Summary
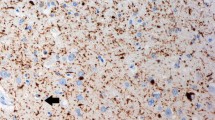
Silver techniques for intraneuronal cytoskeleton abnormalities (neurofibrillary tangles and neuropil threads) and extracellular A4-amyloid deposits were used to examine lesions of the cerebral cortex in six cases of progressive supranuclear palsy (three were mentally unimpaired and three showed moderate degrees of dementia). Deposits of A4-amyloid protein occurred in small numbers or were absent. Neurofibrillary tangles and neuropil threads were present in all cases and were largely confined to the allocortex. A characteristic pattern of changes was found in the entorhinal cortex. The three mentally unimpaired individuals had mild cortical changes virtually confined to the transentorhinal region while all of the demented patients showed severe destruction of the superficial cellular layer in both the transentorhinal and entorhinal region. This pattern of allocortical destruction closely resembles that seen in clinically incipient Alzheimer's disease or in mentally impaired cases of Parkinson's disease. The entorhinal region receives dense input from isocortical association areas and projects via the perforant path to the hippocampal formation. The cells of origin of major portions of the perforant path are located within the superficial entorhinal cellular layer. Destruction of this layer partially or totally disconnects the hippocampus from the isocortex. The specific pattern of entorhinal destruction is considered to contribute to cognitive impairment and personality changes, frequently seen in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agid Y, Javoy-Agid F, Ruberg M, Pillon B, Dubois B, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ, Baron JC, Scatton B (1986). Progressive supranuclear palsy: anatomo-clinical and biochemical considerations. Adv Neurol 45:191–206
Agid Y, Ruberg M, Dubois B, Pillon B, Cusimano G, Raisman R, Cash R, Lhermitte F, Javoy-Agid F (1986) Parkinson's disease and dementia. Clin Neuropharmacol 9 [Suppl 2]:22–36
Albert ML (1978) Subcortical dementia. In: Katzman R, Terry D, Bick KL (eds) Alzheimer's disease: senile dementia and related disorders. Raven Press, New York, pp 173–180
Albert ML, Feldman RG, Willis AL (1974) The “subcortical dementia” of progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 37:121–130
Alexander GE, Crutcher MD, DeLong MR (1990) Basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits: parallel substrates for motor, oculomotor, “prefrontal” and “limbic” functions. Prog Brain Res 85:119–146
Alheid GF, Heimer L, Switzer RC (1990) Basal ganglia. In: Paxinos G (ed) The human nervous system. Academic Press, New York, pp 483–582
Amaral DG, Insausti R (1990) Hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G (ed) The human nervous system. Academic Press, New York, pp 711–755
Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Flory J, Damasio AR, Van Hoesen GW (1991) The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Cerebral Cortex 1:103–116
Behrman S, Carroll JD, Janota I, Matthews WB (1969) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Clinico-pathological study of four cases. Brain 92:663–678
Blin J, Baron JC, Dubois B, Pillon B, Cambon H, Cambier J, Agid Y (1990) Positron emission tomography study in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain hypometabolic pattern and clinicometabolic correlations. Arch Neurol 47:747–752
Braak H (1980) Architectonics of the human telencephalic cortex. In: Braitenberg V, Barlow HB, Bizzi E, Florey E, Grüsser OJ, van der Loos H (eds) Studies of brain function, vol 4. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo. pp 1–147
Braak H, Braak E (1985) On areas of transition between entorhinal allocortex and temporal isocortex in the human brain. Normal morphology and lamina-specific pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:325–332
Braak H, Braak E (1990) Cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and neuropil threads in the cerebral cortex. J Neural Transm (PD-Sect) 2:45–57
Braak H, Braak E (1990) Neurofibrillary changes confined to the entorhinal region and an abundance of cortical amyloid in case of presenile and senile dementia. Acta Neuropathol 80:479–486
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Demonstration of amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary changes in whole brain sections. Brain Pathol 1:213–216
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Braak H, Braak E, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1986) Occurrence of neuropil threads in the senile human brain and in Alzheimer's disease: a third location of paired helical filaments outside of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques. Neurosci Lett 65:351–355
Braak H, Braak E, Ohm TG, Bohl J (1988) Silver impregnation of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes counterstained for basophilic material and lipofuscin pigment. Stain Technol 63:197–200
Cambier J, Masson M, Viader F, Limodier J, Strube A (1985) Le syndrome frontal de la maladie de Steele-Richardson-Olszewski. Rev Neurol (Paris) 141:528–536
Campbell SK, Switzer RC, Martin TL (1987) Alzheimer's plaques and tangles: a controlled and enhanced silver-staining method. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:678
D'Antona R, Baron JC, Samson Y, Serdaru M, Viader F, Agid Y, Cambier J (1985) Subcortical dementia. Frontal cortex hypometabolism detected by positron tomography in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 108:785–799
Dubois B, Pillon B, Lagault F, Agid Y, Lhermitte F (1988) Slowing of cognitive processing in progressive supranuclear palsy. A comparison with Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol 45:1194–1199
Dubois B, Pillon B, Lhermitte F, Agid Y (1990) Cholinergic deficiency and frontal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 28:117–121
Freedman M, Albert ML (1985) Subcortical dementia. In: Frederks JAM (ed) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 311–316
Gallyas G (1971) Silver staining of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes by means of physical development. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung 19:1–8
Gomori AJ, Sima AAF (1984) An atypical case of progressive supranucler palsy. Can J Neurol Sci 11:48–52
Hauw JJ, Verny M, Delaère P, Cervera P, He Y, Duyckaerts C (1990) Constant neurofibrillary changes in the neocortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. Basic differences with Alzheimer's disease and aging. Neurosci Lett 119:182–186
Hof PR, Delacourte A, Bouras C (1992) Distribution of cortical neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy: a quantitative analysis of six cases. Acta Neuropathol 84:45–51
Hyman BT, van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL (1984) Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 225:1168–1170
Hyman BT, van Hoesen GW, Kromer LJ, Damasio AR (1986) Perforant pathway changes and the memory impairment of Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 20:472–481
Hyman BT, van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR (1990) Memory-related neural systems in Alzheimer's disease: an anatomic study. Neurology 40:1721–1730
Iqbal K, Braak E, Braak H, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I (1991) A silver impregnation method for labeling both Alzheimer paired helical filaments and their polypeptides separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Neurobiol Aging 12:357–361
Ishino H, Otsuki S (1976) Frequency of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex in progressive supranuclear palsy (subcortical argyrophilic dystrophy). J Neurol Sci 28:309–316
Jellinger K (1971) Progressive supranuclear palsy (subcortical argyrophilic dystrophy). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 19:347–352
Jellinger K (1989) Pathology of Parkinson's syndrome In: Calne DB (ed) Drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 47–112
Jellinger K (1991) Pathology of Parkinson's disease: changes other than nigrostriatal pathway. Mol Chem Neuropathol 14:153–197
Jellinger K, Bancher C (1992) Progressive supranuclear palsy: neuroanatomoclinical aspects. In: Litvan I, Agid Y (eds) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinical and research approaches. Oxford University Press, New York, (in press)
Jellinger K, Riederer P, Tomonaga M (1980) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinico-pathological and biochemical studies. J Neural Transm [Suppl] 16:111–128
Jellinger K, Braak H, Braak E, Fischer D (1991) Alzheimer lesions in the entorhinal region and isocortex in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 640:203–209
Karbe H, Grond M, Huber M, Herholz K, Kessler H, Heiss W-D (1992) Subcortical damage and cortical dysfunction in progressive supranuclear palsy demonstrated by positron emission tomography. J Neurol 239:98–102
Kemper TL (1978) Senile dementia: a focal disease in the temporal lobe. In: Nandy E (ed) Senile dementia: a biomedical approach. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 105–113
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1105
Litvan I, Grafman J, Gomez C, Chase TN (1989) Memory impairment in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 46:765–767
Maher ER, Smith EM, Lees AJ (1985) Cognitive deficits in the Steele-Richardson-Olszweski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:1234–1239
Matsushita M, Ito K, Oyanagi S, Uchikoshi T, Ishiko T, Kase M, Kosaka K (1980) An autopsy case of progressive supranuclear palsy with massive appearance of neurofibrillary tangles in the limbic system including nucl. accumbens septi and nucl. amygdala. Neuropathology (Kyoto) 1:119–132
Mayeux R, Stern Y, Rosen J, Leventhal J (1981) Depression, intellectual impairment and Parkinson's disease. Neurology 31:645–650
Pandya DN, Yeterian EJ (1985) Architecture and connections of cortical association areas. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, vol 4. Plenum Press, New York, pp 3–61
Price JL, Davis PB, Morris JC, White DL (1991) The distribution of tangles, plaques and related immunohistochemical markers in healthy aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 12:295–312
Probst A, Langui D, Lautenschlager C, Ulrich J, Brion JP, Anderton BH (1988) Progressive supranuclear palsy: extensive neuropil threads in addition to neurofibrillary tangles. Very similar antigenicity of subcortical neuronal pathology in progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 77:61–68
Rose M (1935) Cytoarchitektonik und Myeloarchitektonik der Großhirnrinde. In: Bumke O, Foerster O (eds) Handbuch der Neurologie, vol 1. Springer, Berlin, pp 588–778
Ruberg M, Javoy-Agid F, Hirsch E, Scatton B (1985) Dopaminergic and cholinergic lesions in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 18:523–529
Smithson KG, MacVicar BA, Hatton GI (1983) Polyethylene glycol embedding: a technique compatible with immunocytochemistry, enzyme histochemistry, histofluorescence and intracellular staining. J Neurosci Methods 7:27–41
Steele JC (1972) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 95:693–704
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Tagliavini F, Pilleri G, Gemignani F, Lechi A (1983) Neuronal loss in the basal nucleus of Meynert in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 61:157–160
Takahashi H, Takeda S, Ikuta F, Homma Y (1987) Progressive supranuclear palsy with limbic system involvement: report of a case with ultrastructural investigation of neurofibrillary tangles in various locations. Clin Neuropathol 6:271–276
Takahashi H, Oyanagi K, Takeda S, Hinohuma K, Ikuta F (1989) Occurrence of 15-nm-wide straight tubules in neocortical neurons in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 79:233–239
van Hoesen GW (1982) The parahippocampal gyrus. New observations regarding its cortical connections in the monkey. Trends Neurosci 5:345–350
van Hoesen GW, Hyman BT, Damasio AR (1991) Entorhinal cortex pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Hippocampus 1:1–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Bundesministerium für Forschung und Technologie
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braak, H., Jellinger, K., Braak, E. et al. Allocortical neurofibrillary changes in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 84, 478–483 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304466
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304466