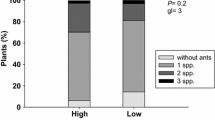
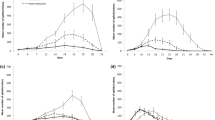
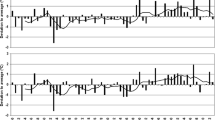
Summary
I used a factorial experiment repeated in two years to assess the relative effects of natural enemy attack, interspecific competition, and water availability to the host plant, and of interactions among these factors, on the population dynamics of the aphid Aphis varians feeding on fireweed (Epilobium angustifolium). The impact of a suite of coccinellid and syrphid predators emerged as the predominant factor affecting the success of aphid colonies: colonies protected from natural enemies grew in size at a rate of ten percent per day, were only one tenth as likely to go extinct, and produced over ten times more dispersing alates. In contrast, I found only minor effects of removing flea beetles, the most abundant herbivore with which A. varians colonies cohabit fireweed stems, and of supplementing water availability to fireweed host plants, in spite of a significant effect of watering frequency on aphid growth in the green-house. There was no evidence of significant two- or three-way interactions among factors. Hence, despite the potential complexity of the food web in which it is embedded, the dynamics of A. varians appears to be driven predominantly by a single factor, i.e. interactions with natural enemies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addicott JF (1978a) Niche relationships among species of aphids feeding on fireweed. Can J Zool 56: 1837–1841
Addicott JF (1978b) Competition for mutualists: aphids and ants. Can J Zool 56: 2093–2096
Addicott JF (1979) A multispecies aphid-ant association: density depedence and species-specific effects. Can J Zool 57: 558–569
Bernays EA, Graham M (1988) On the evolution of host specificity in phytophagous arthropods. Ecology 69: 886–893
Cushman JH, Addicott JF (1989) Intra- and interspecific competition for mutualists: ants as a limited and limiting resource for aphids. Oecologia 79: 315–321
Edson JL (1985) The influences of predation and resource subdivision on the coexistence of goldenrod aphids. Ecology 66: 1736–1743
Faeth SH (1985) Host leaf selection by leaf miners: interactions among three trophic levels. Ecology 66: 870–875
Faeth SH (1986) Indirect interactions between temporally separated herbivores mediated by the host plant. Ecology 67: 479–494
Faeth SH (1987) Community structure and folivorous insect outbreaks: the roles of vertical and horizontal interactions. In: Barbosa P, Schultz JC (eds) Insect Outbreaks. Academic Press, New York, pp 135–171
Gibson C, Visser M (1982) Interspecific competition between two field populations of grass-feeding bugs. Ecol Ent 7: 61–67
Hairston NG, Smith FE, Slobodkin L (1960) Community structure, population control, and competition. Am Nat 44: 421–425
Harrison S, Karban R (1986) Effects of an early-season folivorous moth on the success of a later-season species, mediated by a change in the quality of the shared host, Lupinus arboreus Sims. Oecologia 69: 354–359
Huang C, Sih A (1991) Experimental studies on direct and indirect interactions in a three trophic-level stream system. Oecologia 85: 530–536
Karban R (1986) Interspecific competition between folivorous insects on Erigeron glaucus. Ecology 67: 1063–1072
Karban R (1989) Community organization of Erigeron glaucus folivores: effects of competition, predation, and host plant. Ecology 70: 1028–1039
Karban R, Carey J (1984) Induced resistance of cotton seedlings to mites. Science 225: 53–54
Kareiva P, Sahakian R (1990) Tritrophic effects of a simple architectural mutation in pea plants. Nature 345: 433–434
Lawton JH, McNeill J (1979) Between the devil and the deep blue sea: on the problem of being an herbivore. Symp Br Ecol Soc 22: 223–244
Lawton JH, Strong DR (1981) Community patterns and competition in folivorous insects. Am Nat 118: 317–338
McClure MS, Price PW (1975) Competition among sympatric Erythroneura leafhoppers (Homoptera: Cicadellidae) on American sycamore. Ecology 56: 1388–1397
Michels GJ, Undersander DJ (1986) Temporal and spatial distribution of the greenbug (Homoptera: Aphidae) on sorghum in relation to water stress. J Econ Ent 79: 1221–1225
Morin PJ (1986) Interactions between intraspecific competition and predation in an amphibian predator prey system. Ecology 67: 713–720
Morin PJ, Lawler SP, Johnson EA (1988) Competition between aquatic insects and vertebrates: interaction strength and higher order interactions. Ecology 69: 1401–1409
Morris WF, Wiser SD, Klepetka B (1992) Causes and consequences of spatial aggregation in the phytophagous beetle Altica tombacina. J An Ecol 61: 49–58
Murdoch WW, Walde SJ (1989) Analysis of insect population dynamics. Symp Br Ecol Soc 30: 113–140
Price PW, Bouton CE, Gross P, McPheron BA, Thompson JN, Weis AE (1980) Interactions among three trophic levels: influence of plants on interactions between insect herbivores and natural enemies. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 11: 41–65
Price PW, Clancy KM (1986) Interactions among three trophic levels: gall size and parasitoid attack. Ecology 67: 1593–1600
Service P, Lenski R (1982) Aphid genotypes, plant phenotypes, and genetic diversity: a demographic analysis of experimental data. Evolution 36: 1276–1282
Seifert RP, Seifert FH (1976) A community matrix analysis of Heliconia insect communities. Am Nat 110: 461–483
Smiley JT, Horn JM, Rank NE (1985) Ecological effects of salicin at three trophic levels: new problems from old adaptations. Science 229: 649–651
Stamp NE (1984) Herbivory, timing of defoliation, and plant availability: the effect of checkerspot caterpillars and sawfly larvae on their host plants. Oecologia 63: 275–280
Starks KJ, Muniappan R, Eikenbary RD (1972) Interaction between plant resistance and parasitism against the greenbug on barley and sorghum. Ann Ent Soc Am 65: 650–655
Stiling PD (1980) Competition and coexistence among Eupteryx leafhoppers (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) occurring on stinging nettles (Urtica dioica L.). J An Ecol 49: 793–805
Stiling PD, Strong DR (1983) Competition among Spartina stem borers, by means of murder. Ecology 64: 770–778
Stiling PD, Strong DR (1984) Experimental density manipulation of stem-boring insects: some evidence for interspecific competition. Ecology 65: 1683–1685
Strauss SY (1991a) Direct, indirect, and cumulative effects of three native herbivores on a shared host plant. Ecology 72: 543–558
Strauss SY (1991b) Indirect effects in community ecology: their definition, study, and importance. Trends Ecol Evol 6: 206–209
Strong DR, Lawton JH, Southwood R (1984) Insects on Plants. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, Ch. 5
Sugg PM (1989) Arthropod Populations at Mount St. Helens: Survival and Revival. Ph.D. thesis, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA
Sumner LC, Eikenbarry RD, Johnson RC (1986) Survival and reproduction of Rhopalosiphum maidis (Fitch) (Homoptera: Aphidae) on winter wheat, during simulated drought stress. J Kansas Ent Soc 59: 561–563
Turchin P, Kareiva P (1989) Aggregation in Aphis varians: an effective strategy for reducing predation risk. Ecology 70: 1008–1016
Van Buskirk J (1988) Interactive effects of dragonfly predation in experimental pond communities. Ecology 69: 857–867
Wearing CH (1967) Effects of water stress in host plants on the fecundity of Myzus persicae and Brevicoryne brassicae. Nature 213: 1052–1053
Wearing CH, van Embden HF (1967) Effects of water stress n host plants on infestation by Aphis fabae, Myzus persicae, and Brevicoryne brassicae. Nature 213: 1051–1052
Weis AE, Abrahamson WG (1986) Evolution of host-plant manipulation by gall makers: ecological and genetic factors in the Solidago-Eurosta system. Am Nat 127: 681–695
Wilbur HM (1972) Competition, predation, and the structure of the Ambystoma-Rana sylvatica community. Ecology 57: 3–21
Wilbur HM (1987) Regulation of structure in complex systems: experimental temporary pond communities. Ecology 68: 1437–1452
Wilbur HM, Fauth JE (1990) Experimental aquatic food webs: interactions between two predators and two prey. Am Nat 135: 176–204
Wilkinson L (1989) SYSTAT: The System for Stastics. SYSTAT Inc., Evanston, IL
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morris, W.F. The effects of natural enemies, competition, and host plant water availability on an aphid population. Oecologia 90, 359–365 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317692
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317692