Summary
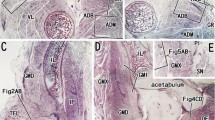
Muscle spindles from the lower lumbrical muscles of rats were studied by transmission and scanning electron microscopy following reinnervation (i) after a single sciatic nerve crush lesion and (ii) after transection and immediate epineurial suture of the sciatic nerve. In all muscle spindles, regenerated sensory or motor nerve endings were encountered 3 months after making the lesions although in the nerve-transection group, regenerated nerve endings were seen less frequently before 6 months of recovery. Abnormalities in reinnervated spindles following neurotomy comprised: (1) multiplicity of axonal sprouts (hyperinnervation), sometimes irregularly related to, although never in direct contact with, regenerated sensory nerve endings; (2) altered contact relationships between sensory nerve endings and intrafusal muscle fibers; (3) abnormal structure of nerve endings; and (4) irregular association of Schwann cell processes to regenerated sensory nerve endings. These findings indicate that reinnervation of muscle spindles following transection and suture of a peripheral nerve, i.e., after complete interruption of its continuity, in fact, occurs although the fine structural abnormalities observed are supposed to interfere with adequate functional restoration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnott ER, Gladden MH, Sutherland F (1982) Autonomic innervation of muscle spindles from the hind limb of the cat. Proc R Microsc Soc [Suppl] 17:1
Ballard KJ (1978) Typical sympathetic noradrenergic endings in a muscle spindle of the cat. J Physiol 285:61–62P
Banker BQ, Girvin JP (1971) The ultrastructural features of the mammalian muscle spindle. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 30:155–195
Banks RW (1981) A histological study of the motor innervation of the cat's muscle spindle. J Anat 133:571–591
Banks RW, Barker D (1983) Recovery of cat hindlimb muscle afferents following nerve section. J Physiol 345:97P
Banks RW, Barker D, Brown HG (1985) Sensory reinnervation of muscles following nerve section and suture in cats. J Hand Surg [Br] 10:340–344
Barker D, Banks RW (1986) The muscle spindle. In: Engel AG, Banker BQ (eds) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 309–341
Barker D, Saito M (1981) Autonomic innervation of receptors and muscle fibres in cat skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond [B] 212:317–332
Barker D, Scott JJA, Stacey MJ (1985) Sensory reinnervation of cat peroneus brevis muscle spindles after nerve crush. Brain Res 333:131–138
Barker D, Scott JJA, Stacey MJ (1986) Reinnervation and recovery of cat muscle receptors after long-term denervation. Exp Neurol 94:184–202
Boyd IA (1985) Internal working of muscle spindles. Review. In: Boyd IA, Gladden MH (eds) The muscle spindle. Macmillan, Basingstoke, pp 129–150
Boyd IA (1985) Muscle spindles and stretch reflexes. In: Swash M, Kennard C (eds) Scientific basis of clinical neurology. Churchill-Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 74–97
Boyd IA, Gladden MH (1985) Morphology of mammalian muscle spindles. Review. In: Boyd IA, Gladden MH (eds) The muscle spindle. Macmillan, Basingstoke, pp 3–22
Boyd IA, Smith RS (1984) The muscle spindle. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Lambert EH, Bunge R (eds) Peripheral neuropathy, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 171–202
Brown MC, Butler RG (1976) Regeneration of afferent and efferent fibres to muscle spindles after nerve injury in adult cats. J Physiol 260:253–266
Carlson BM, Wagner KR, Max SR (1979) Reinnervation of rat extensor digitorum longus muscles after free grafting. Muscle Nerve 2:304–307
Collins WF IIIrd, Mendell LM, Munson JB (1986) On the specificity of sensory reinnervation of cat skeletal muscle. J Physiol 374:587–609
Devor M (1989) The pathophysiology of damaged peripheral nerves. In: Wall PD, Melzack R (eds) Textbook of pain, 2nd edn. Churchill-Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 63–81
Devor M, Bernstein JJ (1982) Abnormal impulse generation in neuromas: electrophysiology and ultrastructure. In: Culp WJ, Ochoa J (eds) Abnormal nerves and muscles as impulse generators. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 363–380
Dieler R, Völker A, Schröder JM (1990) Scanning electron microscopy of denervated and reinnervated intrafusal muscle fibres in isolated rat muscle spindles (in preparation)
Gregory JE, Luff AR, Proske U (1982) Muscle receptors in the cross-reinnervated soleus muscle of the cat. J Physiol 331:367–383
Hennig G (1969) Die Nervenendigungen der Rattenmuskelspindel im elektronen- und phasenkontrastmikroskopischen Bild. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 96:275–294
Hyde D, Scott JJA (1983) Responses of cat peroneus brevis muscle spindle afferents during recovery from nerve-crush injury. J Neurophysiol 50:344–357
Ip MC, Vrbová G (1973) Motor and sensory reinnervation of fast and slow mammalian muscles. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 146:261–279
Ip MC, Luff AR, Proske U (1988) Innervation of muscle receptors in the cross-reinnervated soleus muscle of the cat. Anat Rec 220:212–218
Kucera J (1977) Splitting of the nuclear bag 1 fiber in the course of muscle spindle denervation and reinnervation. J Histochem Cytochem 25:1102–1104
Kucera J, Walro JM, Reichler J (1988) Motor and sensory innervation of muscle spindles in the neonatal rat. Anat Embryol 177:427–436
Merrillees NCR (1960) The fine structure of muscle spindles in the lumbrical muscle of the rat. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 7:725–740
Ochoa J (1982) Pain in local nerve lesions. In: Culp WJ, Ochoa J (eds) Abnormal nerves and muscles as impulse generators. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 568–587
Ovalle WK (1971) Fine structure of rat intrafusal muscle fibers. The polar region. J Cell Biol 51:83–103
Ovalle WK (1972) Fine structure of rat intrafusal muscle fibers. The equatorial region. J Cell Biol 52:382–396
Ovalle WK (1982) Motor nerve terminals on rat intrafusal muscle fibers; a correlated light and electron microscopic study. J Anat 111:239–253
Quick DC, Rogers SL (1983) Stretch receptors in regenerated rat muscle. Neuroscience 10:851–859
Rogers SL (1982) Muscle spindle formation and differentiation in regenerating rat muscle grafts. Dev Biol 94:265–283
Rumpelt HJ, Schmalbruch H (1969) Zur Morphologie der Bauelemente von Muskelspindeln bei Mensch und Ratte. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 102:601–630
Santini M, Ibata Y (1971) The fine structure of thin unmyelinated axons within muscle spindles. Brain Res 33:289–302
Schiaffino S, Pierobon Bormioli S (1976) Morphogenesis of rat muscle spindles after nerve lesion during early postnatal development. J Neurocytol 5:319–336
Schmalbruch H (1977) Regeneration of soleus muscles of rat autografted in toto as studied by electron microscopy. Cell Tissue Res 177:159–180
Schröder JM (1972) Altered ratio between axon diameter and myelin sheath thickness in regenerated nerve fibers. Brain Res 45:49–65
Schröder JM (1974) The fine structure of de- and reinnervated muscle spindles. I. The increase, atrophy and “hypertrophy” of intrafusal muscle fibers. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 30:109–128
Schröder JM (1974) The fine structure of de- and reinnervated muscle spindles. II. Regenerated sensory and motor nerve terminals. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 30:129–144
Schröder JM, Kemme PT, Scholz L (1979) The fine structure of denervated and reinnervated muscle spindles: morphometric study of intrafusal muscle fibers. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 46:95–106
Schröder JM, Bodden H, Hamacher A, Verres C (1989) Scanning electron microscopy of teased intrafusal muscle fibers from rat muscle spindles. Muscle Nerve 12:221–232
Scott JJA (1985) Regeneration of gamma-fusimotor axons after nerve-freeze injury in the cat. Brain Res 348:159–162
Scott JJA (1987) The reinnervation of cat muscle spindles by skeletofusimotor axons. Brain Res 401:152–154
Scott JJA (1988) Responses of cat muscle spindle afferents after short periods of denervation and reinnervation. Brain Res 461:381–383
Soukup T (1988) Regeneration of muscle spindles in grafted extensor digitorum longus muscle of the rat. In: Hník P, Soukup T, Vejsada R, Zelená J (eds) Mechanoreceptors. Development, structure, and function. Plenum Press, New York, pp 111–116
Soukup T, Zelená J (1988) Sensory innervation of atypical spindles after nerve crush in newborn rats. In: Hník P, Soukup T, Vejsada R, Zelená J (eds) Mechanoreceptors. Development, structure, and function. Plenum Press, New York, pp 143–148
Struppler A, Mackel R, Besinger UA, Waldhör F (1981) Electromyography and microneurography following peripheral nerve transplantations. In: Gorio A, Millesi H, Mingrino S (eds) Posttraumatic peripheral nerve regeneration: experimental basis and clinical implications. Raven Press, New York, pp 581–589
Swash M, Fox KP (1985) Adrenergic innervation of baboon and human muscle spindles. In: Boyd IA, Gladden MH (eds) The muscle spindle. Macmillan, Basingstoke, pp 121–126
Thomas PK, Ochoa J (1984) Microscopy anatomy of peripheral nerve fibers. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Lambert EH, Bunge R (eds) Peripheral neuropathy, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 39–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft: Di 386/1-1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dieler, R., Schröder, J.M. Abnormal sensory and motor reinnervation of rat muscle spindles following nerve transection and suture. Acta Neuropathol 80, 163–171 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308920
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308920