Summary
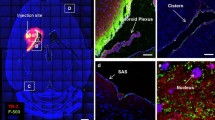
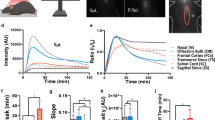
Pathways for drainage of interstitial fluid and cerebrospinal fluid from the rat brain were investigated by the injection of 2–5 μl Indian ink into cerebral white and grey matter and into the subarachnoid space over the vertex of the left frontal lobe. Animals were killed by formalin or glutaraldehyde perfusion 5 min-2 years after injection, and the distribution of ink over the surface of the brain, in 2-mm slices of brain cleared in cedar wood oil, in paraffin sections and by electron microscopy was documented. These investigations showed that carbon particles were distributed diffusely through the interstitial spaces of the white matter whereas they spread selectively along perivascular spaces in the grey matter outlining both arteries and veins and extending to surround capillaries within 1 h. Carbon particles were rapidly ingested by perivascular cells and, to some extent, by meningeal cells surrounding the larger vessels. Very little movement of carbon-labelled perivascular cells and perivascular macrophages was seen after 2 years. Carbon particles entering the subarachnoid space over the vertex of the cerebral hemispheres drained along selected paravascular and subfrontal pathways in the subarachnoid space to the cribriform plate and thence into nasal lymphatics and cervical lymph nodes. These studies demonstrate the diffuse spread of fluidborne tracers through cerebral white matter in the rat, the perivascular spread of tracer in grey matter and the compartmentalised directional flow or tracer through the subarachnoid space to the cribriform plate and nasal lymphatics. Furthermore, particulate matter selectively injected into perivascular spaces in rat grey matter is rapidly and efficiently ingested by perivascular cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcolado R, Weller RO, Parrish EP, Garrod D (1988) The cranial arachnoid and pia mater in man: anatomical and ultrastructural observations. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 14:1–17
Bradbury MWB, Cserr HF, Westrop RJ (1981) Drainage of cerebral interstitial fluid into deep cervical lymph of the rabbit. Am J Physiol 240:F329-F336
Casley-Smith JR, Földi-Börcsök E, Földi M (1976) The prelymphatic pathways of the brain as revealed by cervical lymphatic obstruction and the passage of particles. Br J Exp Pathol 57:179–188
Clark RG, Milhorat TH (1970) Experimental hydrocephalus. III. Light microscopic findings in acute and subacute obstructive hydrocephalus in the monkey. J Neurosurg 32:400–413
Cross AH, Cannella B, Brosnan CF, Raine CS (1990) Homing to central nervous system vasculature by antigen-specific lymphocytes. I. Localization of 14C-labelled cells during acute, chronic, and relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Lab Invest 63:162–170
Cserr HF, Ostrach LH (1974) Bulk flow of interstitial fluid after intracranial injection of Blue Dextran 2000. Exp Neurol 45:50–60
Cserr HF, Harling-Berg C, Ichimura T, Knopf PM, Yamada S (1990) Drainage of cerebral extracellular fluids into cervical lymph: an afferent limb in brain/immune system interactions. In: Johansson BB, Owman C, Widner H (eds) Pathophysiology of the blood-brain barrier. Elsevier Science Publishers (Biomedical Division), Amsterdam, pp 413–420
Erlich SS, McComb JG, Hyman S, Weiss MH (1986) Ultrastructural morphology of the olfactory pathway for cerebrospinal fluid drainage in the rabbit. J Neurosurg 64:466–473
Esiri MM, Gay D (1990) Immunological and neuropathological significance of the Virchow-Robin space. J Neurol Sci 100:3–8
Feuer D, Weller RO (1991) Barrier functions of the leptomeninges: a study of normal meninges and meningiomas in tissue culture. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 17:391–405
Graeber MB, Streit WJ, Kreutzberg GW (1989) Identity of ED2-positive perivascular cells in rat brain. J Neurosci Res 22:103–106
Graeber MB, Streit WJ, Kiefer R, Schoen SW, Kreutzberg GW (1990) New expression of myelomonocytic antigen by microglia and perivascular cells following lethal motor neuron injury. J Neuroimmunol 27:121–132
Harling-Berg C, Knopf PM, Merriam J, Cserr HF (1989) Role of cervical lymph nodes in the systemic humoral immune response to human serum albumin microinfused into rat cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 25:185–193
Hutchings M, Weller RO (1986) Anatomical relationships of the pia mater to cerebral blood vessels in man. J Neurosurg 65:316–325
Ichimura T, Fraser PA, Cserr HF (1991) Distribution of extracellular tracers in perivascular spaces of the rat brain. Brain Res 545:103–113
Kalimo H, Fredricksson K, Nordborg C, Auer RN, Olsson Y, Johansson B (1986) The spread of brain oedema in hypertensive brain injury. Med Biol 64:133–137
Krisch B, Leonhardt H, Oksche A (1984) Compartments and perivascular arrangement of the meninges covering the cerebral cortex of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 238:459–474
McComb JG, Hyman S, Weiss MH (1984) Lymphatic drainage of cerebrospinal fluid in cat. In: Shapiro K, Marmarou A, Portnoy H (eds) Hydrocephalus. Raven Press, New York, pp 83–98
McKeever PE, Balentine JD (1978) Macrophage migration through the brain parenchyma to the perivascular space following particle ingestion. Am J Pathol 93:153–164
Nicholas DS, Weller RO (1988) The fine anatomy of the human spinal meninges. A light and scanning electron microscopy study. J Neurosurg 69:276–282
Ohata K, Marmarou A, Povlishock JT (1990) An immunocytochemical study of protein clearance in brain infusion edema. Acta Neuropathol 81:162–177
Rennels ML, Gregory TF, Blaumanis OR, Fujimoto K, Grady PA (1985) Evidence for a ‘Paravascular’ fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Res 326:47–63
Streit WJ, Graeber MB, Kreutzberg GW (1989) Expression of Ia antigen on perivascular and microglial cells after sublethal and lethal motor neuron injury. Exp Neurol 105:115–126
Szentistvanyi I, Patlak CS, Ellis RA, Cserr HF (1984) Drainage of intertitial fluid from different regions of rat brain. Am J Physiol 246:F835-F844
Weller RO, Wisniewski H (1969) Histological and ultrastructural changes in experimental hydrocephalus. I. Adult Rabbit. Brain 92:819–828
Weller RO, Wisniewski H, Shulman K, Terry RD (1971) Experimental hydrocephalus in young dogs: histological and ultrastructural study of the brain tissue damage. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 30:613–627
Weller RO, Shulman K (1972) Infantile hydrocephalus: clinical, histological and ultrastructural study of brain damage. J Neurosurg 36:255–265
Yamazumi H (1989) Infiltration of Indian ink from subarachnoid space to nasal mucosa along olfactory nerves in rabbits. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 92:608–616
Zhang ET, Inman CBE, Weller RO (1990) Interrelationships of the pia mater and the perivascular (Virchow-Robin) spaces in the human cerebrum. J Anat 170:111–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
E. T. Z. supported by the James Gibson Fund, the Wessex Medical Trust, the Wessex Neurological Centre Research Trust, and the Sino-British Society
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, E.T., Richards, H.K., Kida, S. et al. Directional and compartmentalised drainage of interstitial fluid and cerebrospinal fluid from the rat brain. Acta Neuropathol 83, 233–239 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296784
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296784