Summary
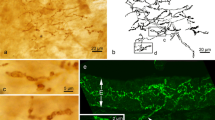
The serous lingual glands of von Ebner secrete lingual lipase, an enzyme that begins fat digestion in the stomach. The objective of this study was to characterize the neuromodulators in the rat tongue and von Ebner glands using immunocytochemical techniques. Rat lingual tissues were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin and sectioned at 4 μm for light microscopic studies. Immunocytochemical localization of neuromodulators was performed with monospecific anti-rat neuromodulator IgG or control (preimmune) IgG as the primary antibody, using the peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) technique. No staining was seen with control antirat IgG. Immunospecific staining for vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), tyrosine hydroxylase and choline acetyltransferase (CHAT) was observed in nerves in the tongue, and cells containing immunospecific staining for serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) were seen in the stroma between the lingual glands. Selected cells in the serous glands stained positively for the presence of substance P and somatostatin. Adrenergic, VIP-containing and cholinergic nerves appear to innervate the tongue and serous glands. Substance P and somatostatin were identified in cells of the lingual serous glands and may be additional local modulators regulating lingual lipase release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosshard A, Chery-Croze S, Cuber JC, Dechelette MA, Berger F, Chayvialle JA (1989) Immunocytochemical study of peptidergic structures in Brunner's glands. Gastroenterology 97:1382–1388
DeCamilli P, Vitadello M, Canevini MP, Zanoni R, Jahn R, Gorio A (1988) The synaptic vesicle proteins synapsin I and synaptophysin (protein P38) are concentrated both in efferent and afferent nerve endings of the skeletal muscle. J Neurosci 8:1625–1631
Field RB, Hand AR (1987) Secretion of lingual lipase and amylase from rat lingual serous glands. Am J Physiol 253:G217–225
Hamosh M (1978) Rat lingual lipase: factors affecting enzyme activity and secretion. Am J Physiol 235:G or E416–421
Hand AR (1970) The fine structure of the von Ebner's gland of the rat. J Cell Biol 44:340–353
Holst JJ (1986) Neural regulation of pancreatic exocrine secretion, chapter 20. In: Go VLW, Gardner JD, Brooks FP, Lebenthal E, DiMagno EP, Scheele GA (eds) The exocrine pancreas. Raven Press, New York, pp 287–300
Larsson L (1981) A novel immunocytochemical model system for specificity and sensitivity screening of antisera against multiple antigens. J Histochem Cytochem 29:408–410
Lazarides E (1980) Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature 283:249–256
Liem RKH, Yen S-H, Salomon GD, Shelanski ML (1978) Intermediate filaments in nervous tissues. J Cell Biol 79:637–645
Ludford JM, Tulamo BR (1980) B-adrenergic and muscarinic receptors in developing rat parotid glands. J Biol Chem 255:4619–4627
Lundberg JM, Hedlung B, Bartfai T (1982) Vasoactive intestinal peptide enhances muscarinic ligand binding in cat submandibular salivary gland. Nature 295:147–149
Roberts IM (1985) Rat lingual lipase: effect of proteases, bile, and pH on enzyme stability. Am J Physiol 249:G496–500
Roberts IM, Jaffe R (1986) Lingual lipase: immunocytochemical localization in the rat von Ebner gland. Gastroenterology 90:1170–1175
Roberts IM, Montgomery RK, Carey MC (1984) Rat lingual lipase: partial purification, hydrolytic properties and comparison with pancreatic lipase. Am J Physiol 247:G385–393
Roberts IM, Nochomovitz LE, Jaffe R, Hanel SI, Rojas M, Agostini RA Jr (1987) Immunocytochemical localization of lingual lipase in serous cells of the developing rat tongue. Lipids 22:764–766
Rohrer H, Acheson AL, Thibault J, Thoenen H (1985) Developmental potential of quail dorsal root ganglion cells analyzed in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci 6:2616–2624
Ruellan C, Moreau J, Bouisson M, Ribet A (1988) The Ebner glands: a pancreatic-like gland secreting an acid lipase. Secretory regulation in vitro. Int J Pancreatol 3:293–300
Shaw G, Chau V (1988) Ubiquitin and microtubule-associated protein tau immunoreactivity each define distinct structures with differeing distributions and solubility properties in Alzheimer brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2854–2858
Thomas L, Hartung K, Langosch D, Rehm H, Bamberg E, Franke WW, Betz H (1988) Identification of synaptophysin as a hexameric channel protein of the synaptic vesicle membrane. Science 242:1050–1053
Walsh JH (1981) Gastrointestinal hormones and peptides, chapter 3. In: Johnson LR (ed) Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. Raven Press, New York, pp 59–144
Wiedemann B, Frank WW (1985) Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000, characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell 41:1017–1028
Williams JA (1984) Regulatory mechanisms in pancreas and salivary acini. Ann Rev Physiol 46:361–375
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, I.M., Solomon, S.E., Brusco, O.A. et al. Neuromodulators of the lingual von Ebner gland: an immunocytochemical study. Histochemistry 96, 153–156 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315986
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315986