Abstract
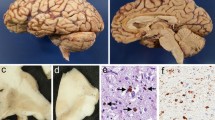
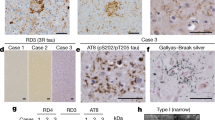
An autopsy case of clinically diagnosed “corticobasal degeneration (CBD)” was investigated. In addition to status spongiosus and neuronal achormasia around the central sulcus, cortical pyramidal neurons and thread-like structures were densely stained by Gallyas stain and tau immunohistochemistry, but apparent fibrillary structures like Alzheimer's disease neurofibrillary tangle were absent. Bodian, methenamine-Bodian, Congo red, thioflavin S, or Bielshowsky stains failed to visualize these structures. They were not stained by immunohistochemical stain with anti-ubiquitin antibody. The widespread cytoskeletal pathology, which is distinct from that in Alzheimer's disease or progressive supranuclear palsy, is suggestive of CBD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bancher C, Lassman H, Budka H, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Wisniewski HM (1987) Neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: antigenic similarities and differences. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74: 39–46
Bancher C, Brunner C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wisniewski HM (1989) Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated tau precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 477: 90–99
Braak H, Jellinger K, Braak E, Bohl J (1992) Allocortical neurofibrillary changes in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 84: 478–483
Dickson DW, Kress Y, Crowe A, Yen S-H (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 2 Demonstration of a common antigenic determinant between ANT and neurofibrillary degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Pathol 120: 292–303
Flament S, Delacourte A, Verny M, Hauw J-J, Javoy-Agid F (1991) Abnormal tau proteins in progressive supra nuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol, 81: 591–596
Gibb WRG, Luthert PJ, Marsden CD (1989) Corticobasal degeneration. Brain 112: 1171–1192
Hauw J-J, Verny M, Delaere P, Cervera P, He Y, Duyckaerts C (1990) Constant neurofibrillary changes in the neocortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett 119: 182–186
Hof PR, Delacourte A, Bouras C (1992) Distribution of cortical neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy: a quantitative analysis of six cases. Acta Neuropathol 84: 45–51
Ishino H, Otsuki S (1976) Frequency of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex in progressive supranuclear palsy (subcortical argyrophyric dystrophy). J Neurol Sci 28: 309–316
Jellinger K, Riederer P, Tomonaga M (1980) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinico-pathological and biochemical studies. J Neural Trans [Suppl] 16: 111–128
Jellinger KA, Bancher C (1992) Neuropathology.In: Litvan I, Agid Y (eds) Progressive supranuclear palsy, clinical and research approach. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 44–48
Leigh PN, Probst A, Dale GE, Power DP, Brion J-P, Dodson A, Anderton BH (1989) New aspects of the pathology of neurodegenerative disorders as revealed by ubiquitin antibodies. Acta Neuropathol 79: 61–72
Lippa CF, Smith TW, Fontneau N (1990) Corticonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. J Neurol Sci 98: 301–310
Mitani K, Uchihara T, Tamaru F, Endo K, Tsukagoshi H (1993) Corticobasal degeneration: clinico-pathological studies on two cases. Clin Neurol 33: 155–161
Nukina N, Quan Y, Nakano I, Otomo E (1992) Widespread tau abnormality in a case of corticobasal degeneration. Clin Neurol 32: 1093–1101 (in Japenese with English abstract)
Paulus W, Selim M (1990) Corticonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia and basal neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol 81: 89–94
Rebeiz JJ, Kolodny H, Richardson EP (1968) Corticodentatonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. Arch Neurol 18: 20–34
Riley DE, Lang AE, Lewis A, Resch L, Ashby P, Hornykiewicz O, Black S (1990) Cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology 40: 1203–1212
Sawle GV, Brooks DJ, Marsden CD, Frackowiak RSJ (1991) Corticobasal degeneration. Brain 114: 541–556
Tabaton M, Perry G, Autilio-Gambetti L, Manetto V, Gambetti P (1988) Influence of neuronal location on antigenic properties of neurofibrillary tangles. Ann Neurol 23: 604–610
Yamada T, McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1992) Appearance of paired nucleated, Tau-positive glia in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy brain tissue. Neurosci Lett 135: 99–102
Yen S-H, Horoupian DS, Terry RD (1983) Immunohistochemical comparison of neurofibrillary tangles in senile dementia of Alzheimer type, progressive supranuclear palsy, and postencephalitic parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 13: 172–175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchihara, T., Mitani, K., Mori, H. et al. Abnormal cytoskeletal pathology peculiar to corticobasal degeneration is different from that of Alzheimer's disease or progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 88, 379–383 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310383
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310383