Summary
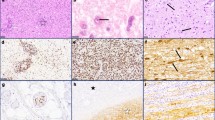
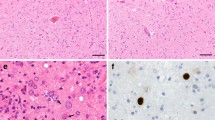
Twenty-five brains with definite, and three brains with possible, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), including six brains of AIDS patients, were studied with special regard to the detection of papovaviruses. Formalin-fixed serial paraffin sections were immunostained with monospecific anti-JC virus (JCV) and genus-specific anti-simian virus (SV) 40 antisera, and hybridized in situ with DNA probes for JCV and SV 40, respectively. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) and in situ hybridization (ISH) were similarly sensitive in detecting virus in classical PML lesions. In all but one definite PML cases at least one method detected virus (96%). Possible PML tissue was never labeled. Labeling patterns were generally similar in ICC and ISH: mainly oligodendroglia and, less frequently, astroglia harbored virus, whereas labeling of neurons and endothelia was absent. Bizarre giant astrocytes were occasionally labeled by ICC and ISH. Burnt-out lesions harbored JCV DNA but not virus antigens. SV 40 DNA was never detectable. PML morphology in AIDS cases did not usually differ from the disease process seen in the pre-AIDS era. However, two AIDS brains presented extremely extended and, in one case, unusually necrotizing PML damage; in the latter case, PML lesions contained large amounts not only of JCV, but also of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antigens. We conclude that ICC and ISH are methods of comparable sensitivity for detection of papovavirus in flourishing PML lesions. In burnt-out PML lesions only ISH may detect virus. The possibility of an exceptional non-JCV (e.g., SV 40) etiology of PML could be neither confirmed for disproved. In AIDS, massive coinfection by HIV of PML lesions may increase damage to tissue, resulting in unusually extended and necrotizing PML.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksamit AJ, Sever JL, Major EO (1986) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: JC virus detection by in situ hybridization compared with immunohistochemistry. Neurology 36: 499–504
Aksamit AJ, Major EO, Ghatak NR, Sidhu GS, Parisi JE, Guccion JG (1987) Diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by brain biopsy with biotin labeled DNA: DNA in situ hybridization. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:556–566
Aström K-E, Mancall EL, Richardson EP (1958) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. A hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukaemia and Hodgkin's disease. Brain 81:93–111
Bernick C, Gregorius JB (1984) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Arch Neurol 41:780–782
Blum LW, Chambers RA, Schwartzman RJ, Streletz LJ (1985) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Arch Neurol 42:137–139
Boerman RH, Arnoldus EPJ, Raap AK, Peters ACB, ter Schegget J, van der Ploeg M (1989) Diagnosis of progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy by hybridization techniques. J Clin Pathol 42:153–161
Breuer AC, Blank NK, Schoene WC (1978) Multifocal pontine lesions in cancer patients treated with chemotherapy and CNS radiotherapy. Cancer 41:2112–2120
Budka H (1982) Pathology of encephalopathies induced by treatment or prophylaxis of neoplastic lesions of the nervous system. In: Hildebrand J, Gangji D (eds) Treatment of neoplastic lesions of the nervous system. Pergamon Press, Oxford New York. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol [Suppl] 3:45–50
Budka H (1989) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-induced disease of the central nervous system: pathology and implications for pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol 77:225–236
Budka H (1990) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) envelope and core proteins in CNS tissues of patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol 79:611–619
Budka H, Shah KV (1983) Papovavirus antigens in paraffin sections of PML brains. Clin Biol Res 105:299–309
Budka H, Costanzi G, Cristina S, Lechi A, Parravicini C, Trabattoni R, Vago L (1987) Brain pathology induced by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A histological, immunocytochemical, and electron microscopical study of 100 autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:185–198
Darvish M, Tourtellotte WW, Shapshak P, Nakamura S, Steiner R, Itabashi HH, Schmid P, Heinzmann C, Hoffmann D, Fareed GC, Graves MC (1984) The detection of papovavirus nucleotide sequences in cortical neurons of a patient with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) (abstract). Neurology 34 [Suppl 1]: 176
Dörries K, ter Meulen V (1983) Detection of papovavirus JC in kidney tissue. J Med Virol 11:307–311
Dörries K, Johnson RT, ter Meulen V (1979) Detection of polyoma virus DNA in PML brain tissue by (in situ) hybridization. J Gen Virol 42:49–57
Gendelman HE, Phelps W, Feigenbaum L, Ostrove M, Adachi A, Howley PM, Khoury G, Ginsberg HS, Martin MA (1986) Transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat sequence by DNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9759–9763
Gray F, Gherardi R Scaravilli F (1988) The neuropathology of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). A review. Brain 111:245–266
Green M (1986) Transformation and Oncogenesis: DNA viruses. In: Fields BN (ed) Virology. Raven Press, New York, pp 183–234
Greenlee JE, Keeney PM (1986) Immunoenzymatic labelling of JC papovavirus T antigen in brains of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 71:150–153
Hickey WF, Kimura H (1987) Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen in vivo. Science 239:290–292
Houff SA, Major EO, Katz DA, Kufta CV, Sever JL, Pittaluga S, Roberts JR, Gitt J, Saim N, Lux W (1988) Involvement of JC-virus infected mononuclear cells from the bone marrow and spleen in the pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med 318:301–305
Ironside JW, Lewis FA, Blythe D, Wakefield A (1989) The identification of cells containing JC papovavirus DNA in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by combined in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry J Pathol 157:291–297
Johnson RT, McArthur JC, Narayan O (1988) The neurobiology of human immunodeficiency virus infections. FASEB J 2:2970–2981
Kleihues P, Lang W, Burger PC, Budka H, Vogt M, Maurer R, Lüthy R, Siegenthaler W (1985) Progressive diffuse leucoencephalopathy in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 68:333–339
Loeber G, Dörries K (1988) DNA rearrangements in organspecific variants of polyomavirus JC strain GS. J Virol 62:1730–1735
Mazlo M, Tariska I (1982) Are astrocytes infected in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)? Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 56:45–51
Monte SM de la, Moore T, Hedley-Whyte ET (1986) Vacuolar encephalopathy in AIDS. N Engl J Med 315:1549–1550
Narayan O, Penney JB, Johnson RT, Herndon RM, Weiner LP (1973) Etiology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Identification of Papovavirus. N Engl J Med 289:1278–1282
Ondek B, Shepard A, Herr W (1987) Discrete elements within the SV 40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J 6:1017–1025
Rand KH, Johnson KP, Rubinstein LJ, Wolinsky JS, Penney JB, Walker DL, Padgett BL, Merigan TC (1977) Adenine arabinoside in the treatment of progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy: use of virus-containing cells in the urine to assess response to therapy. Ann Neurol 1:458–462
Rhodes RH, Ward JM, Walker DL, Ross AA (1988) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and retroviral encephalitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112:1207–1213
Richardson EP (1961) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med 265:815–823
Rubinstein LJ, Herman MM, Long TF, Wilbur JB (1975) Disseminated necrotizing leukoencephalopathy — A complication of treated central nervous system leukemia and lymphoma. Cancer 35:291–305
Scaravilli F, Ellis DS, Tovey G, Harcourt-Webster JN, Guiloff RJ, Sinclair E (1989) Unusual development of polyoma virus in the brains of two patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 15:407–418
Schmidbauer M, Budka H (1989) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in AIDS and in the pre-AIDS era: a neuropathological comparison using immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization (abstr). Clin Neuropathol 8:212–213
Schmidbauer M, Budka H, Ambros P (1989) Herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA in microglial nodular brainstem encephalitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 48:645–652
Schmidbauer M, Budka H, Okeda R, Cristina S, Costanzi G, Lechi A, Trabbatoni GR (1989) Multifocal vacolar leucoencephalopathy: a new type of HIV-induced neuropathology (abstr). Clin Neuropathol 8:249
Scherneck S, Geissler E, Jänisch W, Rudolph M, Vogel F, Zimmermann W (1980) Isolation of a SV 40-like virus from a patient with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Virol 25:191–198
Shah KV (1985) Papovaviruses. In: Fields BN (ed) Virology. Raven Press, New York, pp 371–391
Shapshak P, Tourtellotte WW, Wolman M, Verity N, Verity M, Schmid P, Syndulko K, Bedows E, Boostanfar R, Darvish M, Nakamura S, Tomiyasu U, Steiner RC, Hawkins S, Hoffmann D, Adhami F, Martinez S (1986) Search for virus nucleic acid sequences in postmortem human brain tissue using in situ hybridization technology with cloned probes: some solutions and results on progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis tissue. J Neurosci Res 16:281–301
Stoner GL, Ryschkewitsch CF, Walker DL, Webster HdeF (1986) JC papovavirus large tumor (T)-antigen expression in brain tissue of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and non-AIDS patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2271–2275
Walker DL (1985) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Handb Clin Neurol 47:503–524
Weiner LP, Herndon RM, Narayan O, Johnson RT, Shah K, Rubinstein LJ, Preziosi TJ, Conley FK (1972) Isolation of virus related to SV 40 from patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med 286:385–390
Wiley CA, Grafe M, Kennedy C, Nelson JA (1988) Human immunodeficiency virus and JC virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 76:338–346
Wright DG, Laureno R, Victor M (1979) Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain 102:361–385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Lord Mayor's Medical-Scientific Fund Vienna. Major parts of this study were presented at the Scientific Winter Meeting in Kitzbühel, Austria, March 15–18, 1989
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidbauer, M., Budka, H. & Shah, K.V. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in AIDS and in the pre-AIDS era. Acta Neuropathol 80, 375–380 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307690
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307690