Abstract
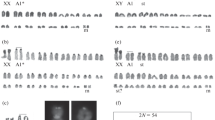
Karyotypes of 13 Rattus species collected in Asia and Oceania were analysed with special interest to karyotype evolution and species differentiation. They were classified into three groups according to their karyotype similarity. Four species (R. annandalei, R. exulans, R. muelleri and R. norvegicus) with 2n=42 and a karyotype similar to some of the polymorphic karyotypes in the Asian black rats (R. rattus) are classified into the first group. Pericentric inversion of some acrocentrics seemed to have caused the differentiation of these species. The other four species (R. bowersii, R. fuscipes, R. leucopus and R. conatus) with similar karyotypes as the above group, but lower chromosome numbers than 2n=42 are classified into the second group. Robertsonian fusion in some acrocentrics observed in the first group are suggested to have caused the development of the species in this group. The remaining four species (R. sabanus, R. canus, R. huang and R. niviventer) with karyotypes markedly different from the above two in having a fewer number of small metacentrics are classified into the third group. They seemed to be more primitive karyotypes than the other Rattus species. By the comparison between the polymorphic karyotypes in the black rat, and karyotypes in its related species it was suggested that the former had occurred as primary events to the differentiation of the latter. Parallelism between the karyotype evolution and the species differentiation was discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badr, F. M., Badr, R.: The somatic chromosomes of a wild population of rats: Numerical polymorphism. Chromosoma (Berl.) 30, 465–475 (1970).
Bianchi, N. O., Paulette-Vanrell, J., Vidal Rioja, L. A.: Complements with 38 chromosomes in two South American populations of Rattus rattus. Experientia (Basel) 25, 1111–1112 (1969).
Capanna, E., Civitelli, M. V., Nezer, R.: The karyotype of the black rat (Rattus rattus L.).Another population with a 38-chromosome complement. Experientia (Basel) 26, 422–425 (1970).
Gropp, A., Marshall, J., Flatz, G., Olbridi, M., Manyanondha, K., Santadusit, A.: Chromosomenpolymorphismus durch überzählige Autosomen. Beobachtungen an der Hausratte (Rattus rattus). Z. Säugetierk. 35, 363–371 (1970a).
Gropp, A., Tettenborn, U., Lehmann, E. von: Chromosomenvariation von Robert-sonischen Typus bei der Tabakmaus, M.poschiavinus, und ihren Hybriden mit der Laboratoriumsmaus. Cytogenetics 9, 9–23 (1970b).
Hsu, T. C., Arvighi, F. E.: Chromosomes of Peromyscus (Rodentia, Cricetidae). Cytogenetics 7, 417–446 (1958).
Malecha, S. P., Tamalin, R. B.: Plasma transferrins in three species of Rattus on Pacific islands. Amer. Naturalist 103, 664–669 (1969).
Martin, J. H. D.: Chromosomes of some native Muridae in Queensland. Queensland J. Agric. and Anim. Sci. 26, 125–141 (1969).
Masuji, H.: Autosomal polymorphism in Donryu strain rat. Acta med. Okayama 24, 81–91 (1970).
Matano, Y.: Mammalian spermatozoa [in Japanese]. Cell (Tokyo) 3, 43–51 (1971).
Matthey, R.: Cytologie comparée et polymorphisme chromosomique chez des Mus africains appartenant aux groupes bufo-triton et minutoides (Mammalia-Rodentia). Cytogenetics 2, 290–322 (1963).
Matthey, R.: Une inversion péricentrique à l'origine d'un polymorphisme chromosomique non-Robertsonian dans une population de Mastomys (Rodentia-Muridae). Chromosoma (Berl.) 18, 188–200 (1966).
Moriwaki, K., Tsuchiya, K., Yosida, T. H.: Genetic polymorphism in the serum transferrin of Rattus rattus. Genetics 63, 193–199 (1969).
Nadler, C. F.: Chromosomal evolution in rodents. In: Comparative mammalian cytogenetics (K. Benirschke, ed.), p. 272–309. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1969.
Ohno, S., Weiler, C., Poole, J., Christian, L., Stenius, C.: Autosomal polymorphism due to pericentric inversions in the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) and some evidence of somatic segregation. Chromosoma (Berl.) 18, 177–187 (1966).
Tate, G. H. H.: Some Muridae of the Indo-Australian region. Bull. Amer. Museum Nat. Hist. 72, 501–728 (1936).
Weber, M.: Die Säugetiere, vol.2. Jena: G. Fischer 1924.
Yong, H. S.: Karyotype of four Malayan rats (Muridae, genus Rattus Fischer). Cytologia (Tokyo) 33, 174–180 (1968).
Yong, H. S.: Karyotypes of Malayan Rats (Rodentia-Muridae, genus Rattus Fischer). Chromosoma (Berl.) 27, 245–267 (1969).
Yosida, T. H., Amano, K.: Autosomal polymorphism in laboratory bred and wild Norway rats, Rattus norvegicus, found in Misima. Chromosoma (Berl.) 16, 658–667 (1965b).
Yosida, T. H., Nakamura, A., Fukaya, T.: Chromosomal polymorphism in Rattus rattus (L.) collected in Kusudomari and Misima. Chromosoma (Berl.) 16, 70–78 (1965a).
Yosida, T. H., Sagai, T.: Banding pattern analysis of polymorphic karyotypes in the black rat by a new differential staining technique. Chromosoma (Berl.) 37, 387–394 (1972).
Yosida, T. H., Tsuchiya, K., Imai, H. T., Moriwaki, K.: New chromosome types of the black rat, Rattus rattus, collected in Oceania and hybrids between Japanese and Australian rats. Jap. J. Genet. 44, 89–91 (1969).
Yosida, T. H., Tsuchiya, K., Moriwaki, K.: Frequency of chromosome polymorphism of Rattus rattus collected in Japan. Chromosoma (Berl.) 33, 30–40 (1971a).
Yosida, T. H., Tsuchiya, K., Moriwaki, K.: Karyotype differences of black rats, Rattus rattus, collected in various localities of East and Southeast Asia and Oceania. Chromosoma (Berl.) 33, 252–267 (1971b).
Yosida, T. H., Tsuchiya, K., Moriwaki, K.: Karyotypes and serum transferrin patterns of hybrids between Asian and Oceanian black rats, Rattus rattus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 34, 40–50 (1971c).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 874 from the National Institute of Genetics, Japan. Supported by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education of Japan (No. 92159 and 92332).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yosida, T.H. Evolution of karyotypes and differentiation in 13 Rattus Species . Chromosoma 40, 285–297 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326182
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326182