable (non-X-bearing) spermatocyte, while the viable spermatocyte received both X1 and X2 (either one of which still carried an autosome) and the haploid set of free autosomes. The consequences for sex determination and zygote formation of this unusual system are discussed; a stable chromosomal constitution for the zygote can be achieved only at the expense of considerable gamete wastage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackman RL (1976) Cytogenetics of two species of Euceraphis (Homoptera, Aphididae). Chromosoma 56:393–408
Blackman RL (1985) Spermatogenesis in the aphid Amphorophora tuberculata (Homoptera, Aphididae). Chromosoma 92:357–362
Blackman RL (1987) Reproduction, cytogenetics and development. In: Minks AK, Harrewijn P (eds) Aphids. Their biology, natural enemies and control, vol A. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 163–195
Blackman RL (1988) Stability of a multiple X-chromosome system and associated B chromosomes in birch aphids (Euceraphis spp.; Homoptera: Aphididae). Chromosoma 96:318–324
Blackman RL, Hales DF (1986) Behaviour of X-chromosomes during growth and maturation of parthenogenetic eggs of Amphorophora tuberculata (Homoptera, Aphididae), in relation to sex determination. Chromosoma 94:59–64
Brown SW, Nelson-Rees WA (1961) Radiation analysis of a lecanoid system. Genetics 46:983–1007
Chauhan NS (1977) Gene expression and transmission in Kerria lacca (Kerr). Heredity 38:155–159
Hales DF, Carver M (1976) A study of Schoutedenia lutea (van der Goot, 1917) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Aust Zool 19:85–94
Hales DF, Lardner RM (1988) Genetic evidence for the occurrence of a new species of Neophyllaphis Takahashi (Homoptera, Aphididae) in Australia. J Aust Entomol Soc 27:81–85
Hughes-Schrader S (1948) Cytology of coccids (Coccoidea: Homoptera). Adv Genet 2:127–203
Orlando E (1974) Sex determination in Megoura viciae Buckton (Homoptera, Aphididae). Monitore Zool Ital (NS) 8:61–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hales, D.F. The chromosomes of Schoutedenia lutea (homoptera, aphidoidea, greenideinae), with an account of meiosis in the male. Chromosoma 98, 295–300 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327316
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327316