Abstract
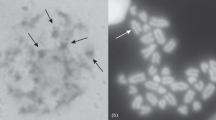
The behavior of the X and Y chromosomes in somatic and testicular cells of the sand rat (P. obesus) has been investigated with light and electron-microscope procedures. The Y chromosome has been identified as the fourth longest of the complement, both by C-banding and by its meiotic behavior. The X chromosome is the longest of the complement and carries two major C-heterochromatic blocks, one in the distal part of the long arm and the other forming most of the short arm. During presynaptic stages in spermatocytes, separate C-heterochromatic blocks, representing the sex chromosomes, are observed in the nuclei. An XY body is regularly formed at pachytene. During first meiotic metaphase the X and Y chromosomes show variable associations, none of them chiasmatic. Second meiotic metaphases contain, as in other mammals, a single sex chromosome, suggesting normal segregation between the X and the Y. — Electron microscopic observations of the autosomal synaptonemal complexes (SCs) and the single axes of the X and Y chromosomes during pachytene permit accurate, statistically significant identification of each of the largest chromosomes of the complement and determination of the mean arm ratios of the X and Y axes. The X and Y axes always lie close to each other but do not form a SC. The ends of the X and Y axes are attached to the nuclear envelope and associate with each other in variable ways, both autologously (X with X or Y with Y) and heterologously (X with Y), with a tendency to form a maximum number (four) of associated ends. Analysis of 36 XY pairs showed no significant preference for any single specific attachment between arm ends. The eighth longest autosomal bivalent is frequently partially asynaptic during early pachytene, and only at that time is often near or touching one end of the X axis. — It is concluded that while axis formation and migration of the axes along the plane of the nuclear envelope proceed normally in the X and Y chromosomes, true synapsis (with SC formation) does not occur because the pairing region of the X chromosome has probably been relocated far from the chromosome termini by the insertion of distal C-heterochromatic blocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley, T.: Chromosomal order in nuclei (Abstract). J. Cell Biol. 70, 395a (1976)
Ashley, T., Wagenaar, E.B.: Telomeric associations of gametic and somatic chromosomes in diploid and autotetraploid Ornithogalum virens. Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 16, 61–76 (1974)
Counce, S.J., Meyer, G.F.: Differentiation of the synaptonemal complex and the kinetochore in Locusta spermatocytes studied by whole mount electron microscopy. Chromosoma (Berl.) 44, 231–253 (1973)
Evans, E.P., Breckon, G., Ford, C.E.: An air-drying method for meiotic preparations from mammalian testes. Cytogenetics 3, 289–294 (1964)
Fredga, K.: Unusual sex chromosome inheritance in mammals. Phil. Trans, roy. Soc. Lond., B 259, 15–36 (1970)
Gillies, C.B.: Synaptonemal complex and chromosome structure. Ann. Rev. Genet. 9, 91–109 (1975)
Hinton, T.: A study of chromosome ends in salivary gland nuclei of Drosophila. Biol. Bull. 88, 144–165 (1945)
Hsu, T.C., Benirschke, K.: An atlas of mammalian chromosomes. 4, Folio 170. Berlin-HeidelbergNew York: Springer 1970
Hsu, T.C., Cooper, J.E., Mace, M.L., Brinkley, B.R.: Arrangement of centromeres in mouse cells. Chromosoma (Berl.) 34, 73–87 (1971)
John, B., Lewis, K.: The meiotic system. Protoplasmatologia VI/F1. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer (1965)
Kofman-Alfaro, S., Chandley, A.C.: Meiosis in the male mouse. An autoradiographic investigation. Chromosoma (Berl.) 31, 404–420 (1970)
Lee, M.R.: A widely applicable technique for direct processing of bone marrow for chromosomes of vertebrates. Stain Technol. 44, 155–157 (1969)
McClung, C.E.: Synapsis and related phenomena in Mecostethus and Leptysma (Orthoptera). J. Morph. 43, 181–265 (1927)
Moens, P.B.: The fine structure of meiotic chromosome polarization and pairing in Locusta migratoria spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 28, 1–25 (1969)
Moses, M.J.: Synaptinemal complex. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2, 363–412 (1968)
Moses, M.J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus) I. Morphology of the autosomal complement in spread preparations. Chromosoma (Berl.) 60, 99–125 (1977a)
Moses, M.J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus) II. Morphology of the XY pair in spread spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 60, 127–137 (1977b)
Moses, M.J.: The Synaptonemal complex and meiosis. Proc. 6th Ann. ICN-UCLA Symp. molec. cell. Biol., molec. hum. cytogenetics. New York: Academic Press (in press) 1977c
Moses, M.J., Counce, S.J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spreads of mammalian spermatocytes. In: Mechanisms in recombination (R.F. Grell, ed.), pp. 385–390. New York: Plenum Publ. Corp. 1974
Moses, M.J., Counce, S.J., Paulson, D.F.: Synaptonemal complex complement of man in spreads of spermatocytes, with details of the sex chromosome pair. Science 187, 363–365 (1975)
Moses, M.J., Slatton, G.H., Gambling, T.M., Starmer, C.F.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus). III. Quantitative evaluation. Chromosoma (Berl.) 60, 345–375 (1977)
Ohno, S., Beçak, W., Beçak, M.L.: X-autosome ratio and the behavior pattern of individual X chromosomes in placental mammals. Chromosoma (Berl.) 15, 14–30 (1964)
Ohno, S., Kaplan, D.W., Kinosita, R.: On the end-to-end association of the X and Y chromosomes of Mus musculus. Exp. Cell Res. 18, 282–290 (1959)
Pathak, S., Hsu, T.C.: Chromosomes and DNA of Mus. The behavior of constitutive heterochromatin in spermatogenesis of M. dunni. Chromosoma (Berl.) 57, 227–234 (1976)
Rasmussen, S.W.: The meiotic prophase in Bombyx mori females analyzed by three-dimensional reconstructions of Synaptonemal complexes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 54, 245–293 (1976)
Schrader, F.: The formation of tetrads and the meiotic mitoses in the male of Rhytidolomia senilis Say (Hemiptera Heteroptera). J. Morph. 61, 123–136 (1940)
Smith, A.G., Hackel, D.B., Schmidt-Nielsen, K.: Chromosomes of the sand rat (Psammomys obesus). Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 8, 756–758 (1966)
Solari, A.J.: The morphology and ultrastructure of the sex vesicle in the mouse. Exp. Cell Res. 36, 160–168 (1964)
Solari, A.J.: The spatial relationship of the X and Y chromosomes during meiotic prophase in mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 29, 217–236 (1970)
Solari, A.J.: The behavior of the XY pair in mammals. Int. Rev. Cytol. 38, 273–317 (1974a)
Solari, A.J.: The relationship between chromosomes and axes in the chiasmatic XY pair of the Armenian hamster (Cricetulus migratorius). Chromosoma (Berl.) 48, 89–106 (1974b)
Solari, A.J., Bianchi, N.: The synaptic behavior of the X and Y chromosomes in the marsupial Monodelphis dimidiata. Chromosoma (Berl.) 52, 11–25 (1975)
Solari, A.J., Counce, S.J.: Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in Melanoplus differentialis. J. Cell Sci. (in press, 1977)
Solari, A.J., Tres, L.L.: The three-dimensional reconstruction of the XY chromosomal pair in human spermatocytes. J. Cell Biol. 45, 43–53 (1970)
Sumner, A.T.: A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 75, 304–306 (1972)
Ure∼na, F., Solari, A.J.: The three-dimensional reconstruction of the XY pair during pachytene in the rat (Rattus norvegiens). Chromosoma (Berl.) 30, 258–268 (1970)
Wagenaar, E.B.: End-to-end attachments in mitotic interphase and their possible significance in meiotic chromosome pairing. Chromosoma (Berl.) 26, 410–426 (1969)
Wilson, E.B.: The cell in development and heredity, 3rd edit. New York: Macmillan 1925
Zenzes, M.T., Wolf, U.: Paarungsverhalten der Geschlechtschromosomen in der männlichen Meiose von Microtus agrestis. Chromosoma (Berl.) 33, 41–47 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solari, A.J., Ashley, T. Ultrastructure and behavior of the achiasmatic, telosynaptic XY pair of the sand rat (Psammomys obesus). Chromosoma 62, 319–336 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327031
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327031