Abstract
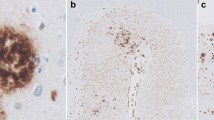
Pick's disease (PD) brains were examined immunohistochemically for the expression of antigens known to be associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) lesions. Most antibodies which label intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in AD were found to stain Pick bodies (PBs). Among them was the monoclonal antibody A2B5, which is known to recognize neuronal surface gangliosides. This result indicates that membrane proteins are probably incorporated into PBs as into NFTs. However, PBs, in contrast to NFTs, showed a paucity of staining for heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). Staining for midline, seen in senile plaques in AD, was not seen in PD. The relative lack of staining for these two neurotrophic factors in PD brain may reflect underlying mechanisms which are distinct from those in AD. We also describe two glial abnormalities in PD: glial fibrillary tangles and clusters of granules positive for the complement protein C4d in the hippocampal dentate fascia. These are presumably related to complement-activated oligodendroglia, and both pathological structures are more abundant in advanced cases, suggesting that they may be hallmarks of the disease progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, Yamada T, Kawamata T, McGeer PL (1991) Association of amyloid P component with complement proteins in neurologically diseased brain tissue. Brain Res 548:349–352
Ball MJ (1979) Topography of Pick inclusion bodies in hippocampi of demented patients. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 42:73–80
Bancher C, Brunner C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wisniewski HM (1989) Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated τ precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 477:90–99
Buée L, Hof PR, Delacourte A, Surini M, Bouras C (1992) Laminar and regional distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and Pick bodies in Pick's disease: comparison with Alzheimer's disease. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18:566
Eisenbarth GS, Walsh FS, Nirenberg M (1979) Monoclonal antibody to a plasma membrane antigen of neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4913–4917
Emory CR, Ala TA, Frey WH II (1987) Ganglioside monoclonal antibody (A2B5) labels Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles. Neurology 37:768–772
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Kondo H, Ikeda K (1993) Anti-tau-positive glial fibrillary tangles in the brain of postencephalitic parkinsonism of Economo type. Neurosci Lett 162:176–178
Itagaki S, Akiyama H, Saito H, McGeer PL (1994) Ultrastructural localization of complement membrane attack complex (MAC)-like immunoreactivity in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 645:78–84
Jellinger K, Danielczyk W, Fischer P, Gabriel E (1990) Clinicopathological analysis of dementia disorders in the elderly. J Neurol Sci 95:239–258
Kato S, Nakamura H (1990) Presence of two different fibril subtypes in the Pick body: an immunoelectron microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol 81:125–129
Kawamata T, Tooyama I, Yamada T, Walker DG, McGeer PL (1993) Lactotransferrin immunocytochemistry in Alzheimer and normal human brain. Am J Pathol 142:1574–1585
Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ (1986) Microtubule-associated protein tau (τ) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4044–4048
Lassman H, Weiler R, Fischer P, Bancher C, Jellinger K, Floor E, Danielczyk W, Seitelberger F, Winkler H (1992) Synaptic pathology in Alzheimer's disease: immunological data for markers of synaptic and large dense-core vesicles. Neuroscience 46:1–8
Love S, Saitoh H, Quijada S, Cole GM, Terry RD (1988) Alz-50, ubiquitin and tau immunoreactivity of neurofibrillary tangles, Pick bodies and Lewy bodies. J Neurophathol Exp Neurol 47:393–405
Lowe J, Blanchard A, Morrell K, Lennox G, Reynolds L, Billett M, Landon M, Mayer RJ (1988) Ubiquitin is a common factor in intermediate filament iclusion bodies of diverse type in man, including those of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as Rosenthal fibers in cerebellar astrocytomas, cytoplasmic bodies in muscle, and Mallory bodies in alcoholic liver disease. J Pathol 155:9–15
Majocha RE, Jungalwala FB, Rodenrys A, Marotta CA (1989) Monoclonal antibody to embryonic CNS antigen A2B5 provides evidence for the involvement of membrane components at sites of Alzheimer degeneration and detects sulfatides as well as gangliosides. J Neurochem 53:953–961
Manetto V, Perry G, Tabaton M, Mulvihill P, Fried VA, Smith HT, Gambetti P, Autilio-Gambetti L (1988) Ubiquitin is associated with abnormal cytoplasmic filaments characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4501–4505
McGeer PL, Akiyama H, Itagaki S, McGeer EG (1989) Immune system response in Alzheimer's disease. Can J Neurol Sci 16:516–527
McGeer PL, Akiyama H, Itagaki S, McGeer EG (1989) Activation of the classical complement pathway in brain tissue of Alzheimer patients. Neurosci Lett 107:341–346
McGeer PL, Walker DG, Akiyama H, Kawamata T, Guan AL, Parker CJ, Okada N, McGeer EG (1991) Detection of the membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis (CD59) in diseased neurons of Alzheimer brain. Brain Res 544:315–319
McGeer PL, Akiyama H, Kawamata T, Yamada T, Walker DG, Ishii T (1992) Immunohistochemical localization of betaamyloid precursor protein sequences in Alzeheimer and normal brain tissue by light and electron microscopy. J Neurosci Res 31:428–442
Munoz DG (1991) Chromogranin A-like immunoreactive neurites are major constitutes of senile plaques. Lab Invest 64: 826–832
Munoz-Garcia D, Ludwin SK (1984) Classic and generalized variants of Pick's disease: a clinicopathological, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical comparative study. Ann Neurol 16: 467–480
Murayama S, Mori H, Ihara Y, Tomonaga M (1990) Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural studies of Pick's disease. Ann Neurol 27:394–405
Nishimura M, Namba Y, Ikeda K, Oda M (1992) Glial fibrillary tangles with straight tubules in the brains of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett 143:35–38
Nishizawa Y, Kurihara T, Takahashi Y (1981) Immunohistochemical localization of 2′3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase in the central nervous system. Brain Res 212:219–222
Papasozomenos SCh, Binder LI (1987) Phosphorylation determines two distinct species of tau in the central nervous system. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 8:210–226
Perry G, Friedman R, Shaw G, Chau V (1987) Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3033–3036
Perry G, Stewart D, Friedman R, Manetto V, Autilio-Gambetti L, Gambetti P (1987) Filaments of Pick's bodies contain altered cytoskeletal elements. Am J Pathol 127:559–568
Perry G, Mulvihill P, Fried VA, Smith HT, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1989) Immunochemical properties of ubiquitin conjugates in the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer disease. J Neurochem 52:1523–1528
Pollock NJ, Mirra SS, Binder LI, Hansen LA, Wood JG (1986) Filamentous aggregates in Pick's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Alzheimer's disease share antigenic determinants with microtubule-associated protein, tau. Lancet II:1211
Probst A, Anderton BH, Ulrich J, Kohler R, Kahn J, Heitz PU (1983) Pick's disease: an immunocytochemical study of neuronal changes. Monoclonal antibodies show that Pick bodies share antigenic determinants with neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 60:175–182
Probst A, Luginbühl M, Langui D, Ulrich J, Landwehrmeyer B (1993) Pathology of the striatum in progressive supranuclear palsy: abnormal tau proteins in astrocytes and cholinergic interneurons. Neurodegeneration 2:183–193
Rasool CG, Selkoe DJ (1985) Sharing of specific antigens by degenerating neurons in Pick's disease and Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 312:700–705
Seno M, Iwane M, Sasada R, Moriya N, Kurokawa T, Igarashi K (1989) Monoclonal antibodies against human basic fibroblast growth factor. Hybridoma 8:209–221
Snow AD, Sekiguchi R, Nochlin D, Fraser P, Kimata K, Mizutani A, Arai M, Schreier WA, Morgan DG (1994) An important role of heparan sulfate proteoglycan (Perlecan) in a model system for the deposition and persistence of fibrillar Aβ-amyloid in rat brain. Neuron 12:219–234
Stopa EG, Gonzalez A-M, Chorsky R, Corona RJ, Alvarez J, Bird ED, Baird A (1990) Basic fibroblast growth factor in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 171: 690–696
Su JH, Cummings BJ, Cotman CW (1992) Localization of heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan core protein in aged brain and Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 51:801–813
Tooyama I, Walker D, Yamada T, Hanai K, Kimura H, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1992) High molecular weight basic fibroblast growth factor-like protein is localized to a subpopulation of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in the rat brain. Brain Res 593:274–280
Tooyama I, Yamada T, Kim SU, McGeer PL (1992) Immunohistochemical study of A2B5-positive ganglioside in postmortem human brain tissue of Alzheimer disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, progressive supranuclear palsy and control cases. Neurosci Lett 136:91–94
Tooyama I, Kawamata T, Walker D, Yamada T, Hanai K, Kimura H, Iwane M, Igarashi K, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1993) Loss of basic fibroblast growth factor in substantia nigra neurons in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 43:372–376
Ulrich J, Haugh M, Anderton BH, Probst A, Lautenschlager C, His B (1987) Alzheimer dementia and Pick's disease: neurofibrillary tangles and Pick bodies are associated with identical phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 73:240–246
Weiler R, Lassman H, Fischer P, Jellinger K, Winkler H (1990) A high ratio of chromogranin A to synaptin/synaptophysin is a common feature of brains in Alzheimer and Pick disease. FEBS Lett 263:337–339
Wisniewski HM, Coblentz JM, Terry RD (1972) Pick's disease: a clinical and ultrastructural study. Arch Neurol 26: 97–108
Wolozin BL, Pruchnicki A, Dickson DW, Davies P (1986) A neuronal antigen in the brain of Alzheimer patients. Science 232:648–650
Yamada T, Akiyama H, McGeer PL (1990) Complement-activated oligodendroglia: a new pathogenic entity identified by immunostaining with antibodies to human complement proteins C3d and C4d. Neurosci Lett 112:161–166
Yamada T, McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1991) Relationship of complement-activated oligodendrocytes to reactive microglia and neuronal pathology in neurodegenerative disease. Dementia 2:71–77
Yamada T, McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1992) Appearance of paired nucleated, Tau-positive glia in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy brain tissue. Neurosci Lett 135:99–102
Yasuhara O, Muramatsu H, Kim SU, Muramatsu T, Maruta H, McGeer PL (1993) Midkine, a novel neurotrophic factor, is present in senile plaques of Alzheimer disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 192:246–251
Yasuhara O, Aimi Y, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1994) Accumulation of amyloid precursor protein in brain lesions of patients with Pick disease. Neurosci Lett 171:63–66
Yasuhara O, Aimi Y, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1994) Expression of the complement membrane attack complex and its inhibitors in brains of patients with Pick disease. Brain Res 652:346–349
Yasuhara O, Kawamata T, Aimi Y, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1994) Two types of dystrophic neurites in senile plaques of Alzheimer disease and elderly non-demented cases. Neurosci Lett 171:73–76
Yasuhara O, Kawamata T, Aimi Y, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1994) Expression of chromogranin A in lesions in the central nervous system from patients with neurological diseases. Neurosci Lett 170:13–16
Yoshimura N (1989) Topography of Pick body distribution in Pick's disease: a contribution to understanding the relationship between Pick's and Alzheimer's disease. Clin Neuropathol 8: 1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasuhara, O., Matsuo, A., Tooyama, I. et al. Pick's disease immunohistochemistry: new alterations and Alzheimer's disease comparisons. Acta Neuropathol 89, 322–330 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309625
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309625