Abstract
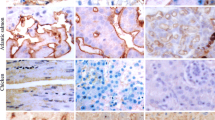
Vascular endothelial cells are associated with a number of anionic molecules. These anions are important in endothelial function, particularly in regulating permeability, haemostasis and cellular traffic. To explore the nature and distribution of anions on the brain endothelial cell (BEC) surface, we have examined rat brain endothelium in culture, and in situ. The anionic sites were probed with cationic colloidal gold and cationised ferritin, and visualised by light microscopy. Additonally we compared the distribution of the anionic sites on BEC with that present on other endothelial cell types in culture. The predominant anion detected on BEC was heparan sulphate (HS). This was distributed throughout the cell membrane, but was most densely associated with intercellular junctions. This pattern was distinct from the anionic locations observed in endothelia from aorta and epididymal fat microvessels. The distribution of anions was dependent on the age of cultured cells, with only minimal levels of HS seen at the periphery of younger cells. The nature and distribution of negative charge was different in situ. Here, sialic acid was the major surface anion, with only a small contribution from HS. The significance of these findings are discussed in relation to endothelial function in normal tissue and in pathological conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott NJ, Hughes CCW, Revest PA, Greenwood J (1992) Development and characterization of rat brain capillary endothelial culture: towards an in vitro blood-brain barrier. J Cell Sci 103:23–37
Bradfield JWB, Born GVR (1969) Inhibition of lymphocyte recirculation by heparin. Nature 222:1183–1184
Bruyn PPH, Michelson S, Becker RP (1978) Nonrandom distribution of sialic acid over the cell surface of bristle-coated endocytic vesicles of the sinusoidal endothelium cells. J Cell Biol 78:379–389
Bush MS, Allt G (1990) Blood-nerve barrier: distribution of anionic sites on the endothelial plasma membrane and basal lamina. Brain Res 535:181–188
Gotloib L, Shostak A, Galdi P, Jaichenko J, Fudin R (1992) Loss of microvaccular negative charges accompanied by interstitial edema in septic rats' heart. Circ Shock 36:45–56
Greenwood J (1992) Characterization of a rat retinal endothelial cell culture and expression of P-glycoprotein in brain and retinal endothelium in vitro. J Neuroimmunol 39:123–132
Hardingham TE, Fosang AJ (1992) Proteoglycans: many forms and many functions. FASEB J 6:861–870
Hart MN, VanDyk LF, Moore SA, Shasby DM, Cancilla PA (1987) Differential opening of the brain endothelial barrier following neutralization of the endothelial luminal anionic charge in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:141–153
Hughes CCW, Lantos PL (1986) Brain capillary endothelial cells in vitro lack surface IgG Fc receptors. Neurosci Lett 68:100–106
Klein NJ, Shennan GI, Heyderman RS, Levin M (1992) Alteration in glycosaminoglycan metabolism and surface charge on human umbilical cells induced by cytokines, endotoxin and neutrophils. J Cell Sci 102:821–832
Klein NJ, Shennan GI, Heyderman RS, Levin M (1993) Detection of glycosaminoglycan on the surface of human umbilical vein cells using gold conjugated poly-l-lysine with silver enhancement. Histochem J 25:291–298
Kobayashi M, Shumada K, Ozawa T (1990) Human recombinant interleukin 1β and tumor necrosis factor a mediated suppression of heparin-like compounds on cultured porcine aortic endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 144:383–389
Male D, Pryce G, Rahman J (1990) Comparison of the immunologic properties of rat cerebral and aortic endothelium. J Neuroimmunol 30:161–168
Marikovsky Y, Danon D (1969) Electron microscope analysis of young and old red blood cells stained with colloidal iron for surface charge evaluation. J Cell Biol 43:1–7
Marikovsky Y, Shlomai Z, Asher O, Lotan R, Ben-Bassat H (1986) Distribution and modulation of surface charges of cells from leukaemia-lymphoma lines at various stages of differentiation. Cancer 58:2218–2223
McGuire PG, Orkin RW (1987) Isolation of rat aortic endothelial cells by primary explant techniques and their phenotypic modulation by defined substrata. Lab Invest 57:94–105
Mills AN, Haworth SG (1991) Greater permeability of the neonatal lung. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 101:909–916
Murch SH, MacDonald TT, Walker-Smith JA, Lavin M, Lionetti P, Klein NJ (1993) Disruption of sulphated glycosaminoglycans in intestinal inflammation. Lancet 341:711–714
Nag S (1984) Cerebral endothelial surface charge in hypertension. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 63:276–281
Nagy Z, Peters H, Huttner I (1983) Charge-related alterations of the cerebral endothelium. Lab Invest 49:662–671
Oohira A, Wight TN, Bornstein P (1983) Sulfated proteoglycans synthesized by vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 258:2014–2021
Pawlowski N, Kaplan G, Abraham E, Cohn ZA (1988) The selective binding and transmigration of monocytes through the junctional complexes of human endothelium. J Exp Med 168:1865–1882
Pryce G, Santos W, Male D (1994) An assay for the analysis of lymphocyte migration across cerebral endothelium in vitro. J Immunol Methods 167:55–63
Schmidley JW, Wissig SL (1986) Anionic sites on the luminal surface of fenestrated and continuous capillaries of the CNS. Brain Res 363:265–271
Simionescu M, Simionescu N, Silbert JE, Palade GE (1981) Differentiated microdomains on the luminal surface of capillary endothelium. II. Partial characterization of their anionic sites. J Cell Biol, 90:614–621
Simionescu M, Simionescu N, Santoro F, Palade GE (1985) Differentiated microdomains of the luminal plasmalemma of murine muscle capillaries: segmental variations in young and old animals. J Cell Biol 100:1396–407
Tanaka Y, Adams DH, Hubscher S, Hirano H, Siebenlist U, Shaw S (1993) T-cell adhesion induced by proteoglycan-immobilized cytokine MIP-1β. Nature 361:79–82
Tanaka Y, Adams DH, Shaw S (1993) Proteoglycans on endothelial cells present adhesion-inducing cytokines to leukocytes. Immunol Today 14:111–115
Vorbrodt AW (1987) Demonstration of anionic sites on the luminal and abluminal fronts of endothelial cells with poly-l-lysine-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem 35:1261–1266
Vorbrodt AW, Trowbridge RS (1991) Ultracytochemical characteristics of cultured sheep brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Histochem Cytochem 39:1555–1563
Wight TS, Kinsella MG, Lark MW, Potter-Perigo S (1986) Vascular cell proteoglycans: evidence for metabolic modulation. Ciba Foudation Sym 124:241–259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos, W.L.C., Rahman, J., Klein, N. et al. Distribution and analysis of surface charge on brain endothelium in vitro and in situ. Acta Neuropathol 90, 305–311 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296515
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296515