Summary
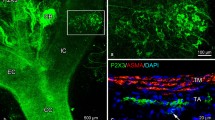
The carotid sinus of the guinea pig was analysed immunohistochemically for the occurrence of neuropeptides. Immunoreactivity (IR) for neurotensin (NT) and substance P (SP) is distributed in two different populations of nerve endings and varicosities. NT-IR fibers penetrate deeply into the tunica media of the elastic segment of the carotid sinus and form the large, branched lanceolate nerve terminals. Electron-microscopic investigations have revealed that the NT-IR varicosities correspond to the large afferent baroreceptor endings containing abundant mitochondria. SP-IR fibers are located mainly at the mediaadventitial border. They seem to be correlated to dense-core, vesiclecontaining varicosities identified in the electron microscope. Therefore, these fibers may constitute afferent and efferent perivascular plexus regulating the vascular tone of the carotid sinus wall.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böck P, Gorgas K (1976) Fine structure of baroreceptor terminals in the carotid sinus of guinea pigs and mice. Cell Tissue Res 170:95–112
Chiba T (1972) Fine structure of the baroreceptor nerve terminals in the carotid sinus of the dog. J Electron Microsc 21:139–148
Ciriello J, Hrycyshyn AW, Calaresu FR (1981) Horseradish peroxidase study of brain stem projections of carotid sinus and aortic depressor nerves in the cat. J Autonom Nerv System 4:43–61
Davies RO, Kalia M (1981) Carotid sinus nerve projections to the brain stem in the cat. Brain Res Bull 6:531–541
DeGroat WC, Nadelhaft I, Morgan C, Schauble T (1979) The central origin of efferent pathways in the carotid sinus nerve of the cat. Science 205:1017–1018
Dropmann K (1965) Über den Feinbau der Karotissinuswand unter besonderer Berücksichtigung nervaler Strukturen. Z Kreisl-Forsch 54:50–63
Forssmann WG (1981) General methods in transmission electron microscopy of the nervous system. In: Heym Ch, Forssmann WG (eds) Techniques in neuroanatomical research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 21–40
Forssmann WG, Pickel V, Reinecke M, Hock D, Metz J (1981) Immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry of nervous tissue. In: Heym Ch, Forssmann WG (eds) Techniques in neuroanatomical research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York, pp 171–205
Furness JB, Papka RE, Della NG, Costa M, Eskay RL (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerves associated with the vascular system of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 7:447–459
Fuxe K, Andersson K, Locatelli V, Mutt V, Lundberg J, Hökfelt T, Agnati LF, Eneroth P, Bolme P (1980) Neuropeptides and central catecholamine systems: interactions in neuroendocrine and central cardiovascular regulation. In: Costa E, Trabucchi M (eds) Neural peptides and neuronal communication. Raven Press, New York, pp 37–50
Gillis RA, Helke CJ, Hamilton BL, Norman WP, Jacobowitz DM (1980) Evidence that substance P is a neurotransmitter of baro- and chemoreceptor afferents in nucleus tractus solitarius. Brain Res 181:476–481
Helke CJ (1982) Neuroanatomical localization of substance P: implications for central cardiovascular control. Peptides 3:479–483
Helke CJ, O'Donohue TL, Jacobowitz DM (1980a) Substance P as a baro- and chemoreceptor afferent neurotransmitter: immunocytochemical and neurochemical evidence in the rat. Peptides 1:1–9
Helke CJ, Goldman W, Jacobowitz DM (1980b) Demonstration of substance P in aortic nerve afferent fibers by combined use of fluorescent retrograte neuronal labeling and immunocytochemistry. Peptides 1:359–364
Heym Ch, Reinecke M, Weihe E, Forssmann WG (1983) Dopamin-β-hydroxylase-, neurotensin-, substance P-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and enkephalin-immunohistochemistry of cat paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia. Anat Embryol (in press)
Hökfelt T, Elde R, Johansson O, Luft R, Nilsson G, Arimura A (1976) Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P-containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 1:131–136
Hökfelt T, Elfvin L-G, Schultzberg M, Goldstein M, Nilsson G (1977) On the occurrence of substance P-containing fibers in sympathetic ganglia: immunohistochemical evidence. Brain Res 129:29–43
Hökfelt T, Elde R, Johansson O, Ljungdahl Å, Schultzberg M, Fuxe K, Goldstein M, Nilsson G, Pernow B, Terenius L, Ganten D, Jeffcoate SL, Rehfeld J, Said S (1978) Distribution of peptide-containing neurons. In: Lipton MA, DiMascio A, Killam KF (eds) Psychopharmacology: a generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 39–67
Hökfelt T, Johansson O, Ljungdahl Å, Lundberg JM, Schultzberg M (1980a) Peptidergic neurones. Nature (Lond) 284:515–521
Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM, Schultzberg M, Johansson O, Ljungdahl Å, Rehfeld J (1980b) Coexistence of peptides and putative transmitters in neurons. In: Costa E, Trabucchi M (eds) Neural peptides and neuronal communication. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–23
Jennes L, Stumpf WE, Kalivas PW (1982) Neurotensin: topographical distribution in rat brain by immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol 210:211–224
Knoche H, Wiesner-Menzel L, Addicks K (1980) Ultrastructure of baroreceptors in the carotid sinus of the rabbit. Acta Anat (Basel) 106:63–83
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Änggard A, Uvnäs-Wallensten K, Brimijoin S, Brodin E, Fahrenkrug J (1980) Peripheral peptide neurons: distribution axonal transport, and some aspects on possible function. In: Costa E, Trabucchi M (eds) Neural peptides and neuronal communication. Raven Press, New York, pp 25–36
Lundberg JM, Rökaeus Å, Hökfelt T, Rosell S, Brown M, Goldstein M (1982) Neurotensin-like immunoreactivity in the preganglionic sympathetic nerves and in the adrenal medulla of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand 114:153–155
Majcherczyk S, Coleridge JCG, Coleridge HM, Kaufman MP, Baker DG (1980) Carotid sinus nerve efferents: properties and physiological significance. Fed Proc 39:2662–2667
Meijling HA (1938) Bau und Innervation von Glomus caroticum und Sinus caroticus. Eine Untersuchung unter spezifischer Nervenfärbungsmethoden. Acta Neerl Morphol 1:193–288
Ochoterena I (1936) Estudios neurologicos. XXIX. Acerca del senso y glomus caroticum. An Inst Biol Univ Mex 7:397–414
Rees PM (1967) Observations on the fine structure and distribution of presumptive baroreceptor nerves at the carotid sinus. J Comp Neurol 131:517–548
Reinecke M, Weihe E, Carraway RE, Leeman SE, Forssmann WG (1982) Localization of neurotensin-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the guinea-pig heart: evidence derived by immunohistochemistry, radioimmunoassay and chromatography. Neuroscience 7:1785–1795
Reis DJ, Granata AR, Perrone MH, Talman WT (1981) Evidence that glutamic acid is the neurotransmitter of baroreceptor afferents terminating in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS). J Autonom Nerv System 3:321–334
Samnegård H, Thulin L, Tydén G, Johansson C, Muhrbeck O, Björklund Ch (1978) Effect of synthetic substance P on internal carotid artery blood flow in man. Acta Physiol Scand 104:491–495
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry. 2nd. Edition. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Triepel J, Weindl A, Mader J, Volz HP, Forssmann WG, Reinecke M (1982) Substance P immunoreactive neurons in the feline brainstem related to cardiovascular centers. Anat Embryol (in preparation)
Uhl GR, Goodman RR, Snyder SH (1979) Neurotensin-containing cell bodies, fibers and nerve terminals in the brain stem of the rat: immunohistochemical mapping. Brain Res 167:77–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Prof. Dr. R. Ortmann on the occasion of his 70th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorgas, K., Reinecke, M., Weihe, E. et al. Neurotensin and substance P immunoreactive nerve endings in the guinea pig carotid sinus and their ultrastructural counterparts. Anat Embryol 167, 347–354 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315672
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315672