Summary
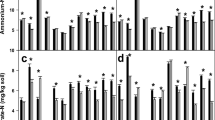
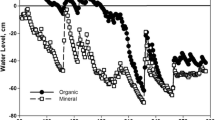
The predominance of annual species in the rangelands of southwestern Spain is not due only to climatic factors but is also strongly influenced by grazing management. Manipulating the grazing system in an experimental plot gave a vegetation structure with patches of annual grasses (mainly Vulpia ssp. and Bromus hordeaceus) and patches of perennial grasses (mainly Phalaris aquatica). This vegetation change allowed us to test the hypothesis that life-cycle differences between annual and perennial grasses affect soil nitrogen availability and plant uptake. Nitrogen availability, measured by in situ incubation, and nitrogen uptake were measured through the growing period (October to June). Amounts of in situ mineralized nitrogen over the whole growth phase were more important for soils supporting perennials (37 ppm) than for soils supporting annuals (27 ppm). The difference between the mineral nitrogen produced in situ and the mineral nitrogen accumulated during the same time in the soil allowed an estimation of the maximum mineral nitrogen quantity which can be taken up by the vegetation during each incubation period. The quantities accumulated over the year were 47 and 38 ppm (or 103 and 83 kg/ha) for soils supporting perennials and annuals respectively. For the same period, amounts of nitrogen immobilized in biomass production were 90 and 70 kg/ha for perennials and annuals respectively. During the autumn, a large proportion of mineral nitrogen was leached from soils supporting annual plants which had only just commenced germination. By contrast, the ability to use mineral nitrogen as soon as autumn rains occurred gave a competitive advantage to the perennial species, but only if they were protected from grazing during this period. The higher mineralization and use of this nitrogen reserve by perennials indicates that they made more efficient use of nitrogen resources than annuals, and validate the initial hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MA, Attiwill PM (1986) Nutrient cycling and nitrogen mineralization in eucalypt forests of south-eastern Australia. II Indices of nitrogen mineralization. Plant Soil 92:341–362
Adams MA, Polglase PJ, Attiwill PM, Weston CJ (1989) In situ studies of nitrogen mineralization and uptake in forest soils; some comments on methodology. Soil Biol Biochem 21:423–429
Alexander M (1971) Biochemical ecology of micro-organisms. Ann Rev Microbiol 25:361–392
Billès G. Lossaint P, Cortez J (1971) L'activité biologique des sols dans les écosystèmes méditerranéens. II Minéralisation de l'azote. Rev Ecol Biol Sol 8:533–552
Billès G, Gandais Riollet N, Bottner P (1986) Effet d'une culture de graminées sur la décomposition d'une litière végétale marquée au 14C et 15N, dans le sol, en conditions contrôlées. Acta Oecol-Oecol Plant 7:273–286
Birch LW (1960) Nitrification in soils after different periods of dryness. Plant Soil 12:81–96
Biswell HH (1956) Ecology of California grasslands. J Range Manag 9:19–24
Bottner P, Mneime G, Billès G (1984) Réponse de la biomasse microbienne à l'adjonction au sol de matériel végétal marqué au 14C: rôle des racines vivantes. Soil Biol Biochem 16:305–314
Cañas R, Aguilar C, Paladines O, Muñoz G (1982) Biomass production and utilization of natural pastures in the Chilean Mediterranean Ecosystems. In: Conrad CE, Oechel WC (eds) Proc Symp Dynamics Manag Medit Type Ecosystems, Gen Techn Rep PSW-58, Calif Pac Southwest For Range Exp Stion, For Serv USDA, pp 34–41
Charlot (1961) Les méthodes de la chimie analytique. Masson, Paris
Clarholm M (1985) Interactions of bacteria, protozoa and plants leading to mineralisation of soil nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 17:181–187
Curl EA, Truelove B (eds) (1986) The rhizosphere. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Daget P (1977) Le bioclimat méditerranéen: analyse des formes climatiques par le système d'Emberger. Vegetatio 34:87–103
Davis EA (1984) Conversion of Arizona chaparral to grass increases water yield and nitrate loss. Water Resour Res 20:1643–1650
Davis EA (1987) Chaparral conversion to increase streamflow in Arizona: Sequential treatments extend duration of nitrate loss to stream water. Forest Sci 33:89–103
Djellali N, Billès G, Bounaga N, Lossaint P (1985) Etude de l'activité biologique des sols de la steppe à alfa d'Algérie. Minéralisation du carbone et de l'azote. Acta Oecol-Oecol Plant 6:289–307
Dommergues Y, Mangenot F (1970) Ecologie microbienne du sol. Masson, Paris
Gulmon SL (1977) A comparative study of the grassland of California and Chile. Flora 166:261–278
Haynes RJ (1986) Origin, distribution, and cycling of nitrogen in terrestrial ecosystems. In: Haynes RJ (ed) Mineral nitrogen in the soil-plant system. Academic Press, London, pp 1–51
Jackson LE, Strauss RB, Firestone MK, Bartolome JW (1988) Plant and soil nitrogen dynamics in California annual grassland. Plant Soil 110:9–17
Joffre R (1987) Contraintes du milieu et réponses de la végétation herbacée dans les dehesas de la Sierra Norte (Andalousie, Espagne). Thèse Univ Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc, Montpellier, p 186
Joffre R, Leiva Morales MJ, Rambal S, Fernandez Ales R (1987a) Dynamique racinaire et extraction de l'eau du sol par des graminées pérennes et annuelles méditerranéennes. Acta Oecol-Oecol Plant 8:181–194
Joffre R, Vacher J, de Los Llanos C, Long G (1987b) The dehesa: an agrosilvopastoral system of the mediterranean region with special reference to the Sierra Morena area of Spain. Agroforestry Systems 6:71–96
Joffre R, Rambal S (1988) Soil water improvement by trees in the rangelands of southern Spain. Acta Oecol-Oecol Plant 9:405–422
Kieft TL, Soroker E, Firestone MK (1987) Microbial biomass response to a rapid increase in water potential when dry soil is wetted. Soil Biol Biochem 19:119–126
Klein DA, Frederick BA, Biondini M, Trlica MJ (1988) Rhizosphere microorganisms effects on soluble amino acids, sugars and organic acids in the root zone of Agropyron cristatum. A. smithii and Bouteloua gracilis. Plant Soil 110:19–25
Lemée G (1967) Investigations sur la minéralisation de l'azote et son évolution actuelle dans les humus forestiers in situ. Oecol Plant 2:285–324
McGill WB, Hunt HW, Woodmansee RG, Reuss JO (1981) Phoenix —a model of the dynamics of carbon and nitrogen in a grassland soil. In: Clark FE, Rosswall T (eds) Terrestrial nitrogen cycles. Ecol Bull (Stockholm) 33:49–115
Nadelhoffer KJ, Aber JD (1983) Leaf-litter production and soil organic matter dynamics along a nitrogen-availability gradient in southern Wisconsin (USA). Canad J For Res 13:12–21
Nadelhoffer KJ, Aber JD, Melillo JM (1984) Seasonal patterns of ammonium and nitrate uptake in nine temperate forest systems. Plant Soil 80:321–335
O'Connor KF (1983) Nitrogen balances in natural grasslands and extensively managed grassland systems. NZ J Ecol 6:1–18
Pastor J, Aber JD, McClaugherty CA, Melillo JM (1984) Above ground production and N and P cycling along a nitrogen mineralization gradient on Blackhawk Island, Wisconsin. Ecology 65:256–268
Pastor J, Stillwell MA, Tilman D (1987) Nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in four Minnesota old fields. Oecologia 71:481–485
Paul EA, Juma NG (1981) Mineralisation and immobilisation of soil nitrogen by microorganisms. In: Clark FE, Rosswall T (eds) Terrestrial nitrogen cycles. Ecol Bull (Stockholm) 33: 179–195
Paustian K (1987) Theoretical analyses of C and N cycling in soil. Ph D Thesis, Dep Ecol and Envir Res, Report 30, Swedish Univ Agr Sciences, Uppsala
Raison RJ, Connell MJ, Khanna PK (1987) Methodology for studying fluxes of soil mineral-N in situ. Soil Biol Biochem 19:521–530
Rossiter RC (1966) Ecology of the mediterranean annual type pasture. Adv Agron 18:1–56
Rosswall T (1976) The internal nitrogen cycle between microorganisms, vegetation and soil. Ecol Bull (Stockholm) 22:157–167
Sallih Z, Bottner P (1988) Effect of wheat (Triticum aestivum) roots on mineralization rates of soil organic matter. Biol Fert Soils 7:67–70
Sarkar AN, Wyn Jones RG (1980) Rhizosphere and its effect on the nutrients availability of plants—A review. Agric Rev 1:1–18
Scheffe R (1959) The analysis of variance. Wiley & Sons, New York
Schimel D, Stillwell MA, Woodmansee RG (1985) Biogeochemistry of C, N and P in a soil catena of the shortgrass steppe. Ecology 66:276–282
Vaughn CH, Center DM, Jones MB (1986) Seasonal fluctuations in nutrient avaibility in some northern California annual range soils. Soil Sci 141:43–51
Vitousek PM, Matson PA (1985) Disturbance, nitrogen availability and nitrogen losses in an intensively managed loblolly pine plantation. Ecology 66:1360–1376
Vlek PLG, Fillery IRP, Burford JR (1981) Accession, transformation and loss of nitrogen in soils of the arid region. In: Monteith J, Webb C (eds) Soil Water and Nitrogen in meditteranean type environments. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences I. M Niijhoff/Dr. W Junk Publ, The Hague, pp 133–176
Westermann DT, Crothers SE (1980) Measuring soil nitrogen mineralization under field conditions. Agron J 72:1009–1012
Woodmansee RG, Duncan DA (1980) Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics and budgets in annual grasslands. Ecology 61:893–904
Woodmansee RG, Vallis I, Mott JJ (1981) Grassland nitrogen. In: Clark FE, Rosswall T (eds) Terrestrial nitrogen cycles. Ecol Bull (Stockholm) 33, pp 443–462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joffre, R. Plant and soil nitrogen dynamics in mediterranean grasslands: a comparison of annual and perennial grasses. Oecologia 85, 142–149 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317355
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317355