Summary
In order to examine the relationship between the Bergmann glial cells and the migrating granule cells, the postnatal development of the Bergmann glial cells in the rat cerebellum was analysed by a rapid Golgi method.
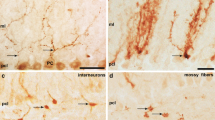
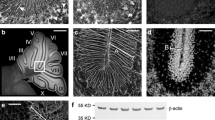
In newborn rats where immature Purkinje cells occupied a rather thick zone (about 8 cells thick) between the thin molecular layer and the intermediate zone, immature Bergmann glial cells were recognized by the irregularly contoured somata situated within the deep part of the zone of Purkinje cells and by several perpendicular thin fibers (filiform fibers) which traversed the external granular layer (EGL) to terminate at the pial surface. After day 2 of the postnatal age (PD2), both somata and fibers of Bergmann glial cells showed gradual or fairly abrupt changes.
The somata migrated upwards toward the molecular layer on PD2 and on PD4 were situated just beneath the Purkinje cells which had become arranged in a single layer. After PD6 the distance between the pial surface and the somata situated in the Purkinje cell layer and concomitantly the length of the Bergmann glial fibers, progressively increased in accordance with the thickening of the molecular layer.
Between PD0 and PD8 the somata were irregularly contoured with short protoplasmic processes exteding radially. After PD8 they gradually lost these short processes and became smooth.
The Bergmann glial fibers were rather smooth with a few beady enlargements and tiny bud-like excrescences on their surface between PD0 and PD8. On PD12 the bushy expansions, characteristic of matured Bergmann glial fibers, suddenly increased in number on most fibers. After PD12 they continued to augment until PD25, when most fibers were entirely covered with the expansions.
The number of fibers issuing from each Bergmann glial cell and entering the EGL increased postnatally reaching a peak on PD8, and then decreased gradually. These changes in the number of Bergmann glial fibers corresponded well with those in the number of external granule cells, suggesting the presence of developmental interactions between these two kinds of cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J (1969) Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis III. Dating the time of production and onset of differentiation of cerebellar microneurons in rats. J Comp Neurol 136:269–294
Altman J (1972) Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat I. The external germinal layer and the transitional molecular layer. J Comp Neurol 145:353–398
Bascó E, Hajós F, Fülöp Z (1977) Proliferation of Bergmann-glia in the developing rat cerebellum. Anat Embryol 151:219–222
Bignami A, Dahl D (1973) Differentiation of astrocytes in the cerebellar cortex and the pyramidal tracts of the newborn rat. An immunofluorescence study with antibodies to a protein specific to astrocytes. Brain Res 49:393–402
Cerro M del, Swarz JR (1976) Prenatal development of Bergmann glial fibers in rodent cerebellum. J Neurocytol 5:669–676
Choi BH, Lapham LW (1980) Evolution of Bergmann glia in developing human fetal cerebellum: A Golgi, electron microscopic and immunofluorescent study. Brain Res 190:369–383
Das GD (1976) Differentiation of Bergmann glia cells in the cerebellum: A Golgi study. Brain Res 110:199–213
Das GD, Lammert GL, McAllister JP (1974) Contact guidance and migratory cells in the developing cerebellum. Brain Res 69:13–29
Fujita S (1967) Quantitave analysis of cell proliferation and differentiation in the cortex of the postnatal mouse cerebellum. J Cell Biol 32:277–288
Ghandour MS, Labourdette G, Vincendon G, Gombos G (1981) A biochemical and immunohistological study of S100 protein in developing rat cerebellum. Develop Neurosci 4:98–109
Heinsen H (1977) Quantitave anatomical studies on the postnatal development of the cerebellum of the albino rat. Anat Embryol 151:201–218
Levitt P, Rakic P (1980) Immunoperoxidase localization of glial fibrillary acidic protein in radial glial cells and astrocytes of the developing rhesus monkey brain. J Comp Neurol 193:815–840
Lewis PD, Fülöp Z, Hajós F, Balázs R, Woodhams PL (1977) Neuroglia in the internal granular layer of the developing rat cerebellar cortex. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 3:183–190
Rakic P (1971) Neuron-glia relationship during granule cell migration in developing cerebellar cortex. A Golgi and electronmicroscopic study in Macacus Rhesus. J Comp Neurol 141:283–312
Rakic P, Sidman RL (1973a) Weaver mutant mouse cerebellum: Defective neuronal migration secondary to abnormality of Bergmann glia. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 70:240–244
Rakic P, Sidman RL (1973b) Sequence of developmental abnormalities leading to granule cell deficit in cerebellar cortex of weaver mutant mice. J Comp Neurol 152:103–132
Shiga T, Ichikawa M, Hirata Y (1983) Spatial and temporal pattern of postnatal proliferation of Bergmann glial cells in rat cerebellum: An autoradiographic study. Anat Embryol 167:203–211
Sommer I, Lagenaur C, Schachner M (1981) Recognition of Bergmann glial and ependymal cells in the mouse nervous system by monoclonal antibody. J Cell Biol 90:448–458
Zecevic N, Rakic P (1976) Differentiation ofPurkinje cells and their relationship to other components of developing cerebellar cortex in man. J Comp Neurol 167:27–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiga, T., Ichikawa, M. & Hirata, Y. A Golgi study of Bergmann glial cells in developing rat cerebellum. Anat Embryol 167, 191–201 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298510
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298510