Abstract
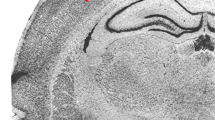
The distribution of viral antigen, histological lesions and inflammatory responses were examined in brains from ovine fetuses following experimental transplacental infection with a cytopathogenic strain of bovine virus diarrhoea virus (BVDV). At 10 and 14 days post inoculation (p.i.) viral antigen-containing cells were found throughout the different zones of the developing telencephalon and cerebellum. Corresponding to the distribution of viral antigen, necrotic lesions both of already differentiated and of undifferentiated fetal brain cells occurred. The extent and severity of microscopic lesions correlated positively with the number of viral antigen-containing cells. The destructive lesions were accompanied by meningeal and parenchymal cellular infiltrations predominantly with phagocytosing macrophages. In fetuses examined at 21 days p.i. a massive necrosis of the cerebral hemispheres and severe infiltrations with macrophages and CD3-positive lymphocytes had developed. In fetuses studied between 32 and 80 days p.i. porencephaly, hydranencephaly and leukoencephalomalacic lesions were present. In brain tissue of these fetuses, with the exception of two cases, BVD viral antigen was no longer detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson CA, Higgins RJ, Smith ME, Osburn BI (1987) Border disease. Virus-induced decrease in thyroid hormone levels with associated hypomyelination. Lab Invest 57: 168–175
Anderson CA, Sawyer M, Higgins RJ, East N, Osburn BI (1987) Experimentally induced ovine border disease: extensive hypomyelination with minimal viral antigen in neonatal spinal cord. Am J Vet Res 48: 499–503
Barlow RM (1983) Some interactions of virus and maternal/foetal immune mechanisms in border disease of sheep. Prog Brain Res 59: 255–268
Barlow RM, Rennie JC, Gardiner AC (1980) Infection of pregnant sheep with the NADL strain of bovine virus diarrhoea virus and their subsequent challenge with border disease IIB pool. J Comp Pathol 90: 67–72
Chung SI, Livingston CW Jr, Edwards JF, Gauer BB, Collison EW (1990) Congenital malformations in sheep resulting from in utero inoculation of Cache Valley virus. Am J Vet Res 51: 1645–1648
Clarke GL, Osburn BI (1978) Transmissible congenital demyelinating encephalopathy of lambs. Vet Pathol 15: 68–82
Coetzer JAW, Barnard BJH (1977) Hydrops amnii in sheep associated with hydranencephaly and arthrogryposis with Wesselsbron disease and Rift Valley fever viruses as aetiological agents. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 44: 119–126
Fernandez A, Hewicker M, Trautwein G, Pohlenz J, Liess B (1989) Viral antigen distribution in the central nervous system of cattle persistently infected with bovine viral diarrhea virus. Vet Pathol 26: 26–32
Friede RL (1989) Developmental Neuropathology, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 28–43
Hartley WJ, De Saram WG, Della-Porta AJ, Snowdon WA, Shepherd NC (1977) Pathology of congenital bovine epizootic arthrogryposis and hydranencephaly and its relationship to Akabane virus. Aust Vet J 53: 319–325
Hewicker-Trautwein M, Trautwein G, Moennig V, Liess B (1992) Infection of ovine fetal brain cell cultures with cytopathogenic and non-cytopathogenic bovine viral diarrhoea virus. Vet Microbiol 33: 239–248
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) The use of anti-avidin antibody and avidin-biotin peroxidase complex in immuno-peroxidase techniques. Am J Clin Pathol 75: 816–821
Jeffrey M, Wells GAH, Bridges AW, Sands JJ (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of border disease virus in the spinal cord of fetal and newborn lambs. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 16: 501–510
MacLachlan NJ, Osburn BI (1983) Bluetongue virus-induced hydranencephaly in cattle. Vet Pathol 20: 563–573
Mason DY, Cordell J, Brown M, Pallesen G, Ralfkiaer E, Rothbard J, Crumpton M, Gatter KC (1989) Detection of cells in paraffin wax-embedded tissue using antibodies against a peptide sequence from the CD3 antigen. J Clin Pathol 42: 1194–1200
McClurkin AW, Littledike ET, Cutlip RC, Frank GH, Coria MF, Bolin SR (1984) Production of cattle immunotolerant to bovine viral diarrhea virus. Can J Comp Med 48: 156–161
Narita M, Kawashima K (1993) Detection of Akabane viral antigen and immunoglobulin-containing cells in ovine fetuses by use of immunoperoxidase staining. Am J Vet Res 54: 420–424
Narita M, Inui S, Hashiguchi (1979) The pathogenesis of congenital encephalopathies in sheep experimentally induced by Akabane virus. J Comp Pathol 89: 229–240
Orban S, Liess B, Hafez SM, Frey HR, Blindow H, Sasse-Patzer B (1983) Studies on transplacental transmissibility of a bovine virus diarrhoea virus (BVD) vaccine virus. I. Inoculation of pregnant cows 15 to 90 days before parturition (190th to 265th day of gestation). Zentralbl Veterinarmed [B] 30: 619–634
Osburn BI, Silverstein AM, Prendergast RA, Johnson RT, Parshall CJ (1971) Experimental viral-induced congenital encephalopathies. I. Pathology of hydranencephaly and porencephaly caused by bluetongue vaccine virus. Lab Invest 25: 197–205
Roeder PL, Jeffrey M, Cranwell MP (1986) Pestivirus fetopathogenicity in cattle: changing sequelae with fetal maturation. Vet Rec 118: 44–48
Roeder PL, Jeffrey M, Drew TW (1987) Variable nature of border disease on a single farm: the infection status of affected sheep. Res Vet Sci 43: 28–33
Scott FW, Kahrs RF, De Lahunta A, Brown TT, McEntee K, Gillespie JH (1973) Virus induced congenital anomalies of the bovine fetus. I. Cerebellar degeneration (hypoplasia), ocular lesions and fetal mummification following experimental infection with bovine viral diarrhea-mucosal disease virus. Cornell Vet 63: 536–560
Terpstra C (1978) Detection of border disease antigen in tissues of affected sheep and cell cultures by immunofluorescence. Res Vet Sci 25: 350–355
Wengler G (1991) Family — Flaviviridae. Classification and nomenclature of viruses. Fifth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Arch Virol [Suppl] 2: 223–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Tr68/1-2)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hewicker-Trautwein, M., Trautwein, G. Porencephaly, hydranencephaly and leukoencephalopathy in ovine fetuses following transplacental infection with bovine virus diarrhoea virus: distribution of viral antigen and characterization of cellular response. Acta Neuropathol 87, 385–397 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313608
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313608